Nucleic acid aptamers for detecting extracellular vesicles of human lung cancer cell strain A549 and application of nucleic acid aptamers
A nucleic acid aptamer and lung cancer cell technology, applied in the fields of biomedicine and clinical medicine, can solve problems such as poor treatment effect, complicated pathogenesis, and difficulty in discovery, and achieve the effects of easy modification, simple preparation, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1 Screening of human lung cancer cell line A549 cell line extracellular vesicle surface protein-specific nucleic acid aptamer based on immunomagnetic bead method
[0033] 1. Design and synthesize upstream and downstream primers and random libraries
[0034] The specific primer pair F / R and the random library sequence were synthesized by Shanghai Sangon Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The sequence of the upstream primer F is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and the sequence of the downstream primer R is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2. The random library The sequence of is shown in SEQ ID NO: 3:
[0035] Upstream primer F (SEQ ID NO: 1): 5'-FAM-GTTGGTGAGGTAACGGCTCA-3'
[0036] Downstream primer R (SEQ ID NO: 2): 5'-biotin-CGGATAACGCTTGCCACCTA-3'
[0037] Random library: (SEQ ID NO: 3): 5'-GTTGGTGAGGTAACGGCTCA-40nt-TAGGTGGCAAGCGTTATCCG-3' (40nt means 40 random bases)
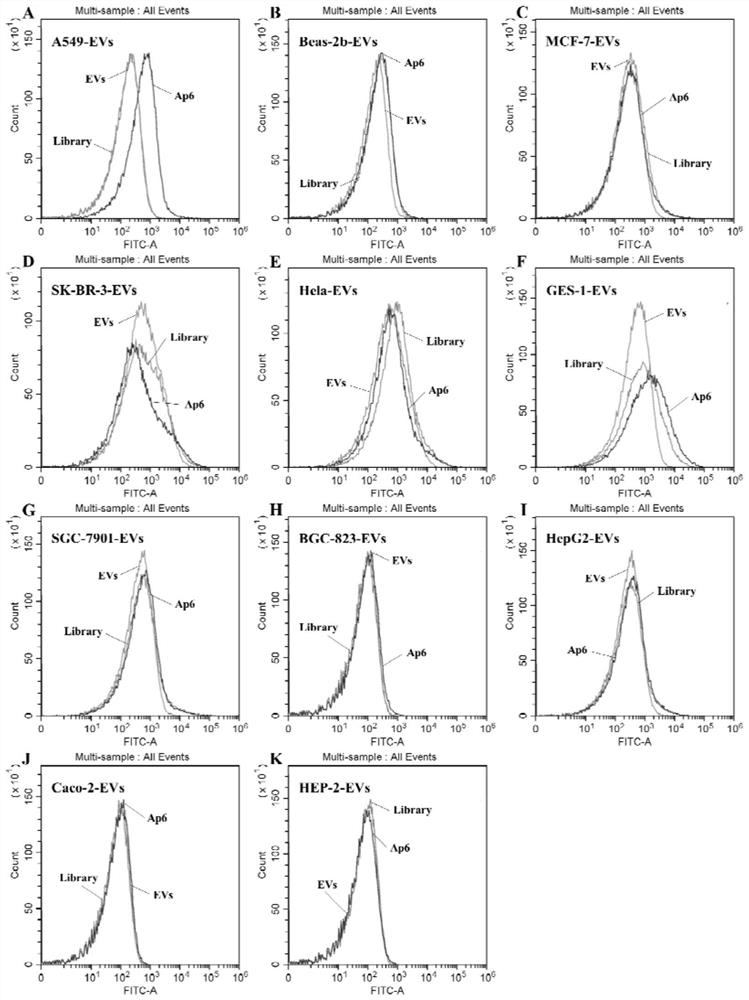
[0038] 2. Acquisition of human lung cancer cell line extracellular vesicle A549-EVs surface protein-specific nucleic acid...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Example 2 Screening of human lung cancer cell line A549 cell line extracellular vesicle surface protein-specific nucleic acid aptamer based on particle size selection method
[0060] 1. Design and synthesize upstream and downstream primers and random libraries
[0061] The specific primer pair F / R and the random library sequence were synthesized by Shanghai Sangon Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The sequence of the upstream primer F is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and the sequence of the downstream primer R is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2. The random library The sequence of is shown in SEQ ID NO: 3:
[0062] Upstream primer F (SEQ ID NO: 1): 5'-FAM-GTTGGTGAGGTAACGGCTCA-3'
[0063] Downstream primer R (SEQ ID NO: 2): 5'-biotin-CGGATAACGCTTGCCACCTA-3'
[0064] Random library: (SEQ ID NO: 3): 5'-GTTGGTGAGGTAACGGCTCA-40nt-TAGGTGGCAAGCGTTATCCG-3' (40nt means 40 random bases)
[0065] 2. Obtaining human lung cancer cell line extracellular vesicle A549-EVs surface protein-specific nucleic acid ...
Embodiment 3
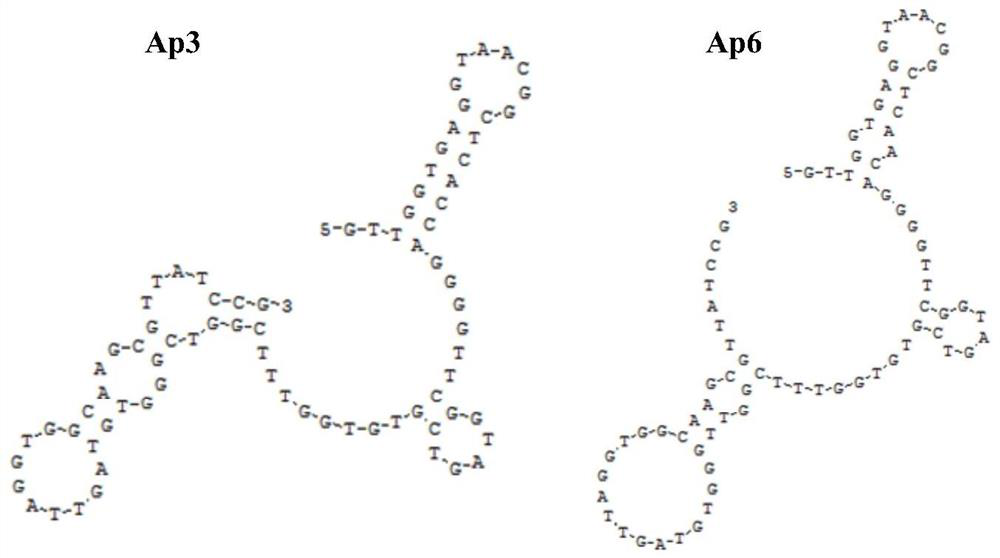
[0084] Example 3 The investigation of the secondary structure, specificity, affinity and dissociation constant of two nucleic acid aptamers
[0085] A human lung cancer cell line A549 extracellular vesicle surface protein-specific nucleic acid aptamer, mainly including the following 5'-end FAM-modified DNA sequence:
[0086] Sequence SEQ ID NO: 4 (Ap3)
[0087] 5'-FAM-GTTGGTGAGGTAACGGCTCACCAGGGGTTCGGTAGTCGTGTGGTTTCGGTCGGGTGTAGTTAGGTGGCAAGCGTTATCCG-3'
[0088] Sequence SEQ ID NO:5(Ap6)
[0089] 5'-FAM-GTTGGTGAGGTAACGGCTCAACAGGGGTTCGGTAGTCGTGTGGTTTCGGTTGGGTGTAGTTAGGTGGCAAGCGTTATCCG-3'
[0090] The above-mentioned nucleic acid aptamer that can specifically recognize and bind to the extracellular vesicles of the human lung cancer cell line A549, its nucleotide sequence can intercept part of the active fragment or increase part of the sequence based on it, and the homology with the above sequence is 60% above.
[0091] The nucleotide sequence of the above-mentioned nucleic acid...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com