Unstable non-Newtonian two-phase fluid displacement simulation method based on pore network model
A pore network model and displacement simulation technology, applied in the fields of instrumentation, electrical digital data processing, computer-aided design, etc., can solve the problem that the immiscible displacement simulation of two-phase non-Newtonian fluids has few studies, is difficult to study, and cannot describe fluids and pores. Problems such as unsteady seepage characteristics of throat compressibility coefficient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
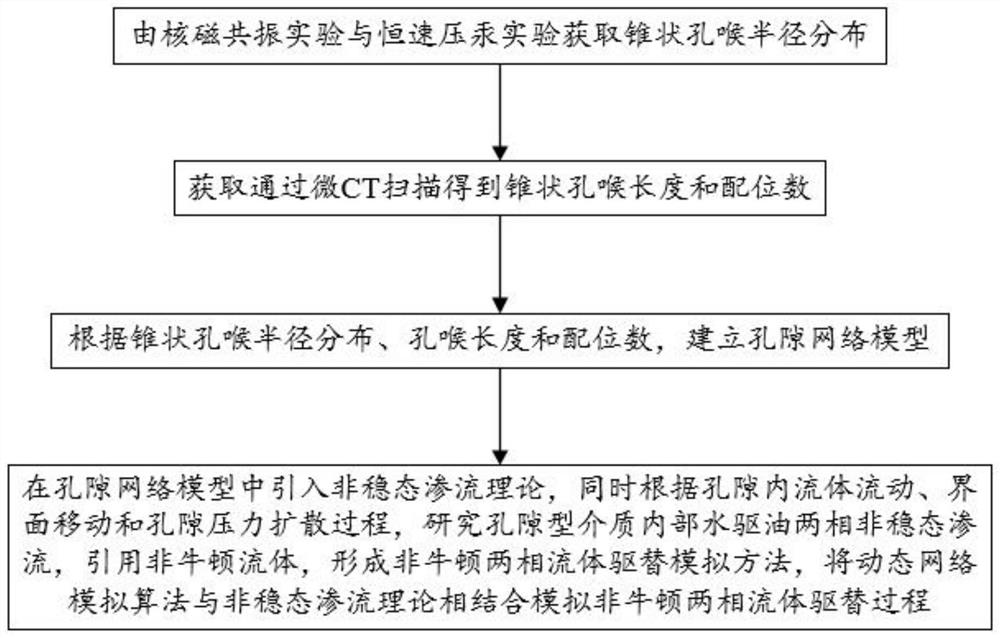
[0084] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a non-steady-state non-Newtonian two-phase fluid displacement simulation method based on the pore network model, and its technical scheme is as follows:
[0085] 1. Pore-throat radius distribution obtained from NMR experiments and constant-velocity mercury intrusion experiments
[0086] 1.1 NMR experiment
[0087] The principle of nuclear magnetic resonance experiments can be briefly described as the corresponding splitting of the spin energy level of the nucleus in an external magnetic field environment and the resonance phenomenon. The charge outside the nucleus revolves around the nucleus, which produces a vector magnetic field with strength and direction. If there is no external magnetic field, the direction of a single nuclear magnetic moment is random, and it does not show magnetism macroscopically. When the detection object is placed in an external magnetic field, the nuclear magnetic moment will precess in th...
Embodiment 2
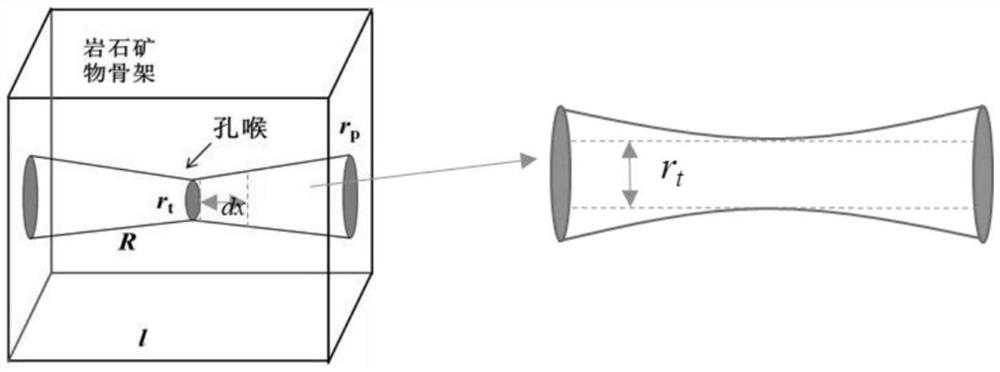
[0189] 1. Micro-CT scanning experiment statistics coordination number
[0190] Based on computerized high-resolution tomography imaging technology (MicroCT), the sample was scanned and the digital core 3D reconstruction was carried out using the equivalent sphere method and the maximum sphere method to construct the pore network, and the structural characteristics of the reservoir were analyzed. Among them, The track length can be calculated by the following formula:
[0191] L=D-R 1 -R 2
[0192] In the formula, R 1 , R 2 are the radii of the two pores connected by the tunnel, in μm; D is the actual coordinate distance between the center points of the two pores, in μm.
[0193] The coordination number is automatically calculated by the software.
[0194] 2. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Core Analysis and Test Statistical Pore Throat Radius Distribution
[0195] The NMR signal intensity is positively correlated with the number of fluid hydrogen nuclei inside the saturated ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com