Method for treating high-concentration cadmium pollution through calcium-enhanced microorganism mineralization and combined phytoremediation
A technology of phytoremediation and calcium enhancement, which is applied in the field of calcium-enhanced microbial mineralization to control high-concentration cadmium pollution and combined phytoremediation. It can solve the problems of long pollution process, pollution, and failure to achieve the repair effect, and achieve simple operation and low cost. The effect of low cost and broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
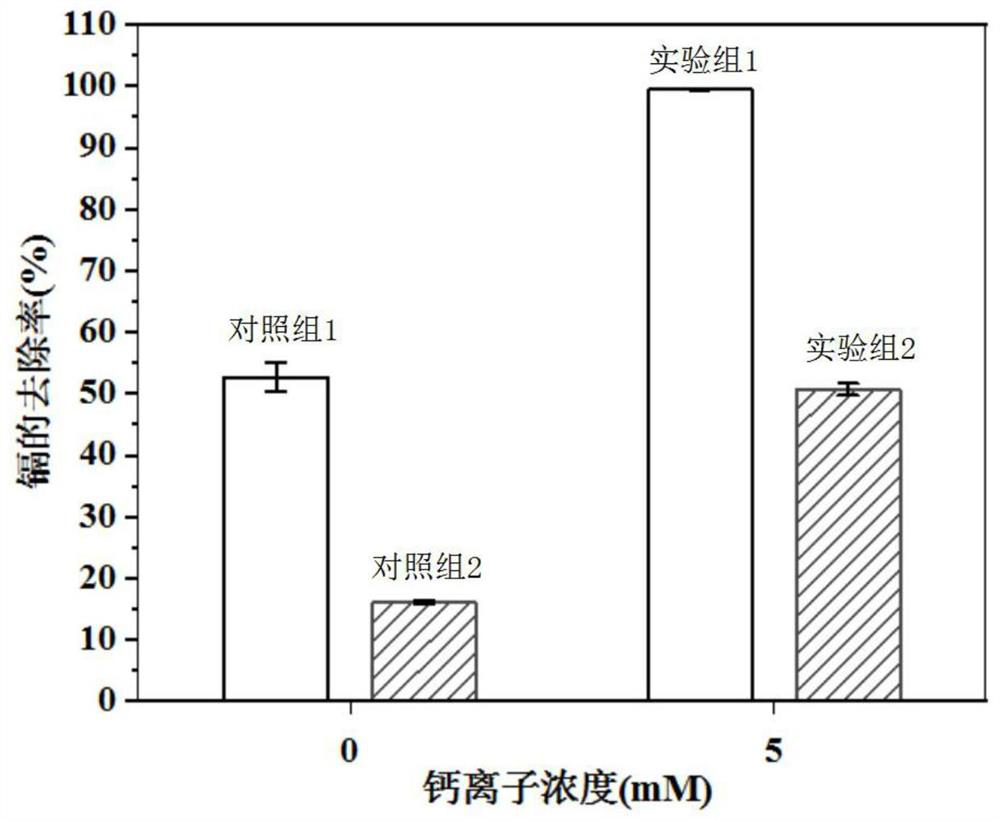
[0025] Example 1 Calcium-intensified conditions to remove high-concentration cadmium-polluted wastewater
[0026] Inoculate the sterilized culture medium with the mother liquor of Bacillus pasteurianum, and shake and cultivate it at 28°C for two days. After the cultivation is completed, use a spectrophotometer to measure the absorbance of the bacterial solution, and adjust the concentration of the bacterial solution to OD by centrifugal concentration and saline 600 =12 for spare;
[0027] Use pure water and cadmium chloride to prepare high-concentration cadmium-containing wastewater with a cadmium concentration of 50 mM, and set aside.
[0028] Experimental group 1: After mixing high-concentration cadmium-containing wastewater, anhydrous calcium chloride, bacterial liquid and urea, add water to configure a 100mL reaction system; in the 100mL reaction system, bacterial liquid, calcium chloride, cadmium ions (Cd 2+ ), the final concentration of urea were OD 600 =1.2, 5mM, 5mM...
Embodiment 2
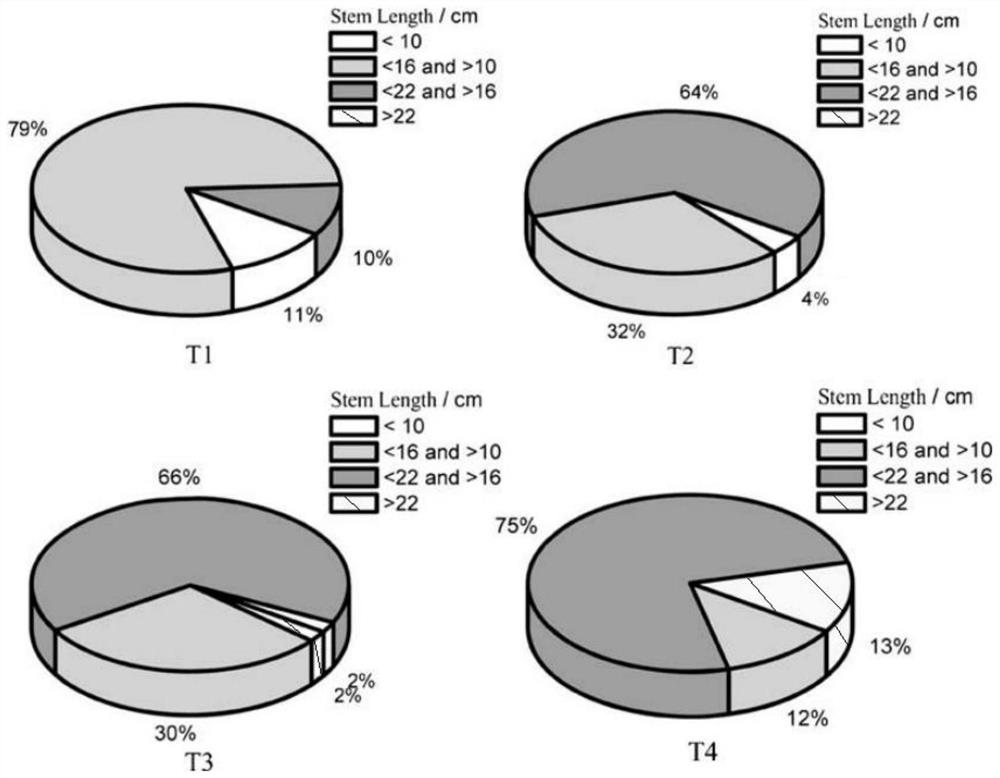
[0034] Example 2 Microbial mineralization improves soil wheat growth
[0035] Inoculate the sterilized culture medium with Bacillus pasteurianum, and culture it with shaking at 28°C for two days. After the cultivation is completed, use a spectrophotometer to measure the absorbance of the bacterial solution, and adjust the concentration of the bacterial solution to OD by centrifugal concentration and saline 600 =12, spare.
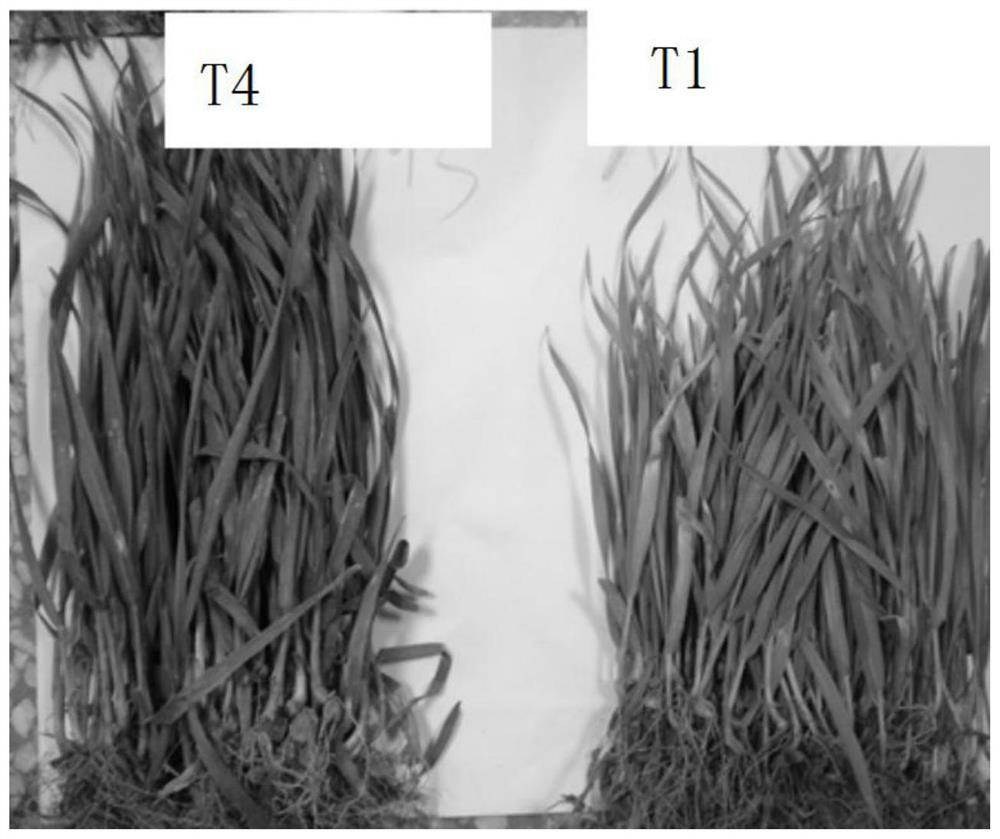
[0036] Preparation of cadmium-contaminated soil samples: 10 mg / L CdCl 2 The solution was mixed well with the soil to ensure 10 µg Cd per gram of soil 2+ . The total volume of prepared contaminated soil was 1.2m 3(depth × width × length = 0.3 m × 2 m × 2 m), the area of each soil sample is 1m 2 , the depth is 30cm. CdCl 2 The solution (336 L×10 mg / L) may pollute the soil.
[0037] Transplant wheat seedlings (stem length less than 10cm) into the soil. Four samples are set in this embodiment:
[0038] T1 is an untreated control group;
[0039] In g...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Example 3 Microbial mineralization remediation of cadmium-contaminated soil
[0045] Inoculate the sterilized culture medium with Bacillus pasteurianum, and culture it with shaking at 28°C for two days. After the cultivation is completed, use a spectrophotometer to measure the absorbance of the bacterial solution, and adjust the concentration of the bacterial solution to OD by centrifugal concentration and saline 600 =12 for backup.
[0046] Take 50 mM high-concentration cadmium-containing wastewater that has been prepared in the laboratory, add fresh soil and stir thoroughly to prepare heavy metal cadmium-contaminated soil, and the concentration of cadmium ions in the soil is 5 mg / kg.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com