Temporary floating bridge capable of reducing water flow impact
A water impact and temporary technology, applied in the direction of pontoon bridges, bridges, bridge forms, etc., can solve the problems of pontoon shaking, poor stability, and greater influence of pontoon bridges, and achieve the effects of ensuring safety in use, improving stability, and preventing tipping
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
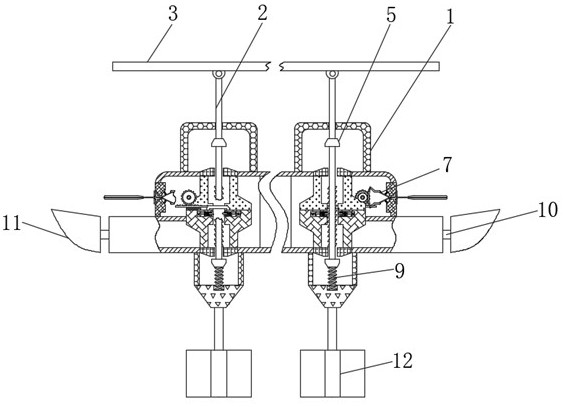
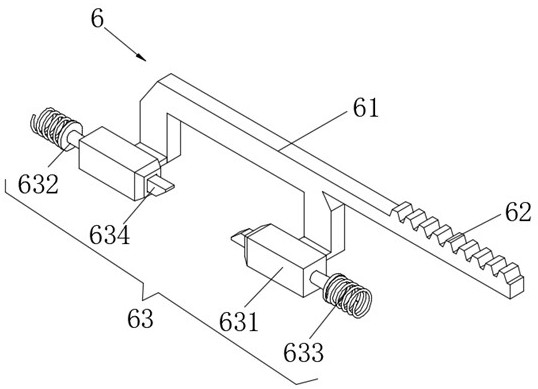
[0036] refer to Figure 2-4 , a temporary pontoon that can reduce the impact of water flow, including a floating block 1, the interior of the floating block 1 is movably connected with a limit rod 4, the outside of the limit rod 4 is provided with a force unloading mechanism 6, and the outside of the force unloading mechanism 6 is provided with an induction The mechanism 7 and the unloading mechanism 6 include a connecting rod 61 , the outside of the connecting rod 61 is fixedly connected with a toothed rod 62 , and the outside of the connecting rod 61 is fixedly connected with a limit mechanism 63 .
[0037] Wherein, the limit mechanism 63 includes a limit slider 631, the outside of the limit slider 631 is fixedly connected with a backing plate 632, and a return spring 633 is arranged between the back plate 632 and the floating block 1, and the limit slider 631 is slidably connected to Inside of float 1.
[0038] Wherein, the limit slider 631 slides inside the limit ratchet ...
Embodiment 2
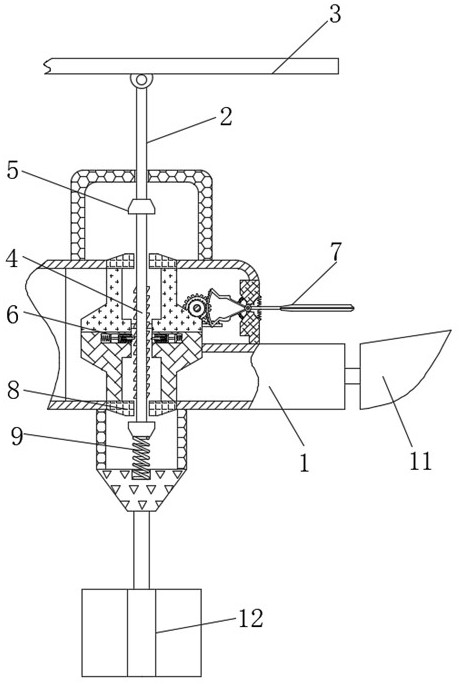
[0043] refer to Figure 5 , a temporary pontoon that can reduce the impact of water flow, including a floating block 1, the interior of the floating block 1 is movably connected with a limit rod 4, the outside of the limit rod 4 is provided with a force unloading mechanism 6, and the outside of the force unloading mechanism 6 is provided with an induction The mechanism 7 and the unloading mechanism 6 include a connecting rod 61 , the outside of the connecting rod 61 is fixedly connected with a toothed rod 62 , and the outside of the connecting rod 61 is fixedly connected with a limit mechanism 63 .
[0044] Wherein, the induction mechanism 7 includes a sailboard 71, and the exterior of the sailboard 71 is fixedly connected with a fork shaft 72, the fork shaft 72 is hinged inside the floating block 1, and a seal is arranged between the fork shaft 72 and the outside of the floating block 1. Sleeve 73, swing spring 74 is arranged between fork shaft rod 72 and the inner side of floa...
Embodiment 3
[0050] refer to Figure 1-6 , a temporary pontoon that can reduce the impact of water flow, including a floating block 1, the interior of the floating block 1 is movably connected with a limit rod 4, the outside of the limit rod 4 is provided with a force unloading mechanism 6, and the outside of the force unloading mechanism 6 is provided with an induction The mechanism 7 and the unloading mechanism 6 include a connecting rod 61 , the outside of the connecting rod 61 is fixedly connected with a toothed rod 62 , and the outside of the connecting rod 61 is fixedly connected with a limit mechanism 63 .
[0051] Wherein, the limit mechanism 63 includes a limit slider 631, the outside of the limit slider 631 is fixedly connected with a backing plate 632, and a return spring 633 is arranged between the back plate 632 and the floating block 1, and the limit slider 631 is slidably connected to Inside of float 1.
[0052] Wherein, the limit slider 631 slides inside the limit ratchet ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com