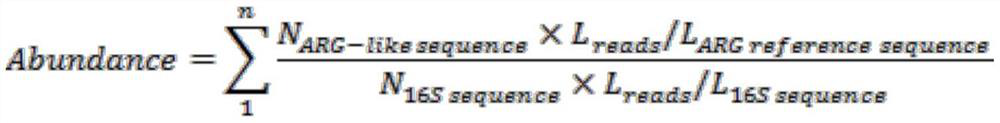Rapid quantitative detection method of novel chloramphenicol resistance gene and application thereof
A quantitative detection method and technology of resistance genes, which are applied in the field of rapid quantitative detection of new chloramphenicol resistance genes in environmental samples, can solve the problems of long verification period, inability to detect high-throughput environmental samples, complicated operation, etc., and achieve High accuracy, improved timeliness, high timeliness effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1: Extraction and sequencing of genomic DNA from different environmental samples
[0030] Surface water and tap water samples were collected in reservoirs and waterworks, respectively, filled into 1.5L sterile glass bottles, and then sent back to the laboratory for subsequent processing. Surface water and tap water samples were filtered with a microporous filter membrane with a pore size of 0.22 μm, and the filter membrane was stored at -80°C until DNA extraction. At the same time, samples of the activated sludge in the reactor were collected and centrifuged at 8000 rpm at 4°C for 10 minutes to collect the precipitate and place it at -80°C for subsequent DNA extraction.
[0031] DNA extraction from different samples was performed using FastDNA TM Spin Kit (MP Biomedicals, USA) kit, specific steps refer to kit instructions. After the genomic DNA was extracted, the integrity and concentration of the genomic DNA were checked by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis and ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Embodiment 2: Alignment of novel chloramphenicol resistance genes
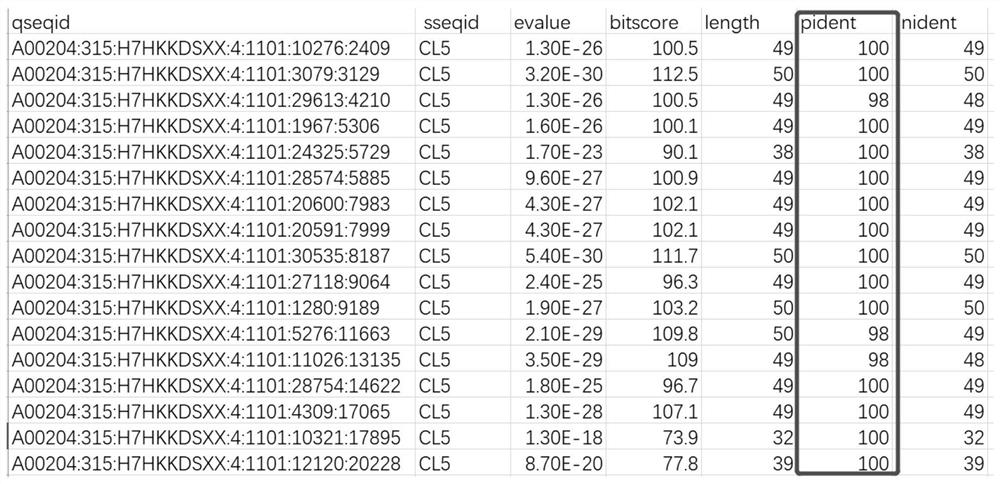
[0033] 利用实施例1中得到的测序数据进行质控获得cleandata,随后采用DIAMOND软件将双端数据与新型氯霉素抗性基因进行比对,这里以氨基酸序列为SEQNo.1(MWPAGKVLGGGSSINGMMYVRGNRGDYDQWAQLGCKGWSYDDVLPFFNKAETNENGGSRFRGDKGPLRVSNARLSTTLADAFIASGVRAGIPHNPDTNGAEQEGIGPCQATQNKGWRHSTARAYLAKAKRRSNLKVETHFMVSRVLIEKGRAIGVEGVQNGRTVRYLANKEVILCGGALSSPKILMLSGIGPAKHLGEHGIPVVVDSPGVGQNLQEHPGVLMSTHVGIDSLNVEVQSVARIVKHGLNFALFGRGPATACVASALAFIRTRDHLEWPNIQLSFSPIAYDFTPDGVHLYKRAAIGVAINICRPETRGQLLLRSTDPSERPIIQHELLGGDDEIKQLIEGCRIVRKIFRSKPFSEYDKGERLPGKQVETDADWIEYIRQSAFLMYHPTGTCAMGIGPTAVLDPELRVKGVTGLRVADASIMPTLVSANTNAPCIMIGERAADLIRRSH)的新型氯霉 Taking the chloramphenicol resistance gene as an example, obtain a sequence with a similarity higher than 95% with the novel chloramphenicol resistance gene (SEQNo.1) in the comparison result, and the specific parameters are set as follows:
[0034] diamond blastx-d CL5-p 16-q CL0-1_1.fq-f 6-o CL0-1-e 1e-10-k 20--id95.
[0035] The present invention uses 16 threads ...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Embodiment 3: the statistics of bacterial 16S rRNA gene number in different environmental samples
[0037] In order to facilitate the quantitative detection of the new chloramphenicol resistance gene, the 16S rRNA gene in the sample is selected as the internal reference here, and the number of 16S rRNA genes in the paired-end data needs to be counted. The present invention selects and adopts Metaxa2 software to count the number of 16S rRNA genes in each sample, and the specific comparison parameters are as follows:
[0038]metaxa2-1CL0-1_1.fq-2CL0-1_2.fq-o CL0-1
[0039] Such as figure 2 As shown, the result of comparison between the reactor sample in Example 1 and the database shows that a total of 36340 bacterial 16S rRNA genes were detected in the paired-end data of the sample.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com