Friction material comprising graphite, methods of making friction materials, and their uses
A friction material, graphite technology, applied in the direction of graphite, friction lining, friction clutch, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0100] Example 1: Hydrophobic CVD coated synthetic graphite using a rotary furnace
[0101] The particle size distribution is D 10 = 5μm and D 90 Ground synthetic graphite "GRAPHITE SGA" = 73 μm was used as starting material to improve its resilience and other properties for use as graphite-containing friction material. The starting material was fed in a continuous manner using a single screw into a rotary kiln reactor heated to 1050°C for two hours and approximately 2000 g of material was produced. A mixture of hydrocarbon and inert gas (amorphous carbon precursor: C 3 h 8 (3L / min) and carrier gas: N 2(1 L / min)) for chemical vapor deposition (CVD) to maintain the pressure in the reactor at 0 to 8 mbar above atmospheric pressure. The inclination of the tube was set at 4°, the rotation speed was set at 6 rpm, and the residence time in the kiln was about 30 minutes. To eliminate any amount of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), inert atmosphere (N 2 ) for further pro...
Embodiment 2
[0106] Example 2: Hydrophilic CVD-coated natural graphite using a rotary furnace and additional heat treatment
[0107] The particle size distribution is D 10 = 6μm and D 90 = 42 μm flake natural graphite "GRAPHITE NGB" was used as a starting material for a hydrophilic graphite friction material based on treated natural graphite with high resilience. The starting material was fed continuously for two hours using a rotary kiln reactor externally heated to 1050 °C and produced approximately 700 g of material. A mixture of hydrocarbon and inert gas (amorphous carbon precursor: C 3 h 8 (3L / min) and carrier gas: N 2 (1 L / min)) for chemical vapor deposition (CVD) to maintain the pressure in the reactor at 0 to 8 mbar above atmospheric pressure. The inclination of the tube was set at 4°, the rotation speed was set at 6 rpm, and the residence time in the kiln was about 30 minutes.
[0108] In order to improve the wettability of the obtained CVD modified "GRAPHITE NGB", another p...
Embodiment 3
[0112] Example 3: CVD Treated Synthetic Graphite Using a Fluidized Bed
[0113] The particle size distribution is D 10 = 7μm and D 90 Potato-shaped synthetic graphite "GRAPHITE PSG" = 36 μm was used as the starting material for the fluidized bed batch process. The starting material (8500 g) was loaded into a fluidized bed reactor, which was then heated to 920°C under nitrogen atmosphere. Using a mixture of hydrocarbon and inert gas (amorphous carbon precursor: toluene C 7 h 8 and carrier gas: N 2 ) was subjected to CVD treatment for 260 minutes. Then, the reactor and the treated graphite were cooled under nitrogen atmosphere. When the material reaches ambient temperature, it is discharged from the fluidized bed.
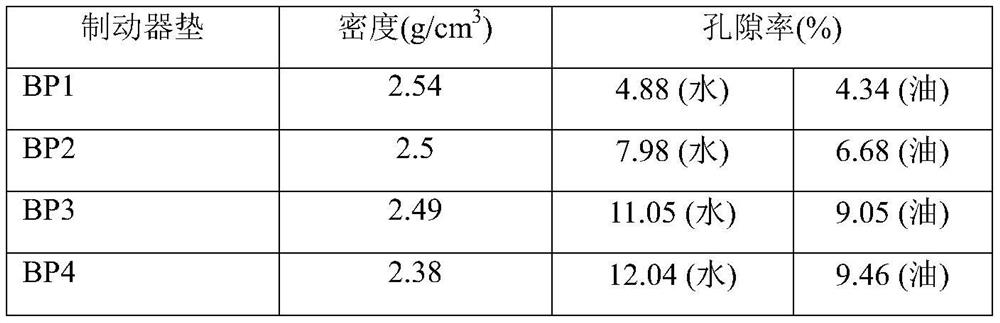
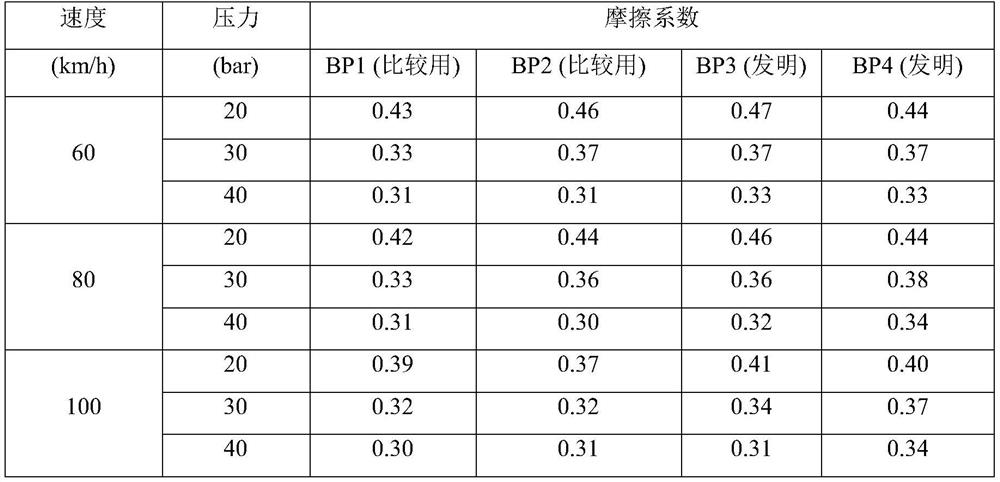
[0114] The properties of the untreated starting material "GRAPHITE PSG" and the obtained high resilience material "GRAPHITE PSG HSBC" are listed in Table 3:
[0115] table 3
[0116] graphite PSG (for comparison) PSG HSB C (Invention) Type...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com