A kind of preparation and purification method of high antioxidant activity Grifola frondosa polysaccharide
A technology of Grifola frondosa polysaccharides and oxidation activity, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, methods based on microorganisms, using added compounds to stimulate growth, etc., can solve problems such as unsatisfactory market applications and production limitations of acidic polysaccharide components , to achieve the effect of improving in vitro antioxidant activity, safety, non-toxic stability, and increasing yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Example 1 (control group)
[0065] Grifola frondosa seed culture: Cut the Grifola frondosa grown on PDA plates into 1cm 2 Take 3 to 5 small pieces of the same size and inoculate them into the seed medium of the conical flask with the liquid volume of 100 mL / 250 mL, and cultivate at 160 r / min and 28 °C for 5 days.
[0066] Grifola frondosa fermentation culture: add 150 mL of fermentation medium to a 500 mL conical flask, the inoculum volume is 15 mL of seed liquid, and cultivate at 160 r / min at 28 °C for 8 days.
[0067] Each L of the seed medium contains potato 200g, glucose 20g, peptone 5g, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 2g, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 1g, vitamin B 1 0.02g, pH natural. Each L of the fermentation medium contains 22 g of glucose, 3 g of peptone, 1.2 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.8 g of magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, and vitamin B 1 0.12g, pH natural.
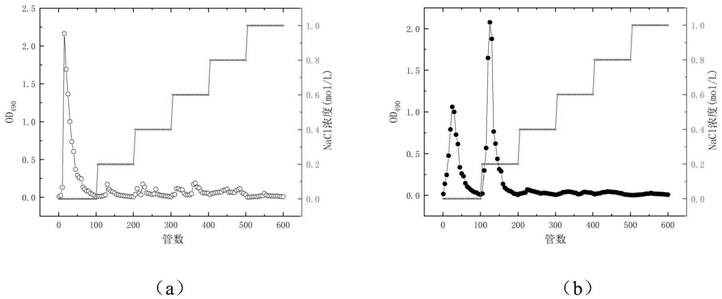
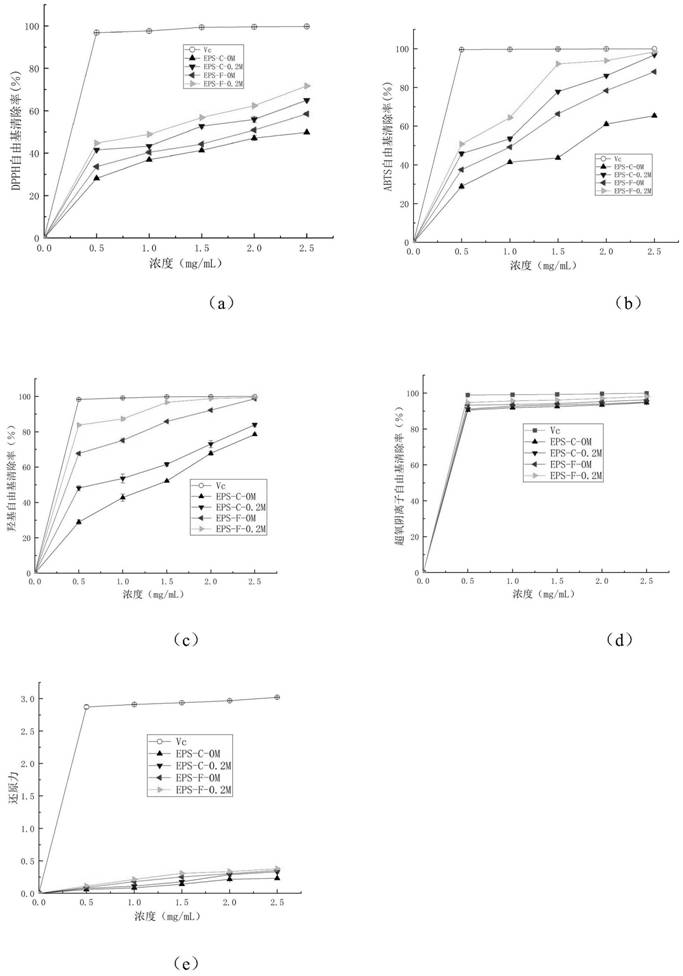
[0068] The extraction method and determination method of Grifola frondosa polysacchar...
Embodiment 2
[0071]Substratum and cultivation method are the same as in Example 1, the difference is that the 0-2d of Grifola frondosa fermented culture, add exogenous additive farnesol 0-0.2mmol / L, add the Grifola frondosa fermented liquid after the addition of farnesol and continue to ferment to 8d. After the fermentation, the mycelium of Grifola frondosa was obtained and the polysaccharide in the fermentation broth was extracted. Wherein, the extraction method and determination method of the polysaccharide in the fermentation broth of Grifola frondosa are the same as those in Example 1, and the polysaccharide content in the fermentation broth of Grifola frondosa was determined to be (0.8371±0.0532) g / L, which was increased by 66% compared with the control group. like figure 2 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0073] The culture medium and the culture method are the same as in Example 1, except that the 0-2 d of the fermentation culture of Grifola frondosa, the addition of an exogenous additive farnesol 0.2-0.4 mmol / L, and the fermentation broth of the Grifola frondosa after the addition of the farnesol continues to ferment to 8d. After the fermentation, the mycelium of Grifola frondosa was obtained and the polysaccharide in the fermentation broth was extracted. Wherein, the extraction method and determination method of the polysaccharide in the fermentation broth of Grifola frondosa are the same as those in Example 1, and the polysaccharide content in the fermentation broth of Grifola frondosa was determined to be (1.0058±0.0128) g / L, which was increased by 98% compared to the control group. like image 3 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com