Novel FGFR inhibitors and uses thereof
A compound and pharmaceutical technology, applied in the field of cancer treatment, pan-FGFR and FGFR4 specific inhibitors, can solve the problem of suboptimal potency and bioavailability of BLU9931
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0075] Design of pyridylpyrimidine-based FGFR inhibitors
[0076] Using structure-based design, two pyridylpyrimidine-based FGFR inhibitors have been discovered: pan-FGFR inhibitors and FGFR4-specific inhibitors. Specifically, docking was performed to assess the binding mode and affinity of candidate inhibitors to FGFRs.
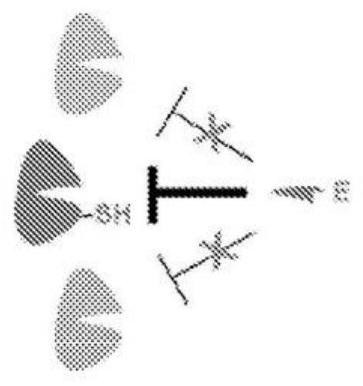
[0077] like Figure 1B As shown, FGFR4 contains a cysteine (Cys552), which is located near the ATP-binding site of the receptor hinge region, unique in the FGFR family, and rare in other kinases. Covalent inhibitors of FGFR4 kinase can potently and selectively inhibit FGFR by covalently targeting the thiol (SH) group in cysteine residues ( Figure 1A ).
[0078] Structure-based design approaches have enabled the discovery of novel pan-FGFR inhibitors, such as Figure 2A Compound 1 and FGFR4 specific inhibitors shown in, such as Figure 2B Compounds 2, 3 and 4 shown in .
example 2
[0080] General structure of novel FGFR4-specific inhibitors
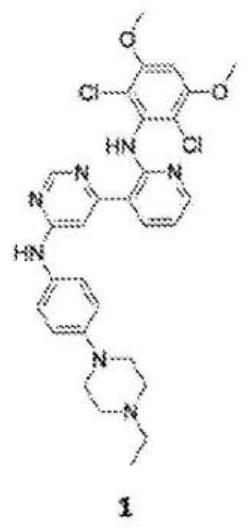
[0081] Using the structure-based design described above, general structures for other FGFR4-specific inhibitors were established. Other FGFR4-specific inhibitors can be synthesized with general structures such as image 3 shown.
[0082] In the general structure above, X is CH or N. In the top benzene ring, each R 1 Substituents are hydrogen, halogen or methoxy, and n is 0-4. In the second benzene ring, each R 2 Substituents are hydrogen, methyl, amino, or propargyloxy, and n is 1-2. The phenyl group contains a warhead, which is usually attached to an N atom and is an electrophilic moiety that can form a covalent bond with a nucleophile. Examples of warheads include, but are not limited to, haloacetamides and acrylamides.
example 3
[0084] In vitro efficacy evaluation of FGFR inhibitors
[0085] The efficacy of compounds to inhibit FGFR kinase activity was measured by determining IC50 values.
[0086] Two of the compounds were tested in vitro against the corresponding FGFRs: Compound 1 and Compound 2 (FGFR2 for Compound 1 pan-inhibitor and FGFR4 for Compound 2 covalent inhibitor). The results are listed in Table 4, expressed as IC 50 value (concentration of compound that inhibits 50% of enzymatic activity).
[0087] Table 4. In vitro inhibition assays for compounds 1 and 2
[0088]
[0089] To assess the efficacy profile of compounds to inhibit enzymatic activity, compounds 1 and 2 were evaluated for their inhibition of 15 different kinases. As shown in Table 5, Compound 1, a pan-FGFR inhibitor, showed significant inhibition of all members of the FGFR family, as well as some inhibitory activity against some other kinases. Compound 2 showed high selectivity and potency for FGFR4 (only selected dat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com