Starting or locked-rotor resisting method of direct-current brush motor
A brushed DC motor and motor rotor technology, which is applied to the starter of a single DC motor, the deceleration device of an AC motor, a motor generator/starter, etc. And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] In order to facilitate the understanding of the present invention, the present invention will be described in more detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
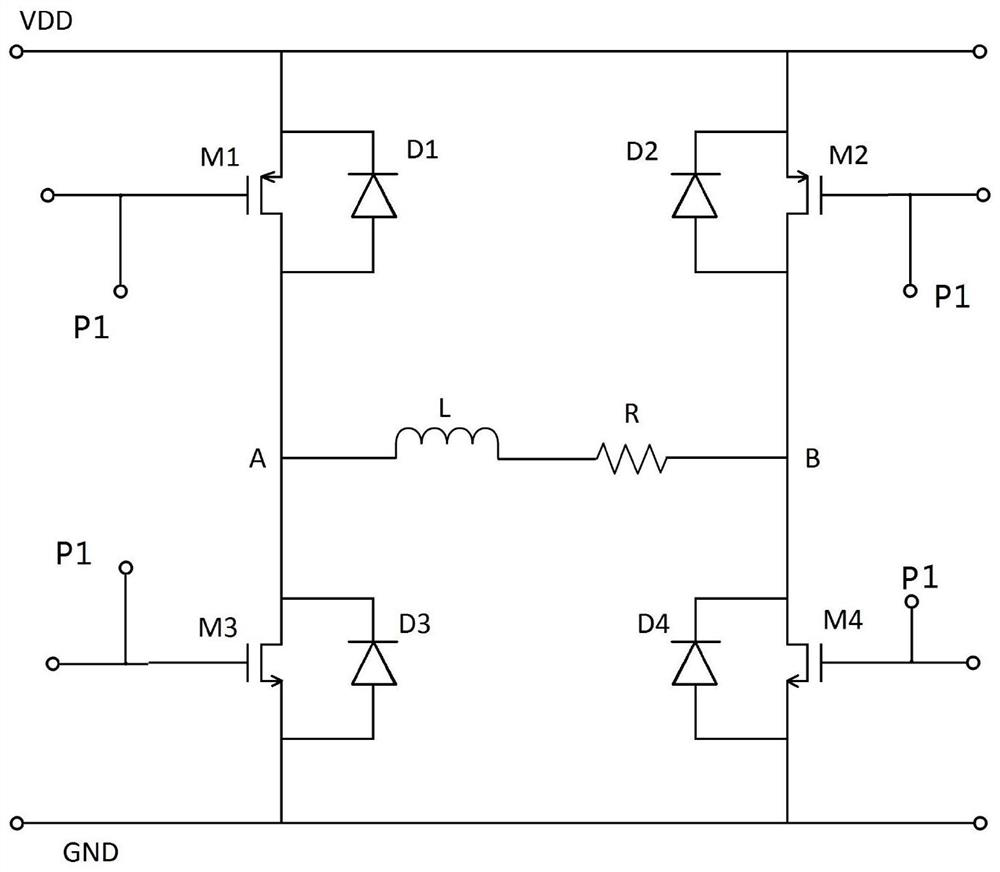
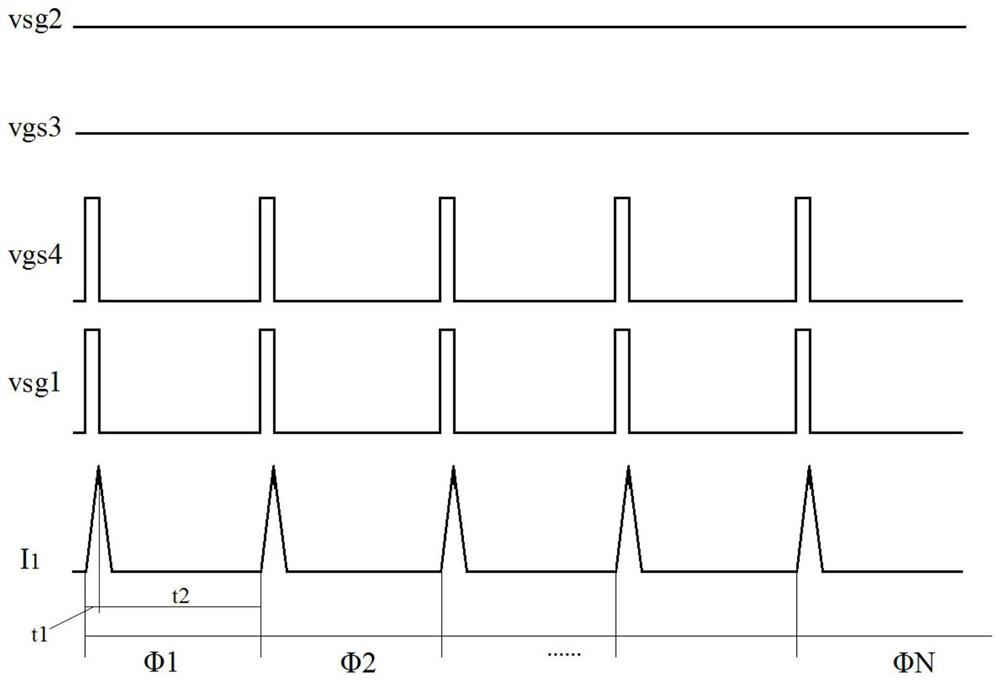
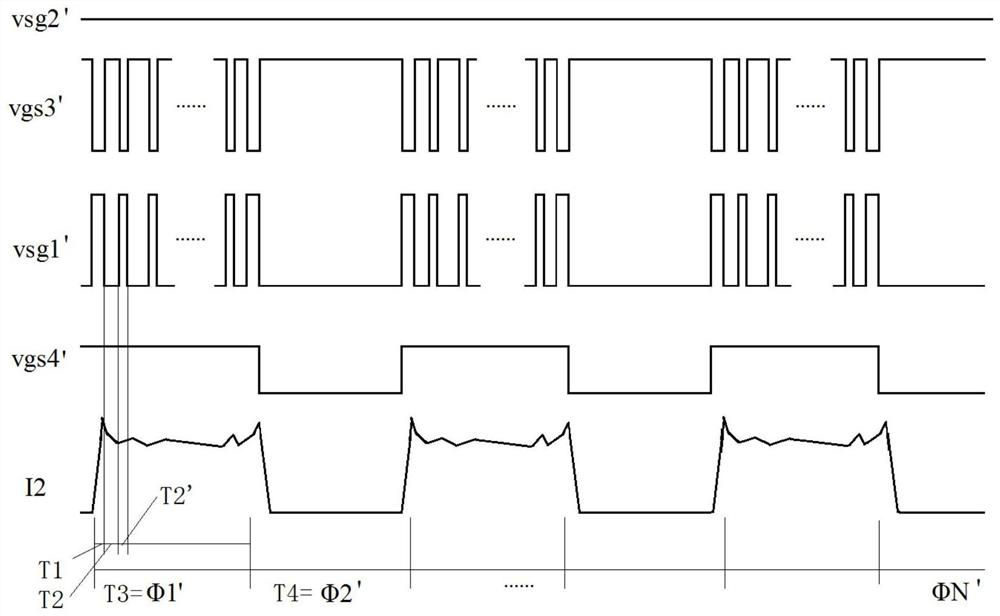
[0030] A method for starting or anti-locking a DC brushed motor, which is different from the prior art in that, in addition to including a traditional overcurrent protection circuit, an overtemperature protection circuit and such as figure 1 The H-bridge driving circuit shown also includes a PWM control module, and the PWM control module P1 controls the first high-side PMOS switch M1, the second high-side PMOS switch M2, the third The low-side NMOS switch M3 and the fourth low-side NMOS switch M4 are turned on and off. The PWM control module P1 is preset with a modulation current threshold Ipwm and a modulation current startup time tp, the modulation current threshold Ipwm is at most not greater than the overcurrent protection threshold Iocp, and the minimum is not less t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com