Porous ceramic for electronic cigarette atomization core with low thermal conductivity and high porosity and preparation method of porous ceramic
A technology with high porosity and low thermal conductivity, which can be used in ceramic products, smoker products, applications, etc., and can solve problems such as low thermal conductivity, low thermal conductivity, and short time intervals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
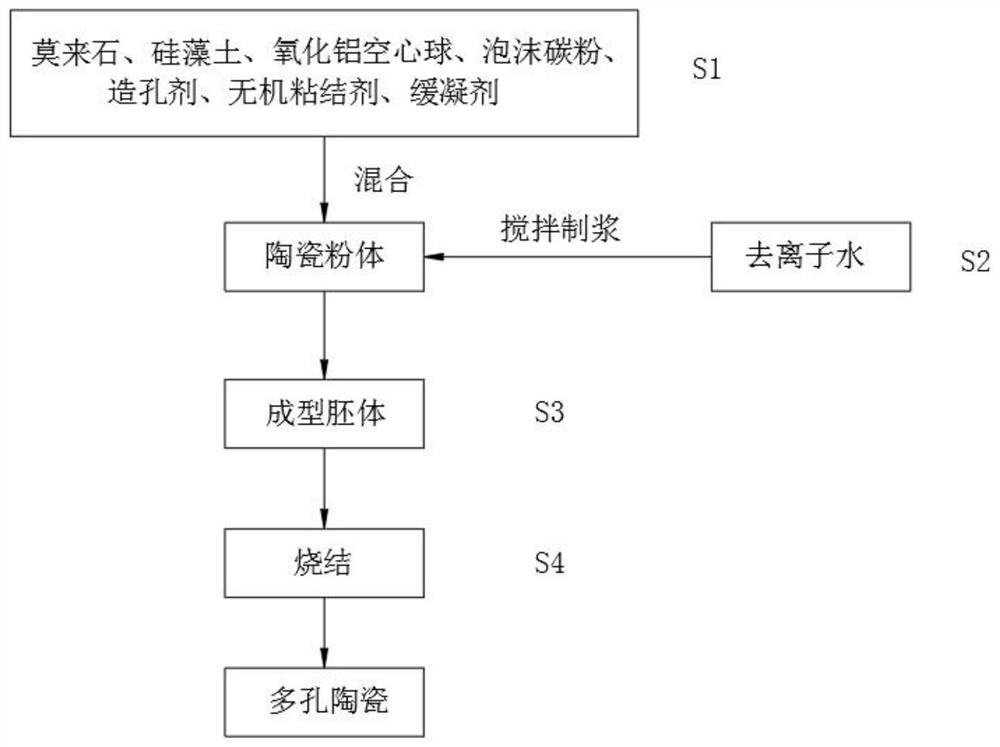
[0025] The specific steps of the preparation method of the porous ceramics for the low thermal conductivity and high porosity electronic smog core are as follows:
[0026] Step S1: Mix raw materials into spare materials.
[0027] Specifically, the process of mixing raw materials into spare materials includes: mixing mullite, diatomaceous earth, foamed carbon, aluminum oxide hollow spheres, inorganic binders, pore-forming agents, and retarders into raw materials with good consistency.
[0028] Specifically, the mixing method adopts one or more combinations of dry ball mill mixing, double-motion mixer mixing, three-dimensional mixer mixing, V-type mixer mixing, and the like.
[0029] Specifically, the mixing time is 1-3 hours.
[0030] Wherein, calculated according to mass percentage, the raw materials include: 1%-15% mullite, 40%-60% diatomite, 5%-25% aluminum oxide hollow spheres, 1-5% foam carbon powder , 10%-15% pore forming agent, 1-8% inorganic binder, 0.1-0.5% retarder....
Embodiment 1
[0052] The preparation process of the porous ceramic atomizing core of this embodiment is as follows:
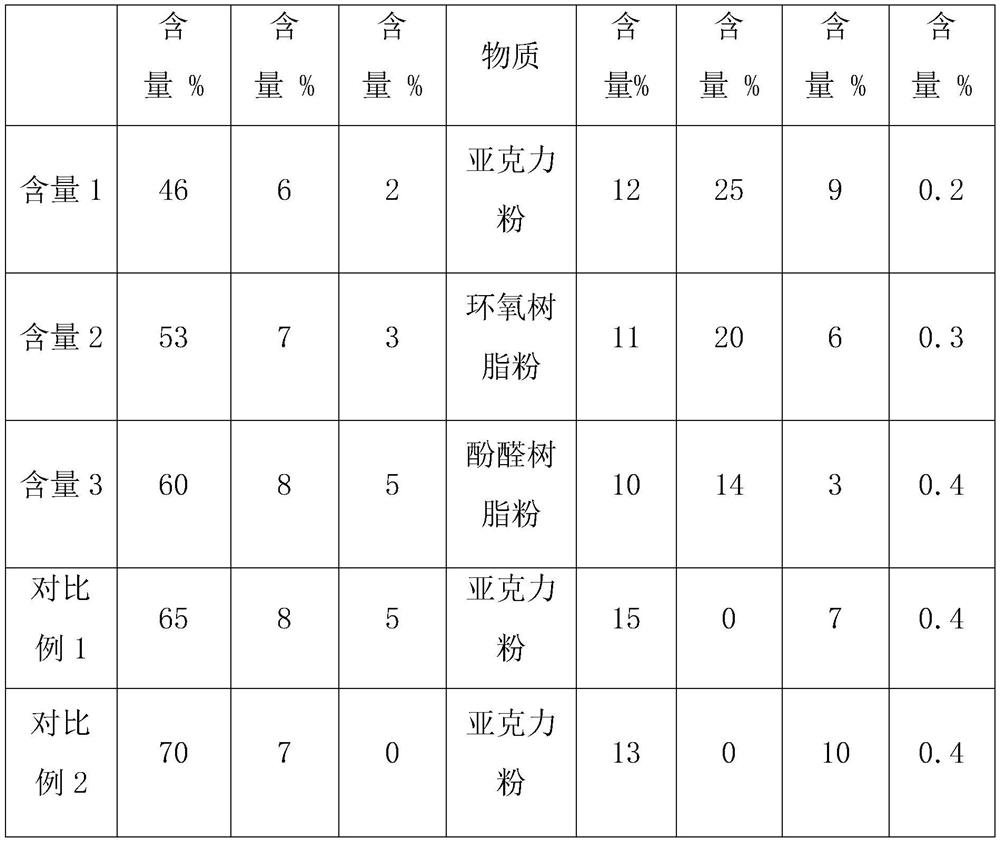
[0053] (1) According to Table 1, each component was weighed according to the mass percentage (referred to as content in the table) to obtain raw materials. Among them, the D50 of mullite is 2 μm; the D50 of diatomite is 15 μm; the D50 of alumina hollow sphere is 80 μm; the D50 of carbon foam is 15 μm, the D50 of pore-forming agent is 8 μm, and the D50 of inorganic binder is 1.5 μm. Add to a ball mill or other mixing equipment and dry mix for 2 hours.
[0054] (2) Mix and stir the mixed raw materials according to a liquid-solid ratio of 1.2:1 to obtain a ceramic slurry.
[0055] (3) Slurry molding the ceramic slurry to obtain a square block porous ceramic blank.
[0056] (4) Put the ceramic blank into a sintering furnace for sintering to obtain a porous ceramic atomizing core product. Specifically, the drying temperature is 260°C, the burning temperature of the pore-formin...
Embodiment 2
[0058] The preparation process of the porous ceramic atomizing core of this embodiment is as follows:
[0059] (1) According to Table 1, each component was weighed according to the mass percentage to obtain raw materials. Among them, the D50 of mullite is 4 μm; the D50 of diatomite is 10 μm; the D50 of alumina hollow sphere is 100 μm; the D50 of carbon foam is 10 μm, the D50 of pore-forming agent is 6 μm, and the D50 of inorganic binder is 3 μm. Add to a ball mill or other mixing equipment and dry mix for 0.5 hours.
[0060] (2) Mix and stir the mixed raw materials according to a liquid-solid ratio of 1:1 to obtain a ceramic slurry.
[0061] (3) Slurry molding the ceramic slurry to obtain a square block porous ceramic blank.
[0062] (4) Put the ceramic blank into a sintering furnace for sintering to obtain a porous ceramic atomizing core product. Specifically, the drying temperature is 240°C, the burning temperature of the pore-forming agent and foam carbon is 500°C, and t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com