Porphyra filament albinism pathogenic bacteria
A technology for albinism and filaments, applied in the direction of bacteria, climate change adaptation, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as unresolved causes of disease
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Embodiment 1: Isolation and purification of pathogenic bacteria
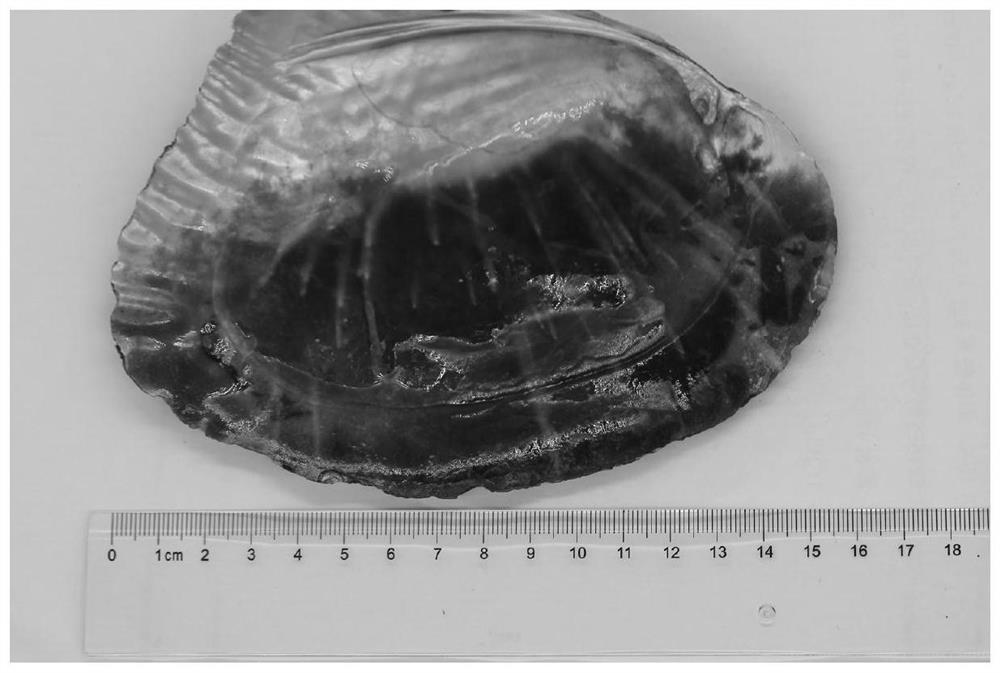
[0019] Albino Porphyra shell filaments from a laver nursery in Lianyungang, Jiangsu in October 2018 ( figure 1 ) to isolate bacteria. Rinse the surface of the diseased shells with sterilized seawater (filtered with glass fiber membrane, heated to boiling, keep boiling for 2 minutes and then cooled for use) for 3 to 2 times, and then wipe dry with sterilized cotton balls (sterilized by moist heat) . Use a sterilized razor blade to scrape the affected part of the shell filament until the white calcareous part is exposed. Dissolve the scrapings with 1mL sterile seawater and fill them into a 1.2mL sterile centrifuge tube. The lysate was then serially diluted to 10 with sterile seawater -2 、10 -3 times.
[0020] Take 100 μL of the above diluted solution and spread them on sterilized TSA medium, 2216E seawater medium and TCBS medium plates with a NaCl concentration of 1%, respectively, and incubate at 28°...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Embodiment 2: the research of bacterial strain pathogenicity
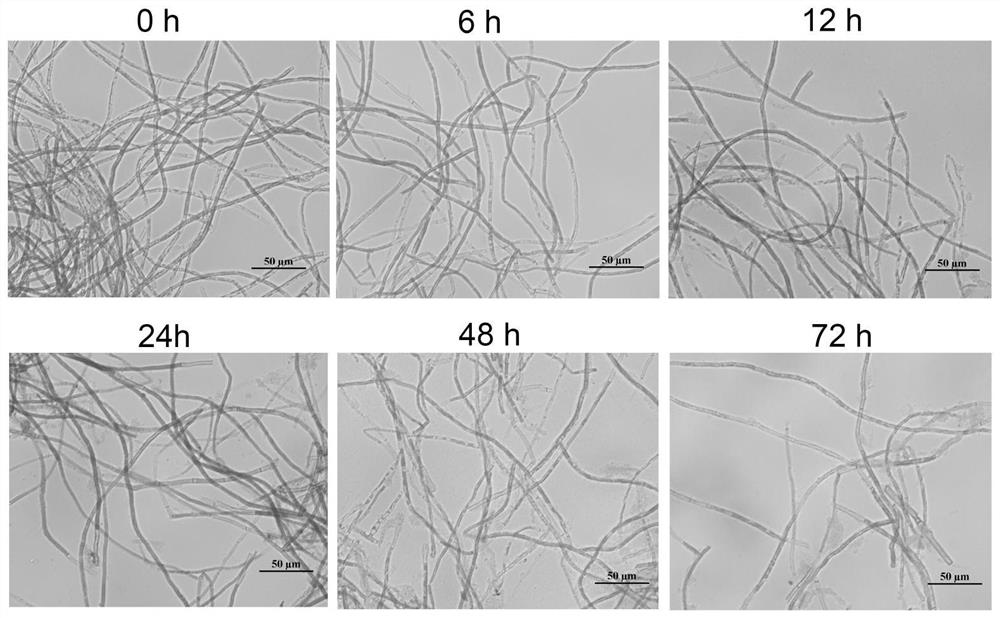
[0024] The GN-R-1 strain was inoculated in 2216E liquid medium at a ratio of 1% (1:100), 180r / min, and cultured at 28°C for 16h. Collect the bacterial solution in a sterile centrifuge tube and centrifuge at 8000 r / min for 2 min. After centrifugation, discard the supernatant and collect the pellet. Resuspend and wash with an appropriate amount of sterilized nutrient seawater, and repeat 3 times. After resuspension and washing, add appropriate amount of sterilized nutrient seawater to resuspend to make bacterial suspension. The bacterial concentration was calculated by the plate colony count method. Adjust the bacterial concentration to 10 7 About CFU / ml.
[0025] The free filaments of Porphyra used for infection were provided by the algae bank of the Key Laboratory of Marine Biotechnology in Zhejiang Province. Use sterile seawater to cultivate filaments, add Ningda No. 3 mother liquor, and the nutrient ...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Example 3: 16S rRNA coding sequence analysis and strain characteristics of GN-R-1
[0030] Bacteria genomic DNA is extracted, with the following primers (sequence information is as follows:
[0031] 27F: 2'-GAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3';
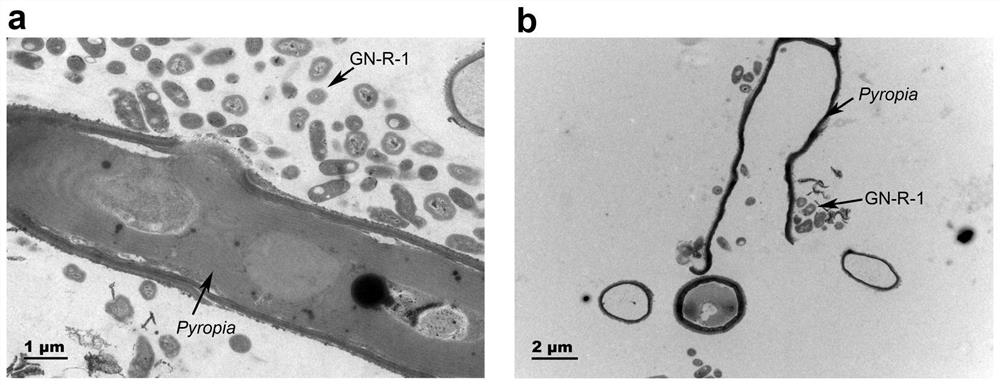
[0032] 1429R: 2'-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3') for PCR amplification of 16S rDNA. After NCBI and phylogenetic tree comparison ( Figure 4 ), the bacteria were identified as belonging to the genus Loktanella.
[0033] The strain was named Loktanella sp. GN-R-1, and it was deposited in the General Microbiology Center of China Committee for the Collection of Microorganisms, with the preservation number CGMCC No.21174, and the preservation date was November 13, 2020; Preservation address: No. 3, Yard No. 1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing.
[0034] The colonies of Loktanella sp. GN-R-1 strain are opaque, raised, and have regular edges. Scanning electron microscopy showed that GN-R-1 was oval and had flagella.
[0035] Set the envir...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com