Near-field source positioning method based on auto-encoder and parallel network
A self-encoding network and self-encoder technology, which is applied in the field of array signal processing parameter estimation, can solve the problems of large training data volume, high training difficulty, and inability to obtain the number of signal sources, so as to reduce the training data volume and the algorithm. Complexity, the effect of reducing the difficulty of training
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0051] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
[0052] The technical solution adopted by the present invention to solve its technical problems comprises the following steps:
[0053] (1) First, the near-field source data X(n) received by the array under the condition of single source is actually collected or simulated, and the length of each piece of data is L, and the covariance is calculated according to the collected data And calculate the feature extraction vector
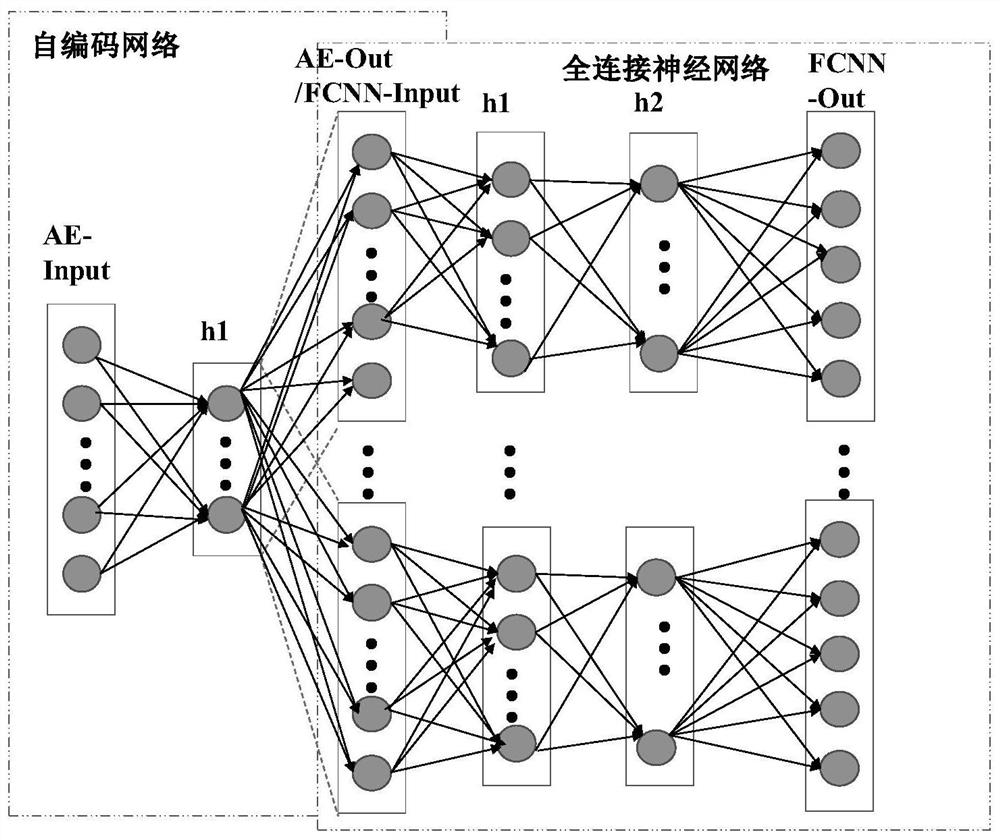
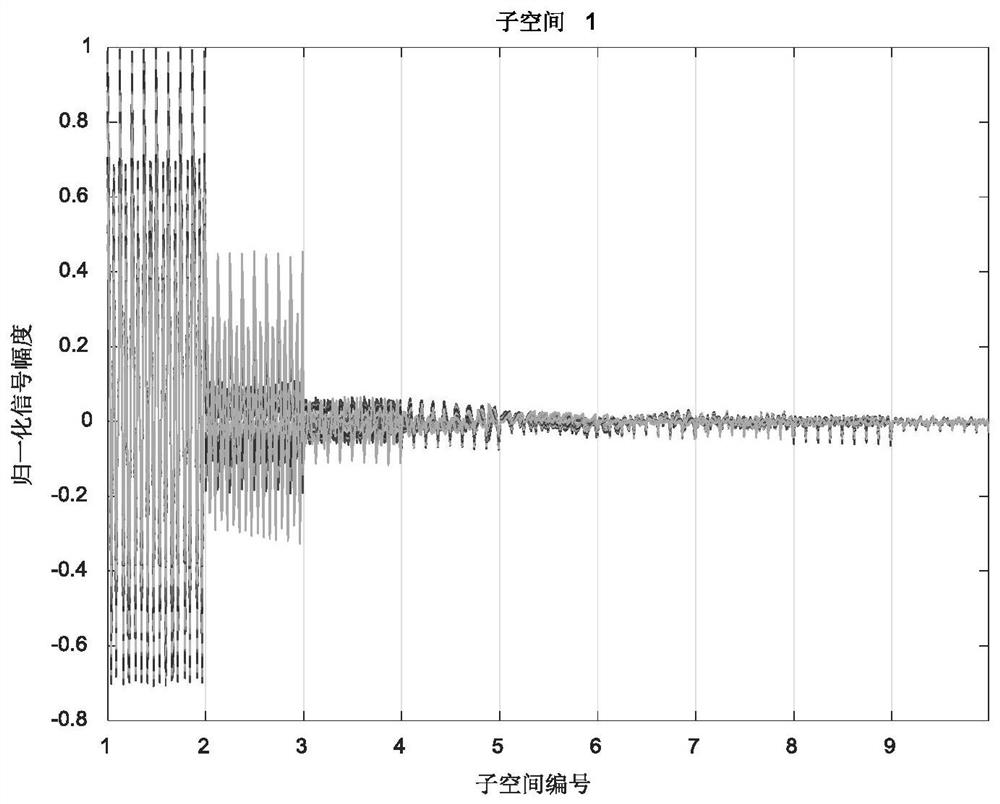
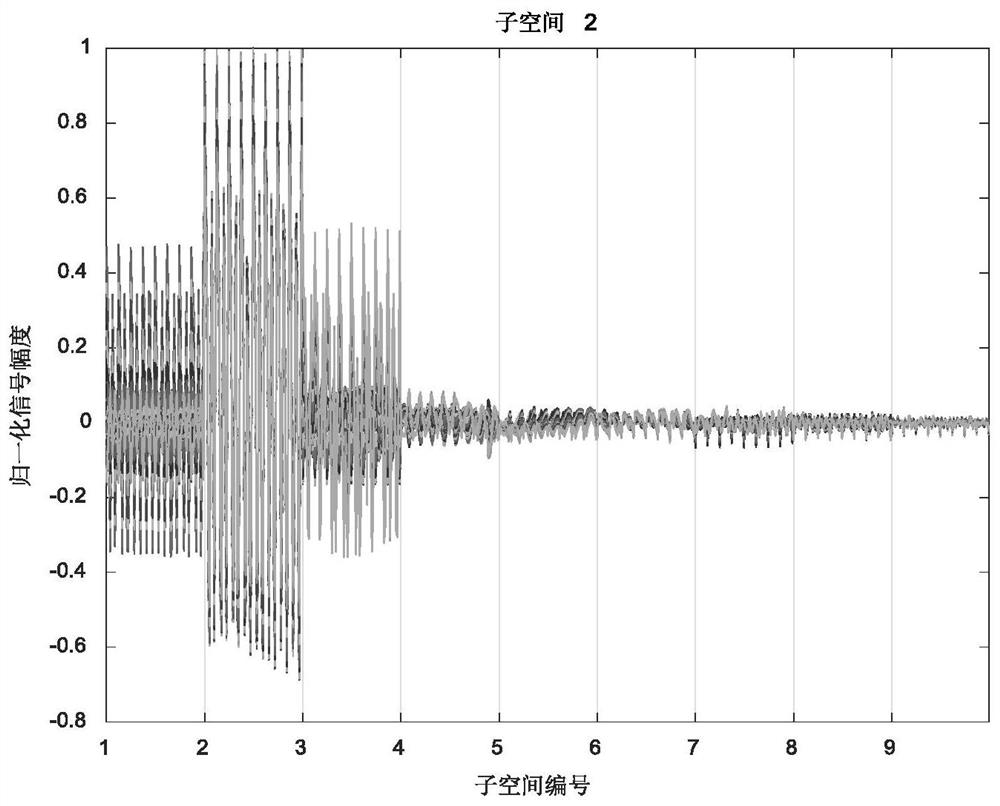
[0054] (2) Build an autoencoder network whose input is the feature extraction vector obtained in step (1) Divide the entire DOA estimation space [-90°, 90°) into 9 subspaces, and each subspace is 20°. If the DOA label of any set of data in the 9 subspaces is in the Pth subspace area, where P=1,2, …, 9, the input is copied to the output of this subspace, and the remaining subspaces are forced to be 0, and the output of the self-enc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com