Hydrogel dressing for wound healing and preparation method thereof
A hydrogel and gelatin technology, applied in medical science, bandages, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in showing efficacy, complex preparation process, high cost, etc., and achieve the effects of accelerating wound healing, depositing collagen, and promoting the formation of new blood vessels.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
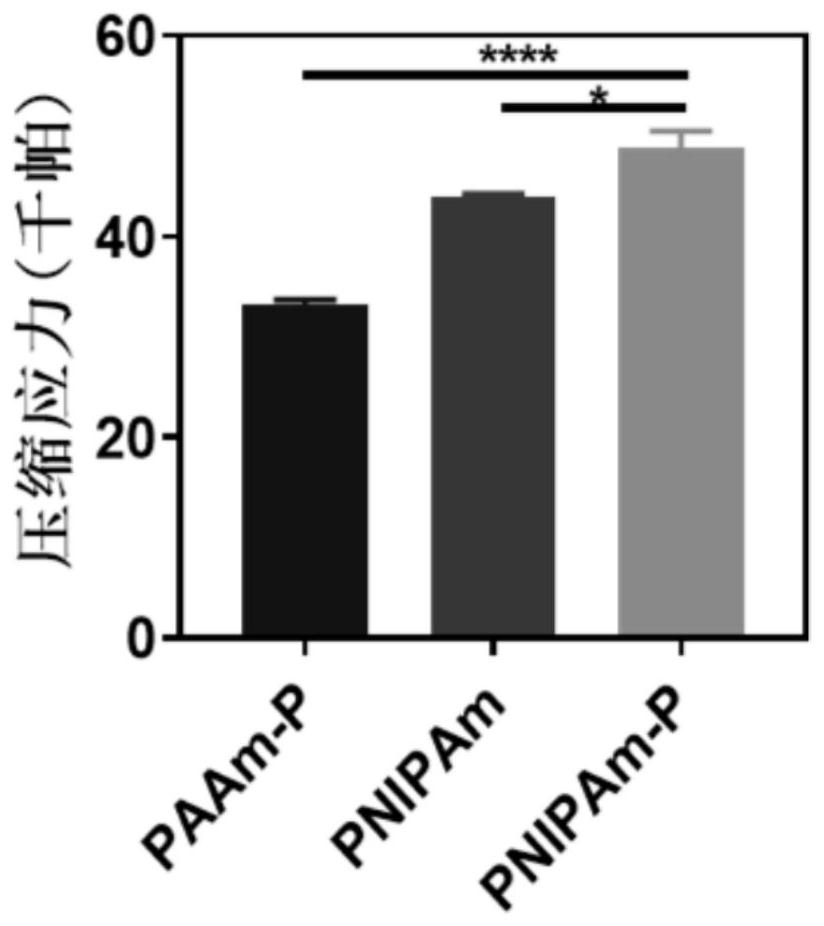
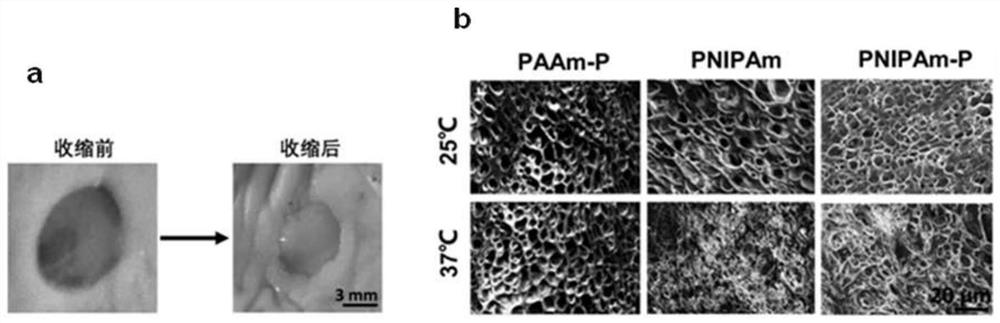
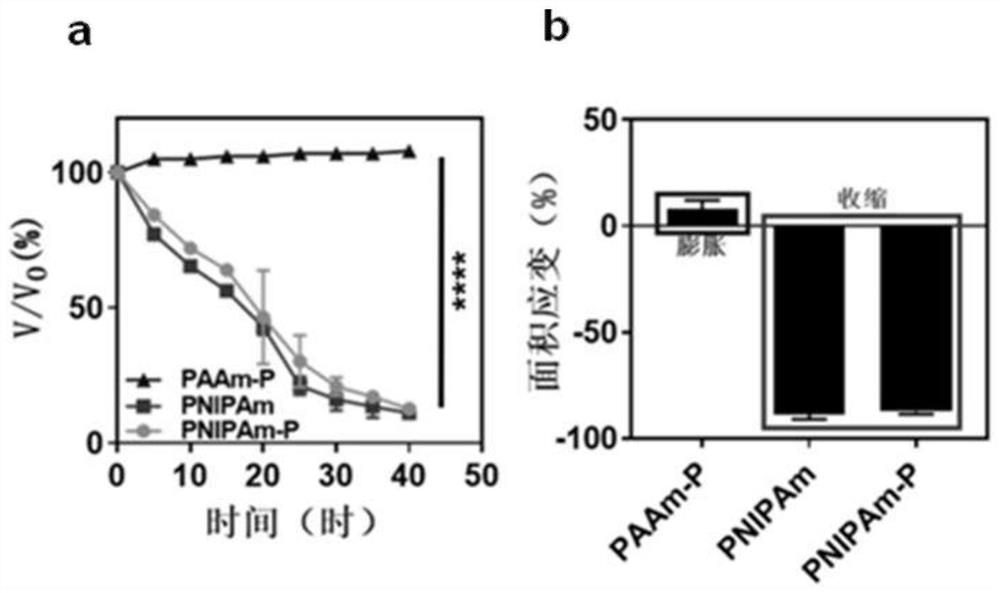
[0044] Embodiment 1: the preparation of PNIPAm-P hydrogel
[0045] First, polymethacrylic acid (PMAA) (6 kDa) was synthesized by conventional radical polymerization and incubated overnight with NaOH to obtain the sodium salt form of PMAA-Na. Next, a NIPAm solution (solution A) having a concentration of 100 mg / mL was prepared by dissolving a certain amount of N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAm) in water. Then, a gelatin solution (solution B) having a concentration of 25 mg / mL was prepared by dissolving a certain amount of gelatin in water. Next, solution B, PMAA-Na (25 mg / mL) and crosslinker Bis were slowly added to solution A (solution C). After uniform mixing, the solution C in N 2 Bubble down for 30 minutes to remove oxygen. Finally, the initiator APS and accelerator TEMED were added to solution C and reacted at 4 °C for 6–8 hours to obtain PNIPAm-P hydrogel. After gelling, the hydrogel was taken out and cut into small pieces, soaked in PBS for 30 min, and rinsed 3 times befor...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Embodiment 2: the preparation of PNIPAm hydrogel
[0047] First, a NIPAm solution having a concentration of 100 mg / mL (solution A) was prepared by dissolving a certain amount of N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAm) in water. Next, a gelatin solution (solution B) having a concentration of 25 mg / mL was prepared by dissolving a certain amount of gelatin in water. After solutions A and B are uniformly mixed, in N 2 Bubble down for 30 minutes to remove oxygen. Finally, the initiator APS and accelerator TEMED were added to the mixed solution and reacted at 4 °C for 6–8 hours to obtain PNIPAm hydrogel. After gelling, the hydrogel was taken out and cut into small pieces, soaked in PBS for 30 min, and rinsed 3 times before use. The hydrogel can be stored freeze-dried.
Embodiment 3
[0048] Embodiment 3: the preparation of PAAm-P hydrogel
[0049] First, polymethacrylic acid (PMAA) (6 kDa) was synthesized by conventional radical polymerization and incubated overnight with NaOH to obtain the sodium salt form of PMAA-Na. Next, an AAm solution having a concentration of 100 mg / mL was prepared by dissolving a certain amount of acrylamide (AAm) in water (solution D). Then, a gelatin solution having a concentration of 25 mg / mL was prepared by dissolving a certain amount of gelatin in water (solution B). Next, solution B, PMAA-Na (25 mg / mL) and crosslinker Bis were slowly added to solution D (solution E). After uniform mixing, solution E was dissolved in N 2 Bubble down for 30 minutes to remove oxygen. Finally, the initiator APS and accelerator TEMED were added to solution E, and reacted at 4°C for 6-8 hours to obtain PAAm-P hydrogel. After gelling, the hydrogel was taken out and cut into small pieces, soaked in PBS for 30 min, and rinsed 3 times before use. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com