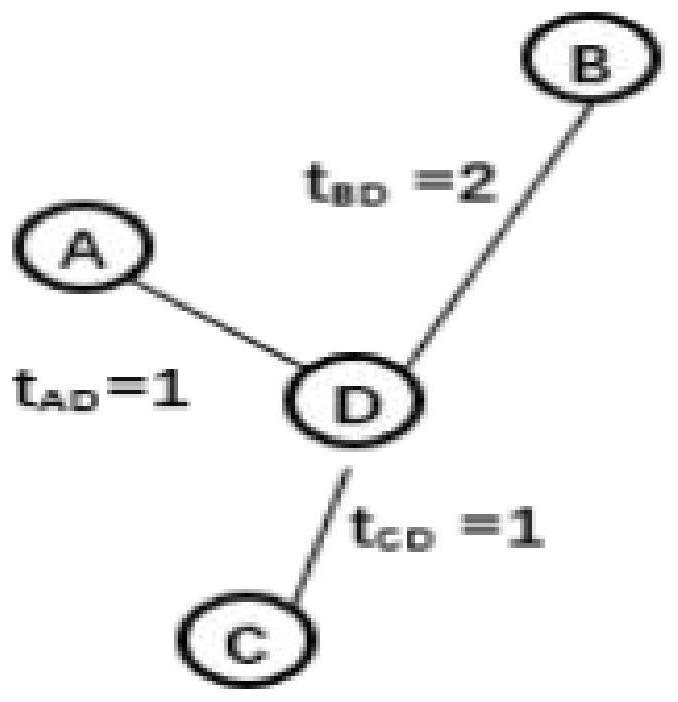
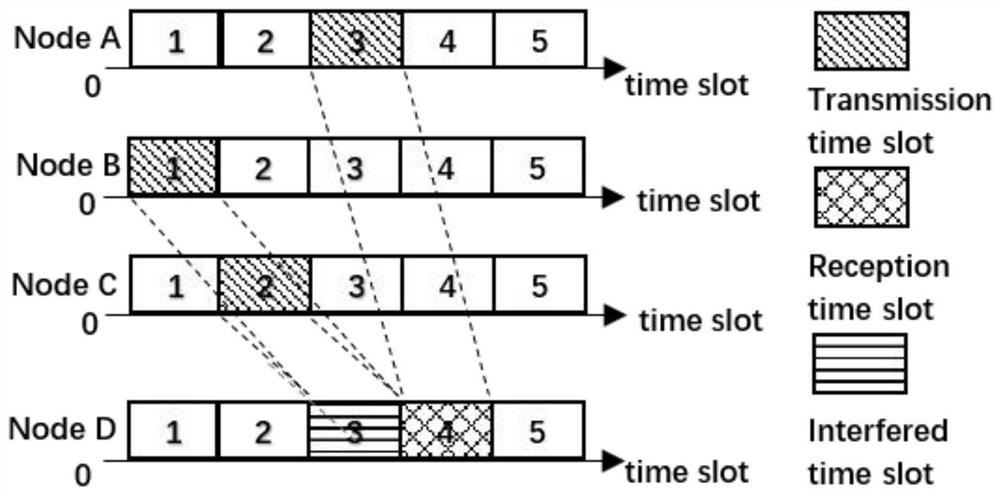
MAC protocol for realizing time domain interference alignment based on deep reinforcement learning in underwater acoustic network
A technology of reinforcement learning and underwater acoustic network, applied in wireless network protocol, network topology, ultrasonic/acoustic/infrasonic transmission system, etc., can solve the problems of algorithm complexity increase and algorithm calculation infeasibility, and achieve the effect of improving throughput
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
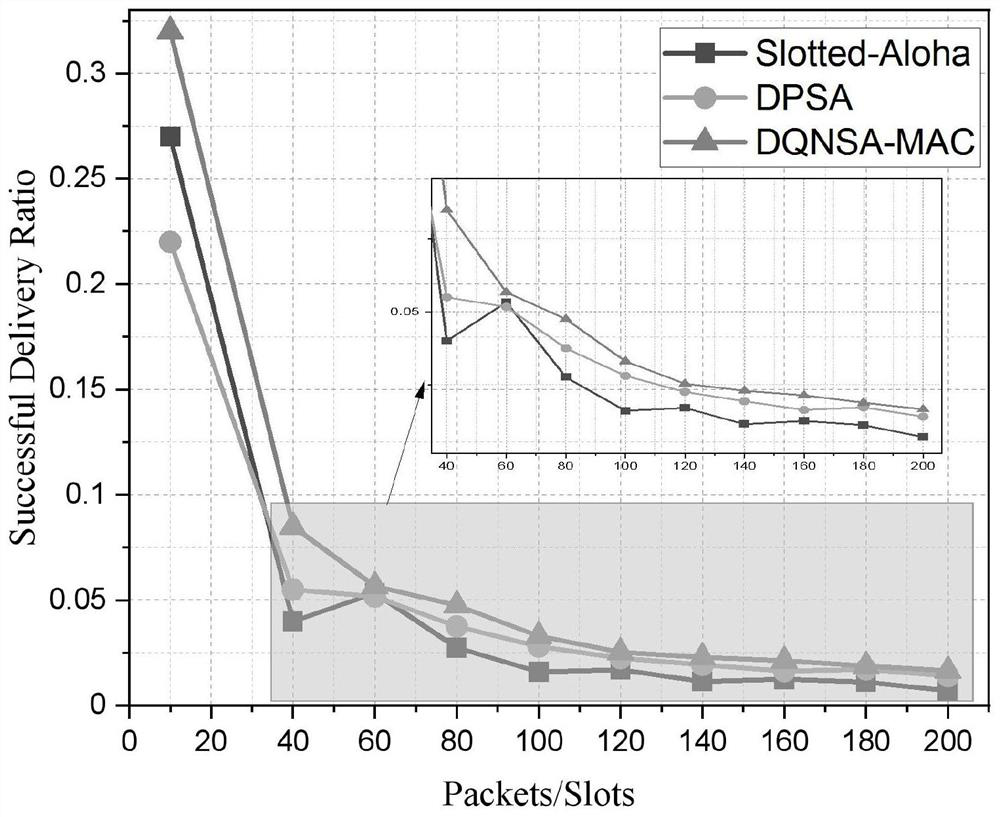
[0058] In order to verify the performance of the DQNSA-MAC protocol of the present invention, carry out following simulation experiments:
[0059] The DQNSA-MAC protocol is implemented and simulated based on the TensorFlow framework using the Python programming language. In the DQNSA-MAC protocol, DQN includes a 100-unit LSTM layer. The minibatch size is set to 200episode, and the step size of each episode is 50. The discount factor was set to γ=0.9. We trained this network for more than 10,000 iterations, and compared the DQNSA-MAC protocol with slotted-Aloha and DPSA protocols in terms of throughput, message forwarding success rate, and fairness index.
[0060] The success rate of message forwarding (SDR) refers to the number of messages successfully received (M received ) and the total number of messages generated in the network (M generated ) ratio, as shown in formula (10). In order to evaluate the fairness of the underlying protocol, we use Jain’s FairnessIndex, as ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com