Blockchain anonymous user auditing method and system applied to blockchain server
A blockchain and server technology, applied in the blockchain field, can solve the problems of inability to guarantee the privacy of participants, slow efficiency, etc., to achieve the effect of ensuring supervision and auditing, and ensuring privacy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
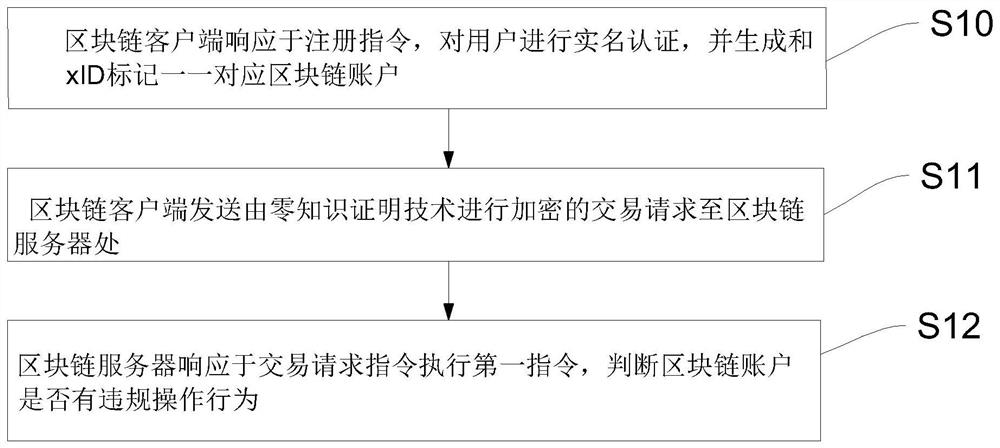
[0049] refer to figure 1 , figure 1 A schematic flow diagram of a blockchain anonymous user audit method provided in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, a blockchain anonymous user audit method, comprising the following steps:
[0050] S10, the block chain client responds to the registration instruction, performs real-name authentication on the user, and generates a block chain account corresponding to the xID mark;
[0051] S11. The blockchain client sends a transaction request to the blockchain server;
[0052] S12. The blockchain server executes the first instruction in response to the transaction request instruction, and judges whether the blockchain account has illegal operations.
[0053] In step S10, generating a one-to-one corresponding block chain account with the xID mark includes: the block chain client generates an eID (electronic IDentity, citizen network electronic identity mark) after the user passes the real-name authentication, and generates a block for t...
Embodiment 2
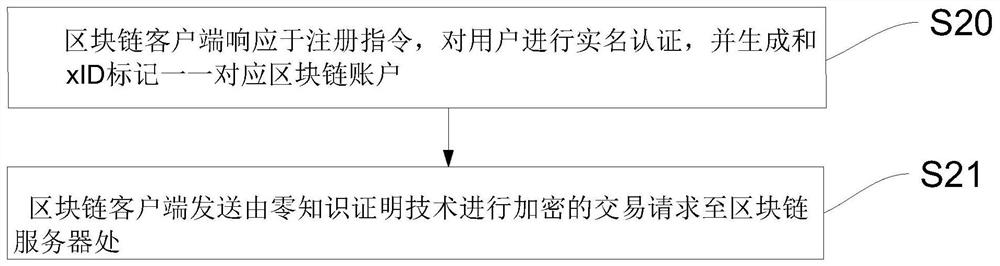
[0073] refer to figure 2 , figure 2 A schematic flow diagram of a blockchain anonymous user audit method applied to a blockchain client provided by Embodiment 2 of the present invention, a blockchain anonymous user audit method applied to a blockchain client, comprising the following steps:
[0074] S20, the blockchain client responds to the registration instruction, performs real-name authentication on the user, and generates a one-to-one corresponding blockchain account with the xID tag;
[0075] S21. The blockchain client sends a transaction request to the blockchain server.
[0076] In step S20, generating a block chain account corresponding to the xID mark includes: the block chain client generates an eID (electronic IDentity, citizen network electronic identity mark) after the user passes the real-name authentication, and generates a block for the user based on the eID chain account, the eID and block chain account are stored in the user information server.
[0077]...
Embodiment 3
[0086] refer to image 3 , image 3 It is a schematic flowchart of a blockchain anonymous user audit method applied to a blockchain server provided by Embodiment 3 of the present invention, a blockchain anonymous user audit method applied to a blockchain server, comprising the following steps
[0087] S30. Execute the first instruction in response to the transaction request instruction to determine whether the blockchain account has illegal operations.
[0088] In step S30, it also includes executing a second instruction in response to the periodic review instruction to determine whether there is any illegal operation in the blockchain account.
[0089] After the blockchain server receives the transaction request, the execution of the first instruction includes:
[0090] S301. Use the zero-knowledge proof of violation rules to verify whether the transaction violates the regulations. If the verification is passed, there is no violation;
[0091] If the verification cannot be...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com