Non-calibration method for quantitative analysis of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy elements
A laser-induced breakdown and quantitative analysis technology, applied in the field of spectroscopy, can solve problems such as low analysis accuracy, complicated calculation steps, and difficult to obtain parameters, and achieve high analysis accuracy, simple calculation steps, and overcome matrix effects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
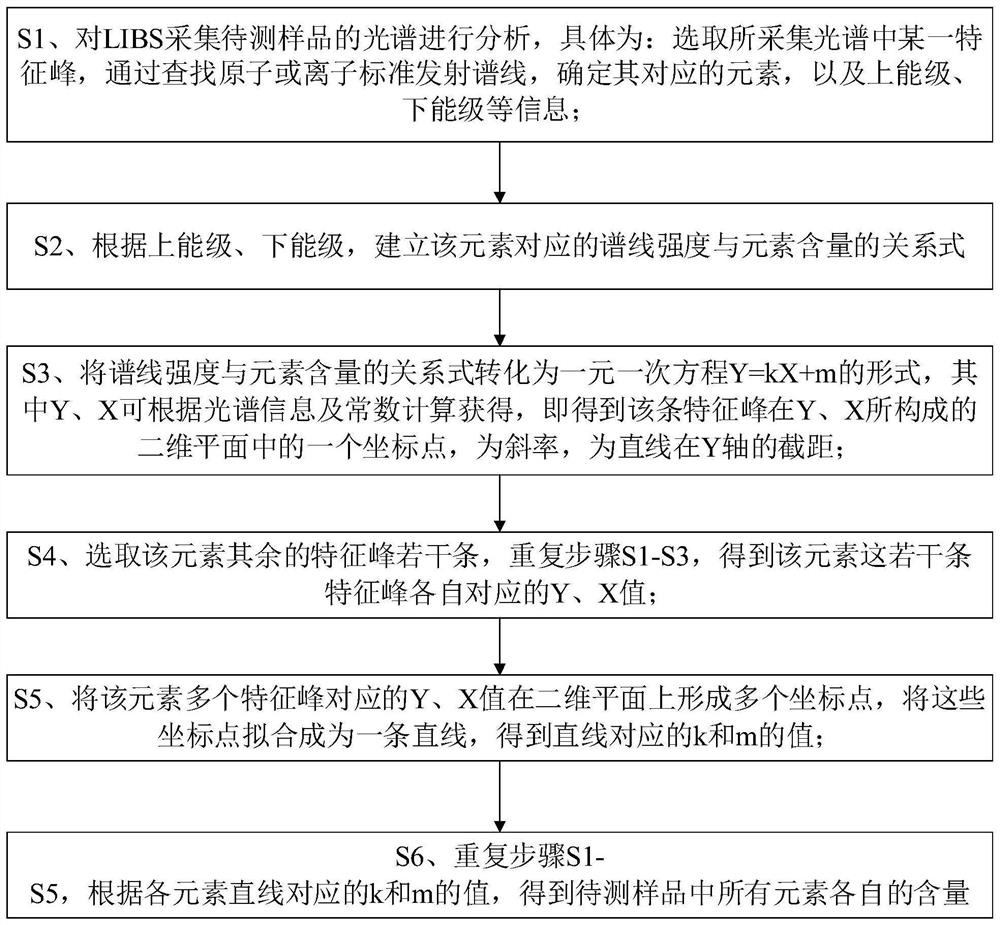
[0040] In order to facilitate those skilled in the art to understand the technical content of the present invention, the content of the present invention will be further explained below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0041] The pulsed laser beam emitted by the laser is focused on the surface of the sample to generate plasma, which can be considered to be in a state of local thermodynamic equilibrium, and meets the assumptions of chemical ablation and optical thinning. Therefore, the distribution law of atoms and ions in the plasma satisfies the Maxwell velocity distribution rate. Due to the disorder of the motion direction of atoms and ions in the plasma, the characteristic light emitted in the plasma will appear Doppler effect.
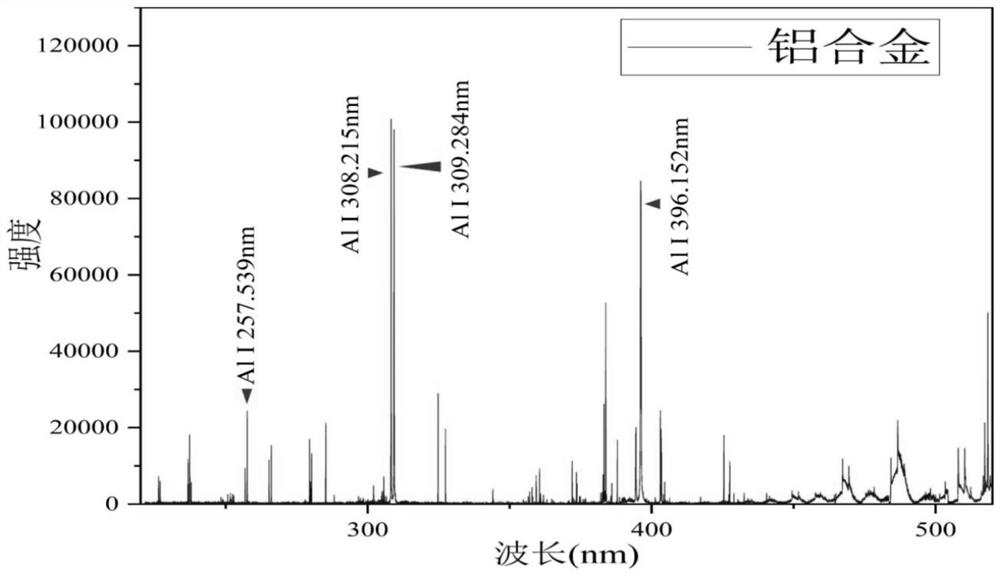
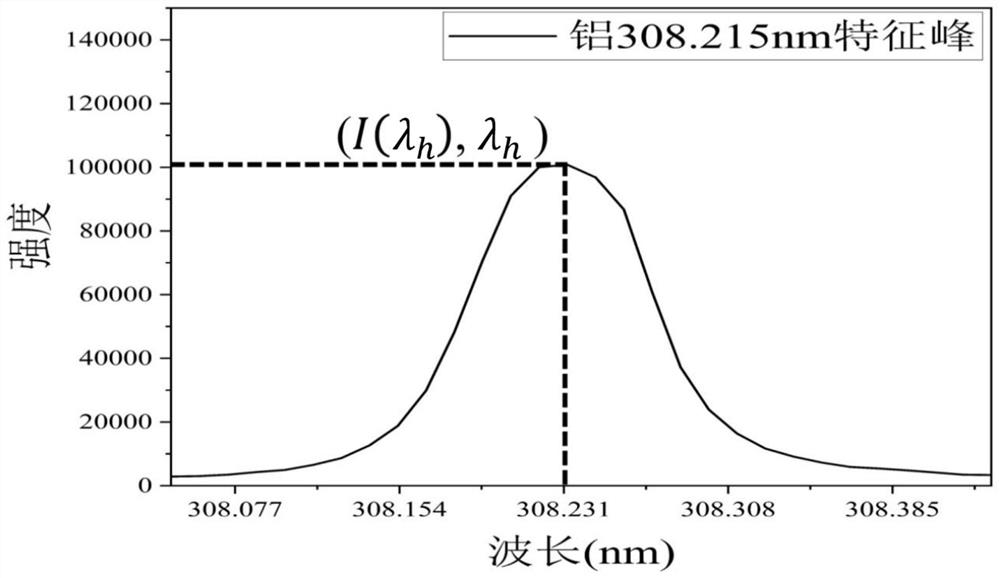
[0042] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention is illustrated by taking the measurement of the element content in an aluminum alloy sample as an example, including the following steps:
[0043] S1. Analyze according to th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com