Knowledge graph information representation learning method, system, equipment and terminal
A knowledge map and learning method technology, applied in knowledge map information representation learning methods, systems, equipment and terminals, can solve problems such as insufficient convergence, increased computational complexity, and inaccurate description, and achieve improved modeling effects, The effect of improving expressive ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0073] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention more clear, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the examples. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
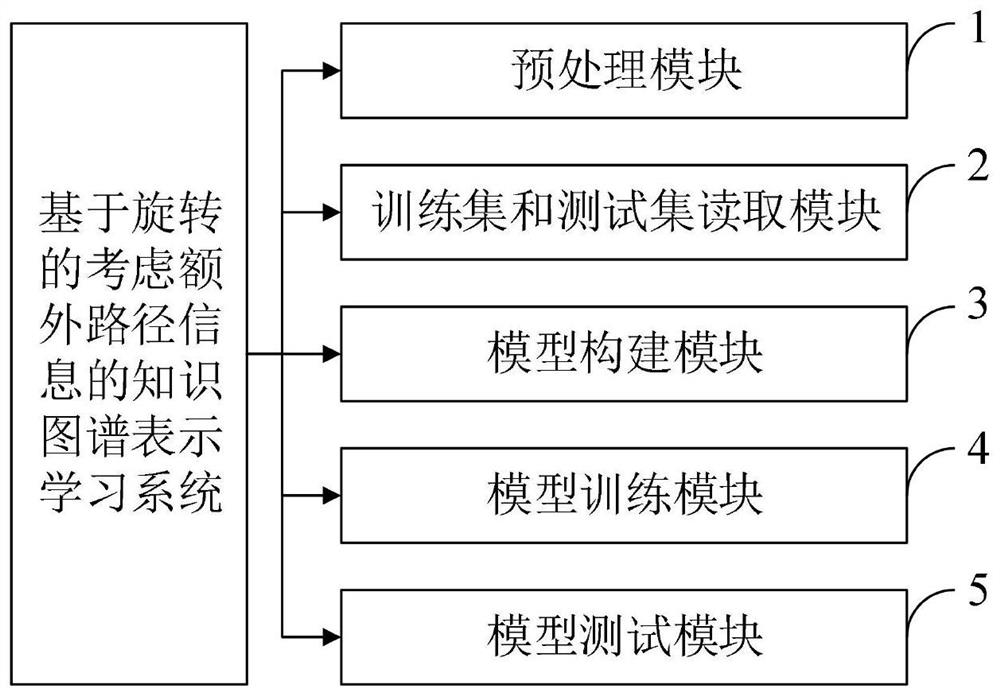
[0074] Aiming at the problems existing in the prior art, the present invention provides a knowledge map information representation learning method, system, device and terminal. The present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
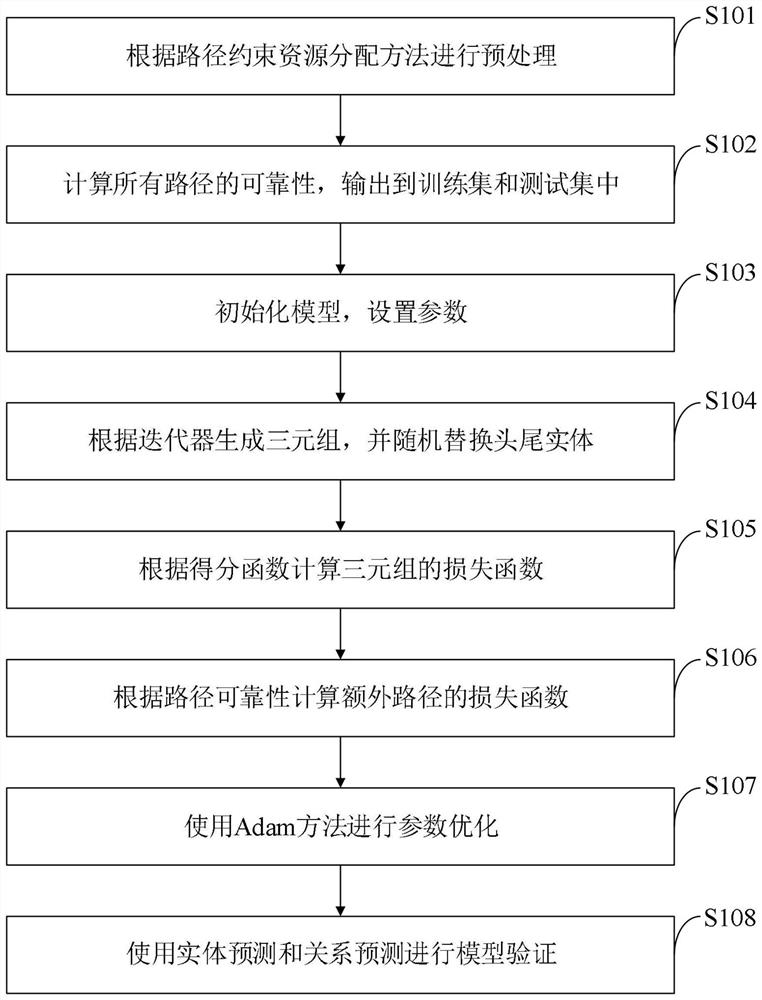
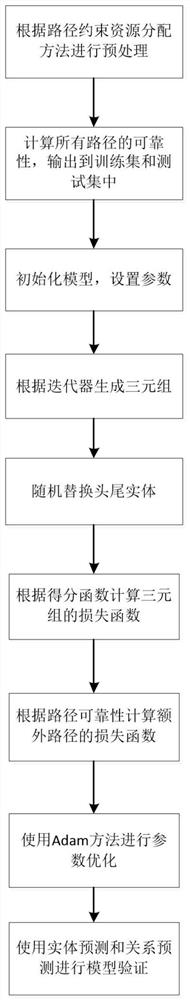
[0075] Such as figure 1 As shown, the knowledge map information representation learning method provided by the embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0076] S101, perform preprocessing according to the path constraint resource allocation method;
[0077] S102, calculate the reliability of all paths, and output to the t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com