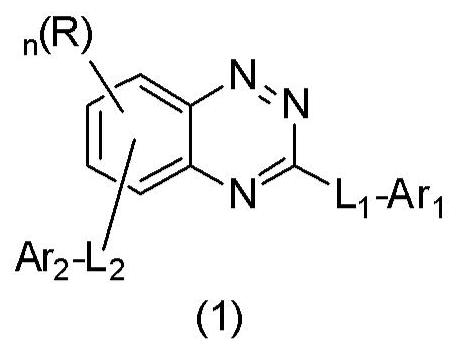
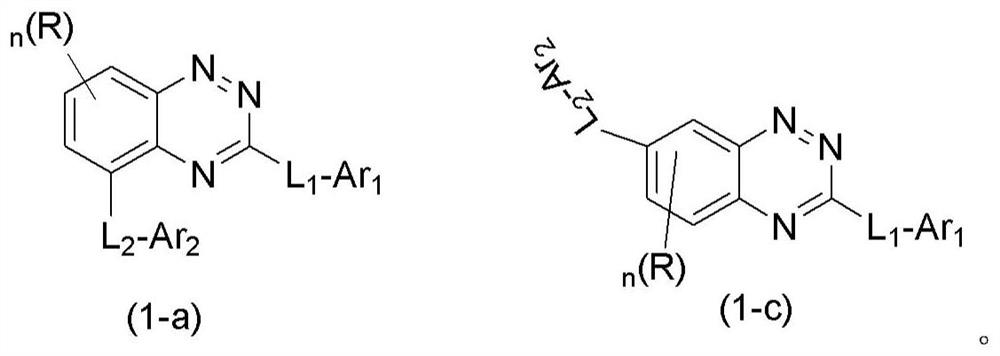
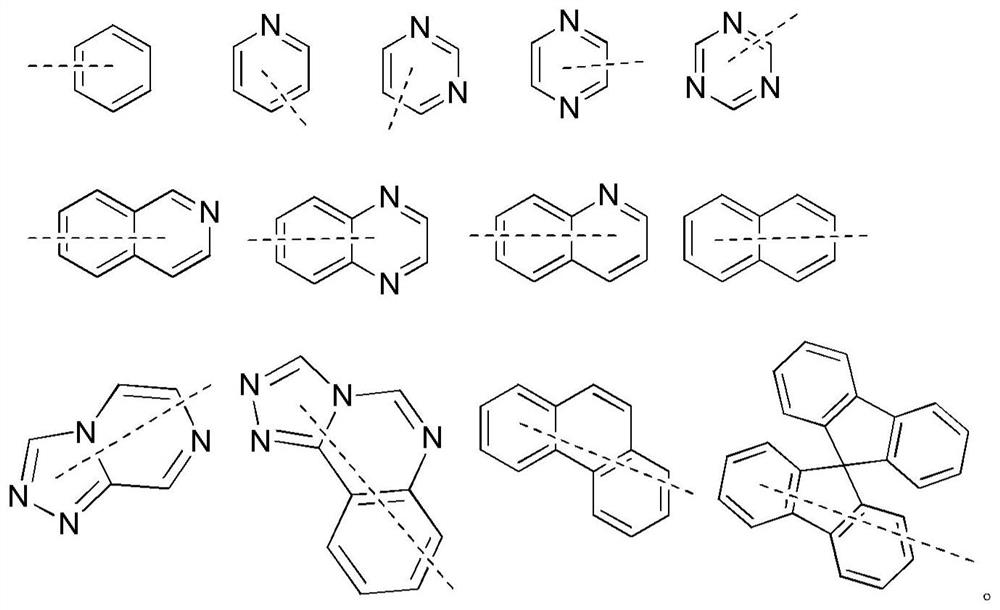
Organic compound and organic electroluminescent device containing same
A technology of organic compounds and organic layers, applied in organic chemistry, electrical solid devices, electrical components, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Synthetic example 1
[0056] Synthesis Example 1: Synthesis of Compound C1
[0057]
[0058] (1) Preparation of compound 1-1
[0059] Compound 3-bromo-2-nitroaniline (217.0g, 1.0mol), phenylboronic acid (134.1g, 1.1mol) potassium carbonate (207g, 1.5mol), Pd(PPh 3 ) 4 (11.6g, 0.01mol) was added to a (5L) flask containing 2L toluene, 400mL ethanol and 400mL water, replaced with nitrogen and heated to reflux in a nitrogen atmosphere for 4 hours, TLC showed that the reaction was complete. Cool to room temperature, separate the liquids, extract the aqueous phase with ethyl acetate, combine the organic phases, dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate, separate and purify by column chromatography to obtain compound 1-1 (167 g, yield 78%).
[0060] (2) Preparation of compound 1-2
[0061] Add compound 1-1 (150 g, 0.7 mol) and cyanamide (44 g, 1.05 mol) into a 2 L flask containing 1 L of 3M HCl, stir and reflux for 8 hours, and monitor the end point of the reaction by TLC. The reaction solution was slowly ...
Synthetic example 2
[0068] Synthesis Example 2: Synthesis of Compound C13
[0069]
[0070] (1) Preparation of compound 2-1
[0071] 2-(4-pinacol borate phenyl)-4,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-triazine (43.5g, 100mmol), 1,4-dibromobenzene (35.4g, 150mmol), potassium carbonate (41.4g, 300mmol), Pd(PPh 3 ) 4 (1.16g, 1mmol), was added into a three-necked flask containing 600mL of toluene, 200mL of ethanol, and 200mL of water, and refluxed for 3 hours under nitrogen protection. It was detected by TLC that the reaction of the raw materials was complete. After stopping the reaction and cooling to room temperature, most of the toluene and ethanol were removed by rotary evaporation. The remaining solid was extracted with dichloromethane and the organic phase was concentrated. Purified by column chromatography to obtain the target compound 2-1 (28.3 g, yield 61%).
[0072] (2) Preparation of compound 2-2
[0073] Compound 2-1 (28.3g, 61mmol), pinacol diboronate (23.2g, 91.5mmol), potassium acetate (17.9g, 183mmo...
Synthetic example 3
[0076] Synthesis Example 3: Synthesis of Compound C29
[0077]
[0078] (1) Preparation of compound 3-1
[0079] Add 3-bromo-2-nitroaniline (217.0 g, 1.0 mol) and cyanamide (44 g, 1.5 mol) into a 2 L flask containing 1 L of 3M HCl, stir and reflux for 8 hours, and monitor the end of the reaction by TLC. The reaction solution was slowly poured into 2L of cold water, and a large amount of solids were precipitated. The filtered solids were rinsed with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution until no bubbles were generated, and dried to obtain compound 3-1 (213 g, yield 88%).
[0080] (2) Preparation of compound 3-2
[0081] Add compound 3-1 (192g, 0.8mol), Pd / C (1.9g, 1mol%) into a 5L flask containing 1L each of ethyl acetate and ethanol, replace the nitrogen with stirring at room temperature and then replace the hydrogen for 3 times, and stir at room temperature The reaction was carried out for 12 hours, and the end point of the reaction was monitored by TLC. The reaction wa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com