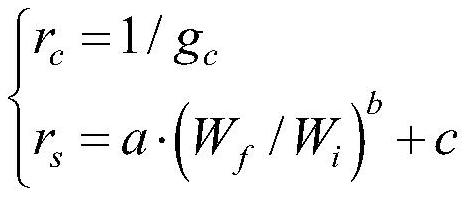Time-varying gain model-based water, energy and carbon coupling numerical simulation method and system
A technology of time-varying gain and numerical simulation, applied in the intersection of hydrology and ecology, can solve problems such as imbalance, affecting the accuracy of calculation, and not fully considering the balance mechanism
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
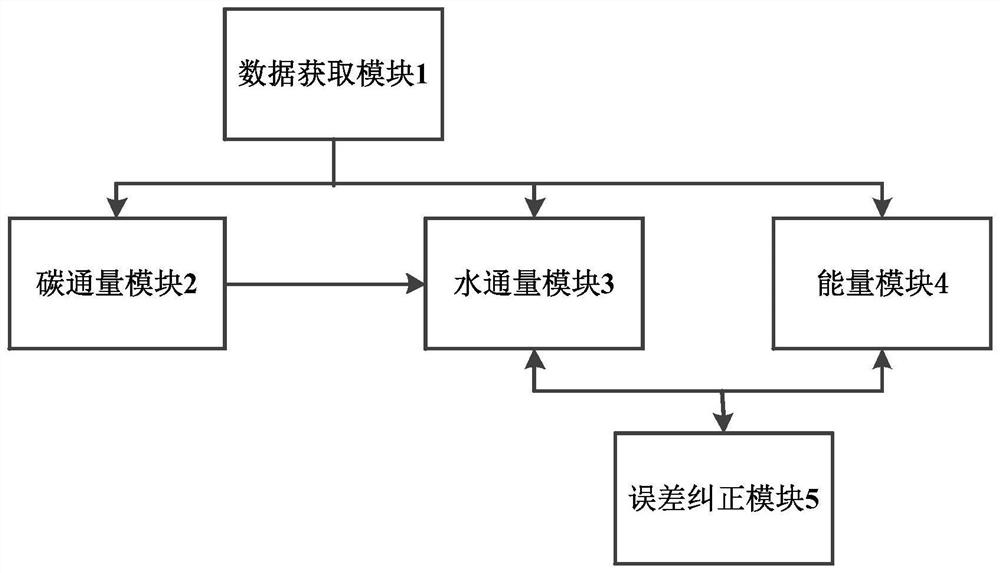
[0073] refer to figure 1 , is a time-varying gain model-based water, energy, and carbon coupling numerical simulation system in this embodiment, including:
[0074] Data acquisition module 1, used to receive meteorological data and soil vegetation underlying surface type data;
[0075] Among them, meteorological data include precipitation, maximum temperature, minimum temperature, average temperature, relative humidity, average wind speed, short-wave radiation, long-wave radiation, CO 2 concentration;
[0076] The type data of the underlying surface of soil vegetation includes soil thickness, saturated water content, field water holding rate, saturated hydraulic conductivity, and albedo.
[0077] The carbon flux module 2 is connected with the data acquisition module 1, and is used to initialize the average canopy temperature and surface temperature in the preset first time period, obtain the net radiation flux of the canopy and the surface, and initialize According to the a...
Embodiment 2
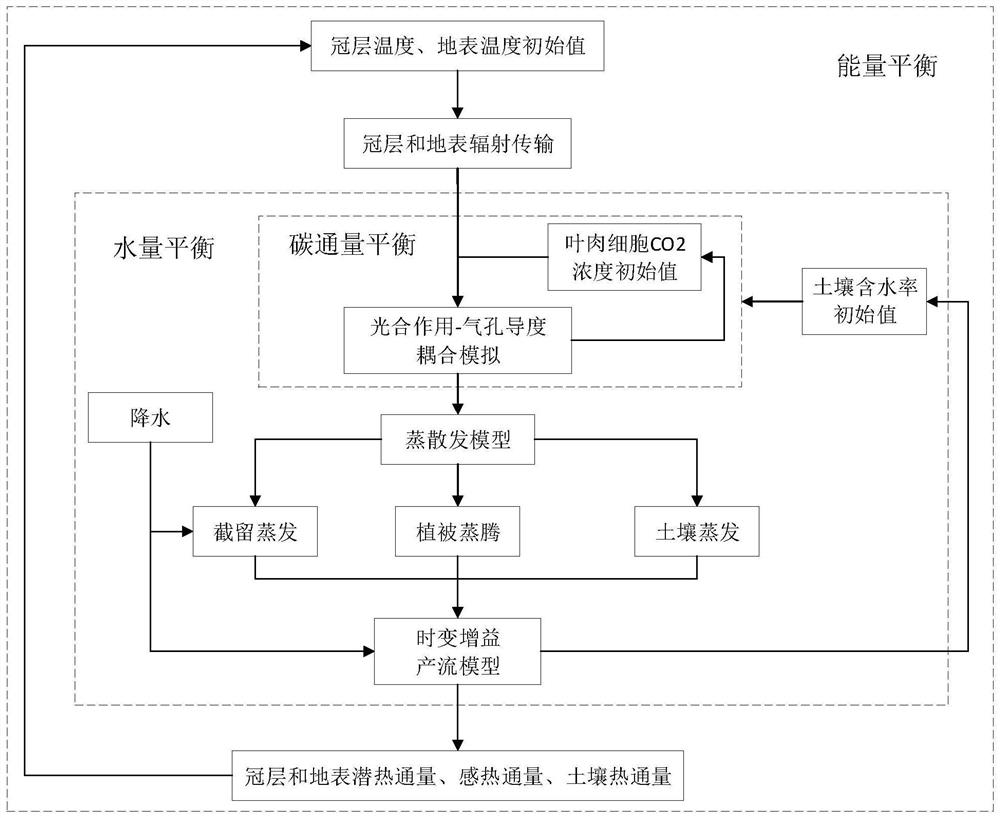
[0097] Based on the system in Embodiment 1, a water, energy, and carbon coupling numerical simulation method based on a time-varying gain model is provided in this embodiment. The flow chart refers to the figure. The method includes the following steps:
[0098] S1, data preparation, collecting and sorting out the measured data including meteorological data and soil vegetation underlying surface type data:
[0099] In this step, the meteorological data of meteorological stations or flux stations in the study area are collected and sorted out, including precipitation, maximum temperature, minimum temperature, average temperature, relative humidity, average wind speed, sunshine time (or short-wave radiation, long-wave radiation), CO 2 Concentration; Soil and vegetation type and related parameters comprise soil thickness, saturated water content, field water holding rate, saturated hydraulic conductivity, albedo etc.; Situation setup simulates computing time series.
[0100] S2:...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com