Conjugated polymer and organic photovoltaic element
A conjugated polymer, repeating unit technology, applied in photovoltaic power generation, electrical components, electrical solid devices, etc., can solve the problems of easy dimerization, weak absorption in the visible light region, and high price
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
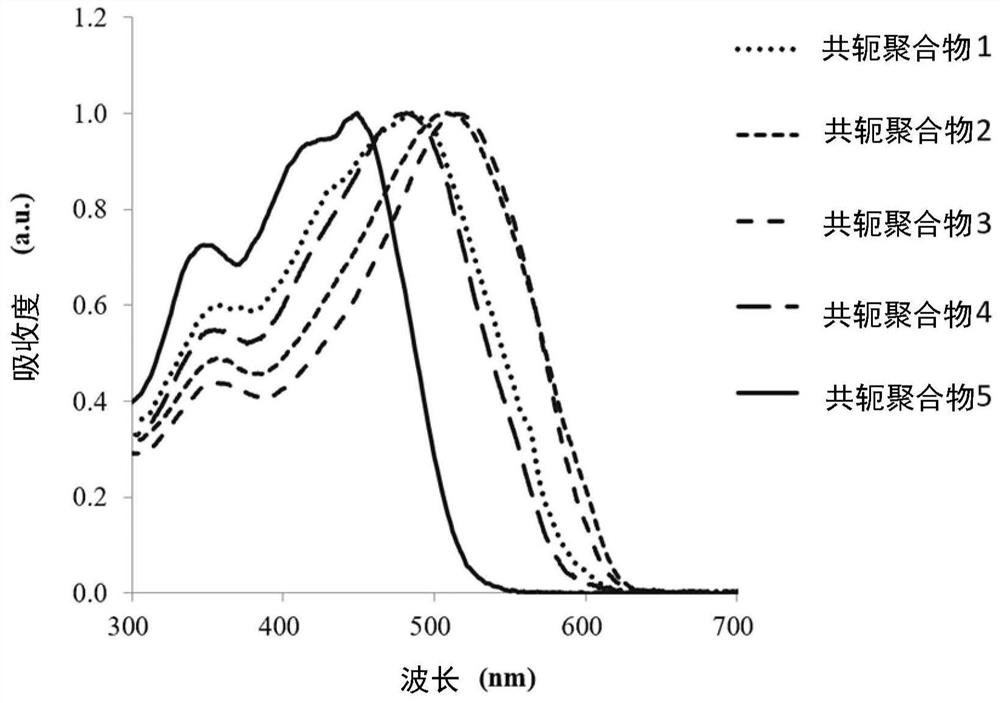
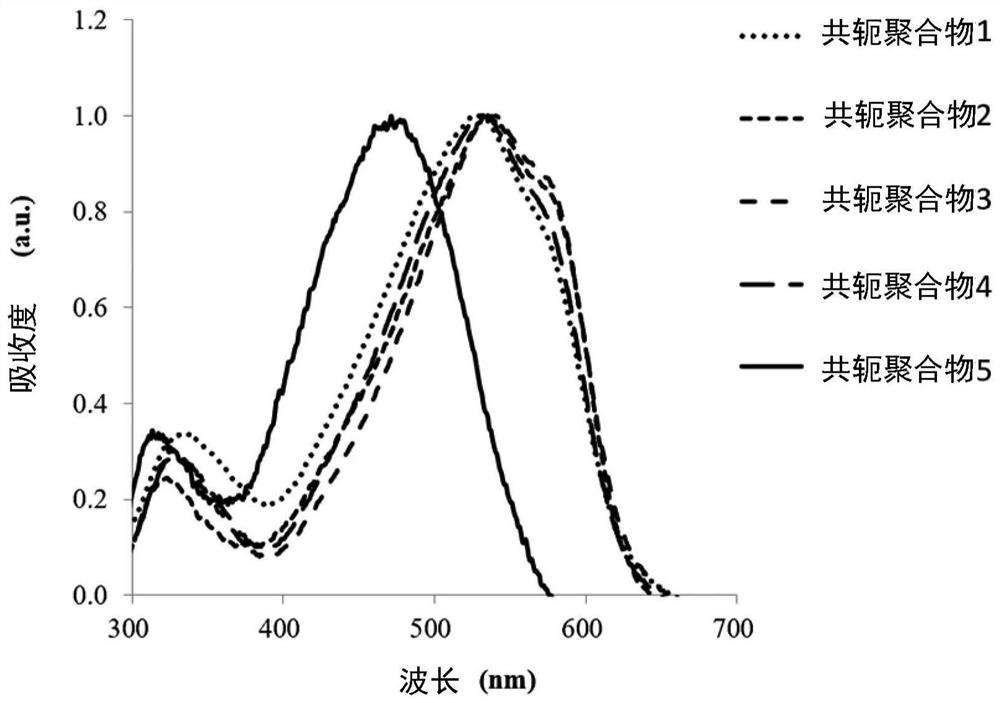
preparation example 1~5
[0097] The following is a description of Preparation Examples 1 to 5 of the conjugated polymer. The following preparation examples 1 to 5 illustrate the conjugated polymers of the aforementioned formula (1) prepared by a first method of preparing conjugated polymers, the main chain of the conjugated polymers contains the group represented by the aforementioned formula (2). group. In the following preparation examples 1-5, R in the formula (2) 1 and R 2 are the same group and are denoted R, that is to say R=R 1 =R 2 , R and R 1 and R 2 For the same group, so formula (2) can also be expressed as formula (4):
[0098]
[0099] Wherein, R is a carbon group having 1 to 40 carbon atoms, which means any monovalent or polyvalent group containing at least one carbon atom without any non-carbon atom or optionally combined with at least one non-carbon atom As an organic moiety, the non-carbon atom is N, O, S, P, Si or F; preferably, R is a carbon group with 1 to 20 carbon atoms...
preparation example 6
[0137] The following is a description of Preparation Example 6 of this conjugated polymer. The following preparation example 6 illustrates the conjugated polymer of the aforementioned formula (1) prepared by a second preparation method of the conjugated polymer, the main chain of the conjugated polymer includes a group shown in the aforementioned formula (2), In the following preparation example 6, R in formula (2) 1 and R 2 for different groups. In addition, in the conjugated polymer of formula (1) in Preparation Example 6, the following conditions are satisfied: a=1, b and c are 0. Therefore, the conjugated polymer of formula (1) can also be expressed as the aforementioned formula (5) in the following preparation example 6, and R 1 and R 2 for different groups.
[0138] The preparation process of the second conjugated polymer in Preparation Example 6 is shown in Reaction Formula 1 and Reaction Formula 2 below. In Preparation Example 6, p and p' are each independently 1...
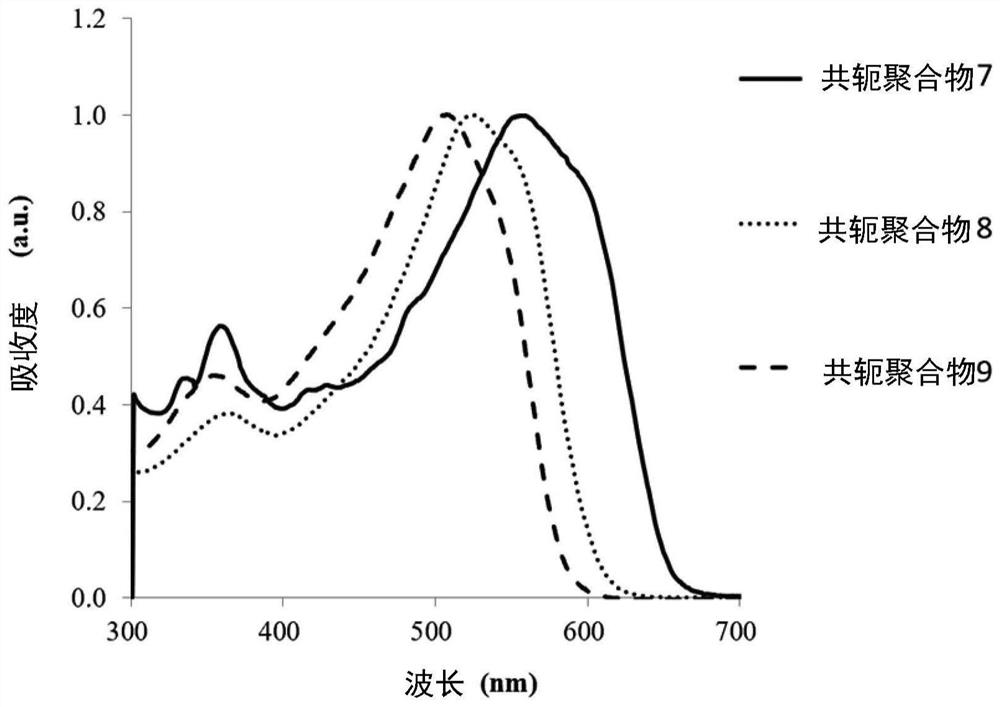
preparation example 7
[0152] The following is a description of Preparation Example 7 of this conjugated polymer. The following preparation example 7 illustrates the preparation of the conjugated polymer of the aforementioned formula (1) by a third preparation method of the conjugated polymer. The main chain of the conjugated polymer includes the group shown in the aforementioned formula (2-1). group. In addition, in the conjugated polymer of formula (1) in Preparation Example 7, the following conditions are met: a and b are not 0, and c is 0, and the sum of a and b is 1, that is to say, a and b are greater than 0 and less than 1, 0
[0153]
[0154] The preparation process of the third conjugated polymer in Preparation Example 7 is shown in the following reaction formula 3 and reaction formula 4. In Preparation Example 7, p, p', q and q' are each...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com