Glucose electrode, micro-fluidic chip, micro-fluidic passive sweat patch, and preparation method and application of micro-fluidic passive sweat patch
A microfluidic chip and passive sweat technology, applied in the field of sensors, can solve the problems of limited extraction, sampling and chemical analysis, inability to achieve accurate fluid capture, storage, volume measurement and chemical analysis, and inconvenient use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0102] This embodiment provides a glucose electrode, the preparation method is as follows:
[0103] (1) Electropolymerize the aniline monomer onto the carbon ink electrode by cyclic voltammetry to obtain an electrode coated with polyaniline film; the conditions of the cyclic voltammetry include: the voltage is -0.2V-1.0V, and the cycle The number of times is 25 times, the voltage rate is 0.1V / s, the reference electrode is an Ag / AgCl electrode, and the electrolyte is a hydrochloric acid solution of aniline monomer (the concentration of aniline monomer is 0.1mol / L, and the concentration of HCl is 1mol / L);
[0104] (2) Dissolve 1% chitosan aqueous solution in 2% acetic acid aqueous solution, then mix with glucose oxidase solution (concentration is 10mg / mL, solution is PBS buffer) with the ratio of volume ratio 2:1, obtain glucose oxidase Membrane solution, drop the mixed solution on the electrode coated with polyaniline membrane, and dry at 4° C. for 12 hours to obtain the glucos...
Embodiment 2
[0106] This embodiment provides a microfluidic chip and a microfluidic passive sweat patch;
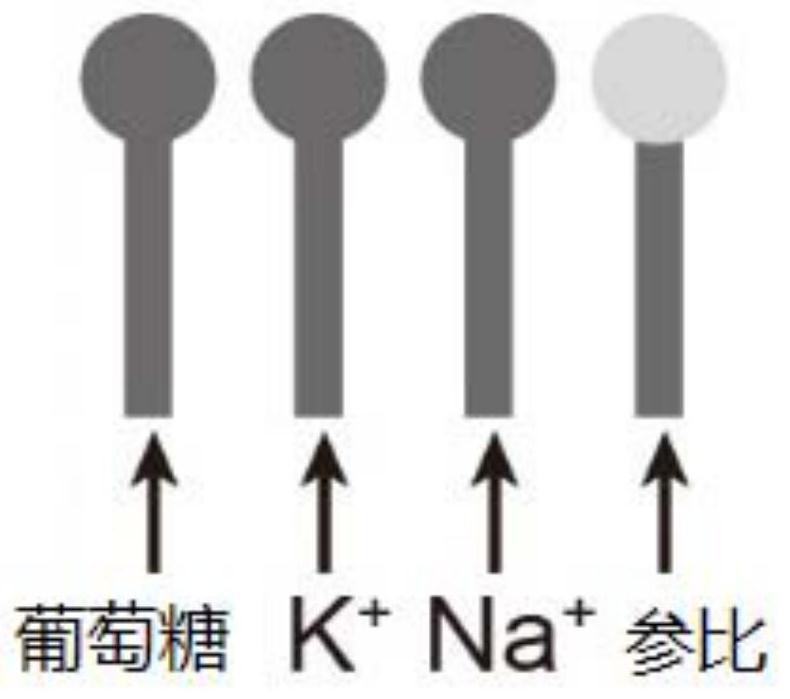
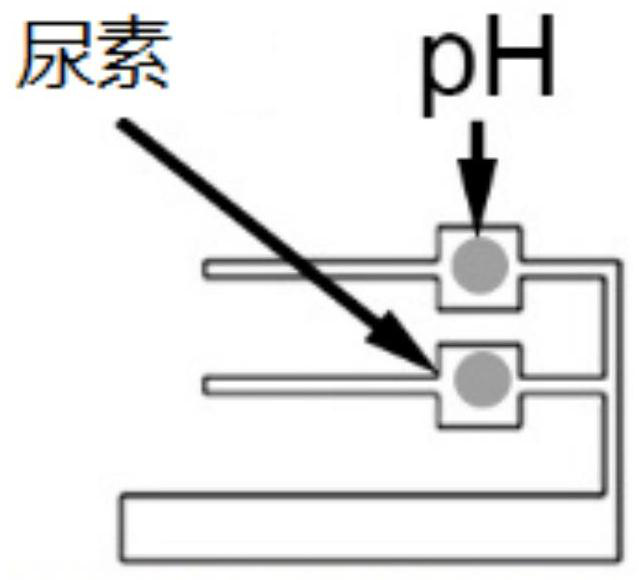
[0107] The microfluidic core includes a PDMS membrane with a microfluidic channel and an ISE sensor attached to the PDMS membrane (such as figure 1 shown) and urea test strips and pH test strips placed in the microfluidic channel (such as figure 2 Shown), wherein, ion selective sensor is made of glucose electrode (embodiment 1), Na + Electrode, K + electrode and reference electrode.
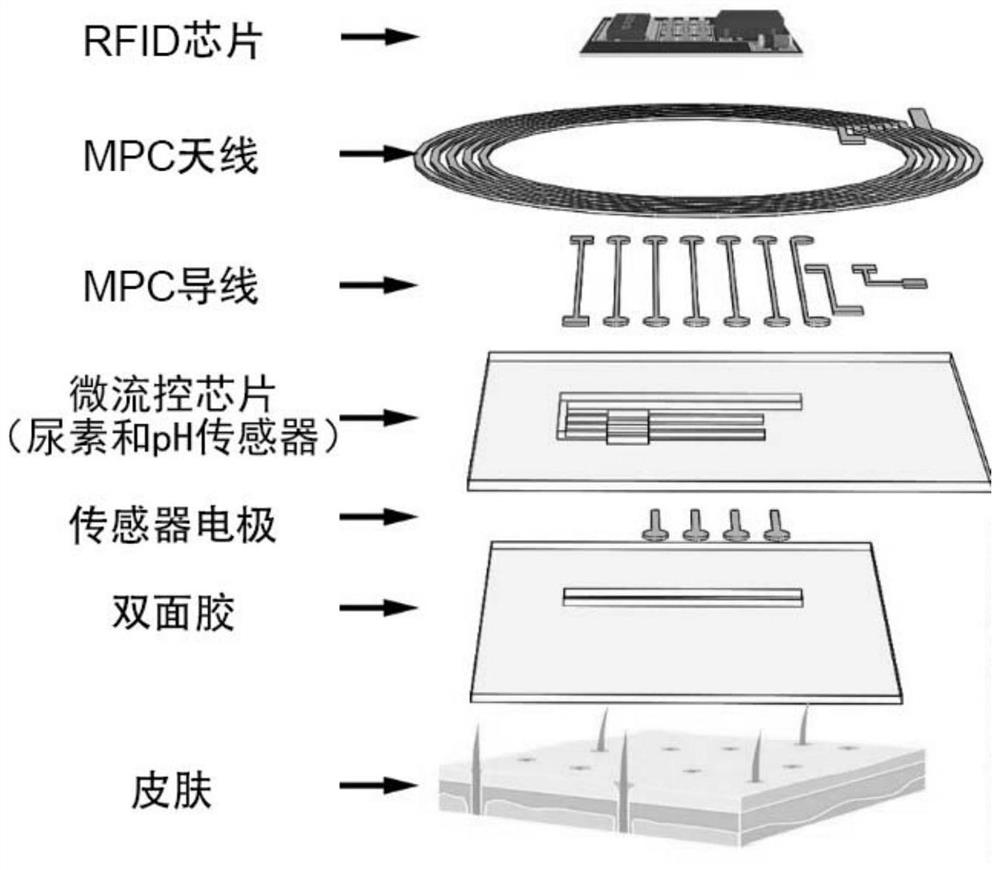
[0108] Microfluidic passive sweat patch includes double-sided adhesive layer, microfluidic chip, MPC wire layer, MPC antenna layer and electronic device layer, such as image 3 shown.
[0109] The specific preparation method of the microfluidic passive sweat patch is as follows (the preparation process is as follows: Figure 4 shown):
[0110] (1) Use oxygen plasma to activate the PDMS film and the metal-polymer conductor wire layer, and then bond the two together;
[0111] (2) Connect the electr...
Embodiment 3
[0130] The difference with Example 1 is that no chitosan is added.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com