A projection area analysis method for rendezvous and docking lidar cooperative targets
A cooperative target and lidar technology, applied in the direction of optical devices, electromagnetic wave re-radiation, instruments, etc., can solve the problem that there is no analysis method for the projected area of the rendezvous and docking lidar
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] The present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
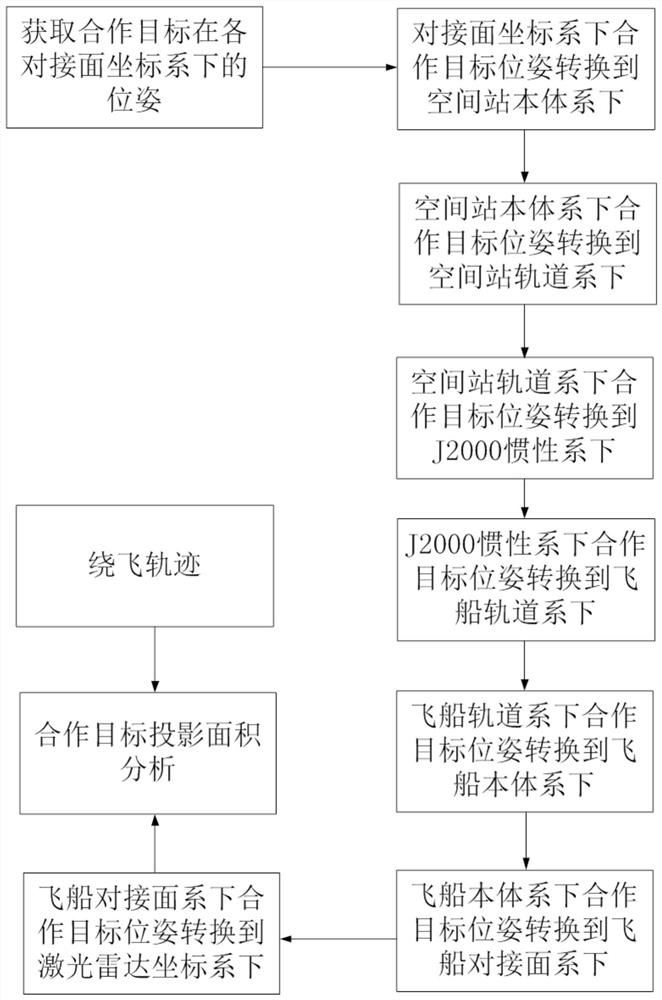
[0022] A projection area analysis method suitable for rendezvous and docking lidar cooperative targets during the orbiting process of the spacecraft. First, according to the installation relationship of the cooperative targets, the poses of the cooperative targets in the coordinate system of each pair of interfaces of the space station are obtained. where M hd is the rotation matrix from the cooperative target coordinate system h to the docking plane coordinate system d, and is the position vector of the cooperative target in the docking plane coordinate system.
[0023] Then the relationship between the coordinate system d of the docking surface of the cooperation target and the system b of the space station is known The pose of the cooperative target can be converted into the space station system, as and,
[0024]
[0025] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com