A low-loss glass-ceramic planar optical waveguide and its preparation method
A technology of planar optical waveguide and glass ceramics, which is applied in the direction of optical waveguide and light guide, can solve the problems of reducing optical efficiency, and achieve the effects of reducing production cost, not demanding preparation time schedule, and high output and yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] Example 1: SiO 2 –30mol%SnO 2 :0.5Er 3+
[0015] Weigh SnCl with a purity greater than 99.9% according to the stoichiometric ratio 2 , Er(NO 3 ) 3 , citric acid and tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) as raw materials. SnCl 2 , Er(NO 3 ) 3 , TEOS and citric acid were mixed, the molar ratio of citric acid to metal ions was 1:0.5, then deionized water with a volume fraction of 50% of the mixture was added, and stirred at 200 rpm for 16 hours to obtain a sol. The solution was filtered using a 200 nm filter and the collected fraction was used for dip coating. Commercially available SiO 2 Dip-coating was carried out on the glass at a immersion speed of 7 cm / min, and a total of 30 deposition layers were deposited. After dip-coating, it was dried at 900° C. for 20 min. Finally, it was heated at 900°C for 3 hours to obtain a glass-ceramic planar optical waveguide.
Embodiment 2
[0016] Example 2: SiO 2 –30mol%SnO 2 :0.4Er 3+
[0017] Weigh SnCl with a purity greater than 99.9% according to the stoichiometric ratio 2 , Er(NO 3 ) 3 , citric acid and tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) as raw materials. SnCl 2 , Er(NO 3 ) 3 , TEOS and citric acid were mixed, the molar ratio of citric acid to metal ions was 1:1, then deionized water with a volume fraction of 20% of the mixture was added, and stirred at 300 rpm for 10 h to obtain a sol. The solution was filtered using a 200 nm filter and the collected fraction was used for dip coating. Commercially available SiO 2 Dip-coating was carried out on the glass at a immersion speed of 7.5cm / min, a total of 20 deposition layers were deposited, and dried at 800°C for 30min after dip-coating. Finally, it was heated at 1100°C for 1 h to obtain a glass-ceramic planar optical waveguide.
Embodiment 3
[0018] Example 3: SiO 2 –30mol%SnO 2 :0.3Er 3+
[0019] Weigh SnCl with a purity greater than 99.9% according to the stoichiometric ratio 2 , Er(NO 3 ) 3 , citric acid and tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) as raw materials. SnCl 2 , Er(NO 3 ) 3 , TEOS and citric acid were mixed, the molar ratio of citric acid to metal ions was 1:0.75, then deionized water with a volume fraction of 40% of the mixture was added, and stirred at 280 rpm for 12 hours to obtain a sol. The solution was filtered using a 200 nm filter and the collected fraction was used for dip coating. Commercially available SiO 2 Dip-coating was carried out on the glass at a immersion speed of 7 cm / min, and a total of 25 deposition layers were deposited. After dip-coating, it was dried at 850° C. for 26 min. Finally, it was heated at 1000°C for 2 hours to obtain a glass-ceramic planar optical waveguide.
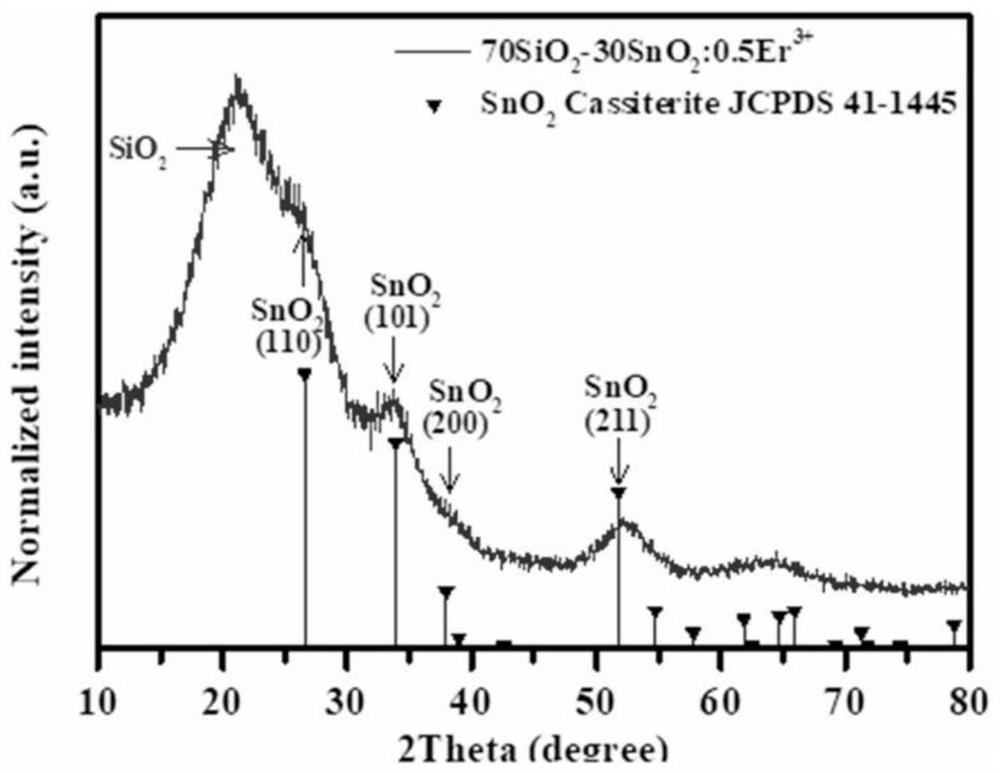
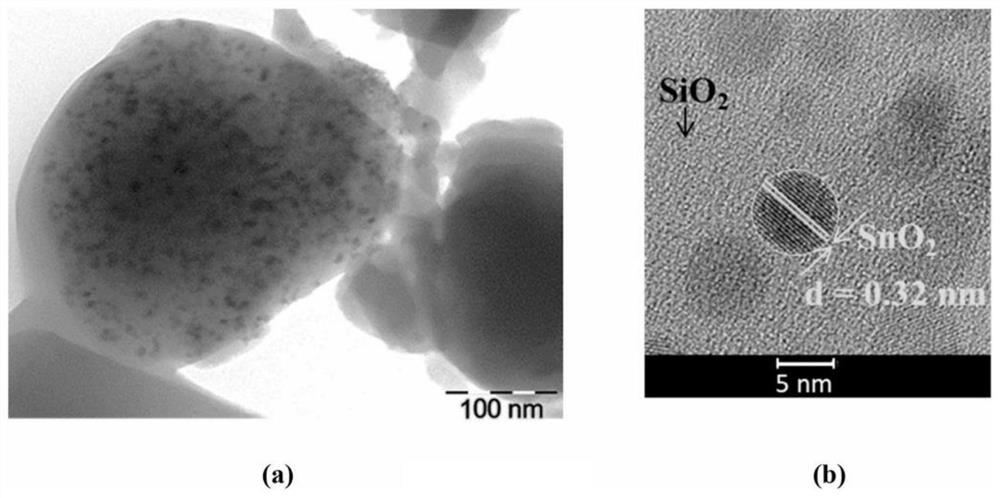
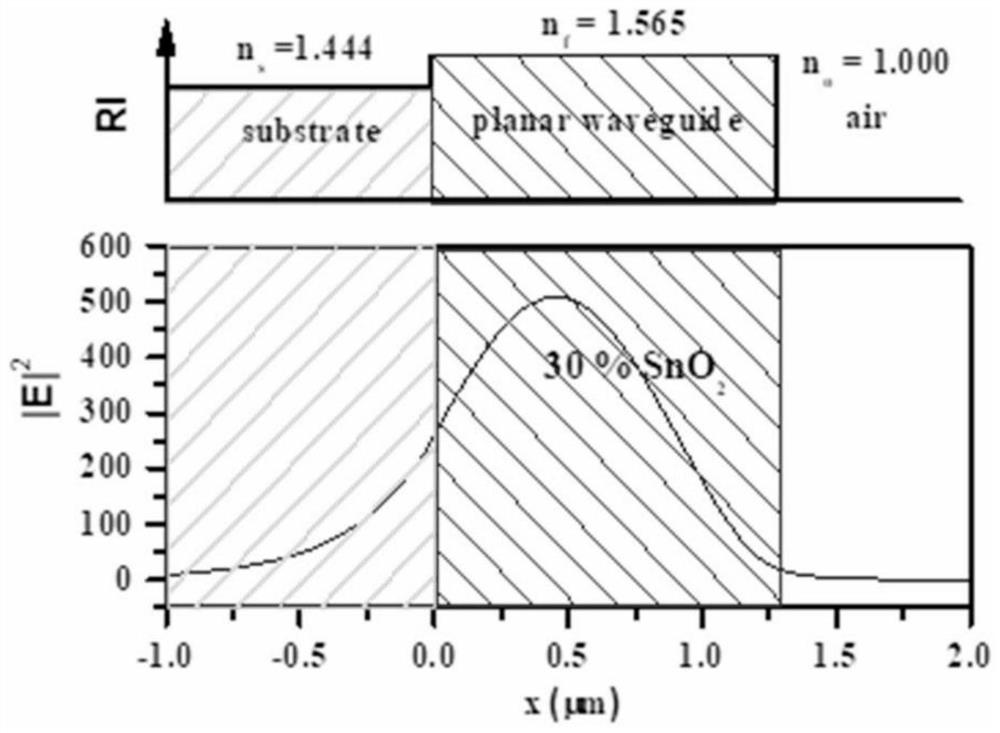
[0020] Taking embodiment 1 as an example, by figure 1 The XRD pattern shows that, by comparison with t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com