Addressing method and system based on IPv6 identity identifier
An identity identification and addressing system technology, applied in the field of computer network communication, can solve the problems of inflexible architecture, the dual identities of topological location and identity identification cannot satisfy fast routing, etc., and achieve the effect of avoiding expansion.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
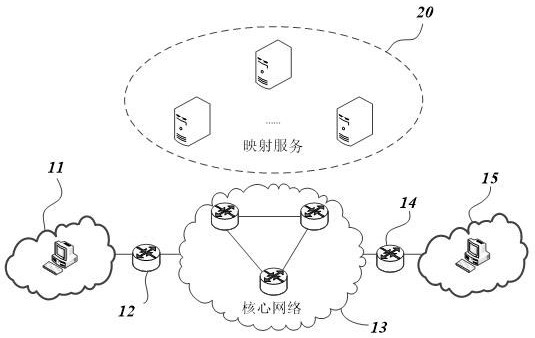
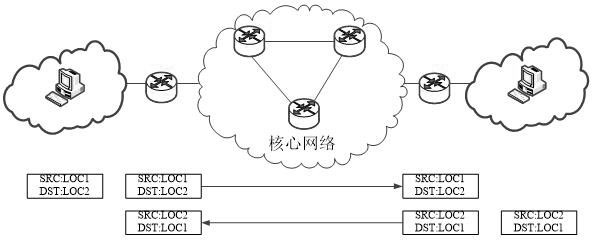
[0043] The first IP address of the sending terminal is consistent with the corresponding second IP address, and the first IP address of the receiving terminal is consistent with the second IP address. For example, both the sending terminal and the receiving terminal are in the original network, and the identity attribute and network topology The attributes are consistent, so both the sending terminal and the receiving terminal use a unified IP address. Such as image 3 As shown, at this time, any IP address (LOC1, LOC2) in the first packet can be routed and forwarded on the normal network, so only normal routing is required.
Embodiment 2
[0045] The first IP address of the sending terminal is inconsistent with the corresponding second IP address. For example, the network where the sending terminal is located when sending is a newly joined network, and there is a difference between the identity attribute and the network topology attribute. At the same time, the first IP address of the receiving terminal is the same as the The second IP address is the same. Such as Figure 4 As shown, at this time, when the sending terminal sends the first message, the source address of the first message is the second IP address (ID1), and the destination address is the first IP address (LOC2) that can be routed normally in the network. ). When the first packet arrives at the originating edge router, the originating edge router needs to convert the source address in the forwarded first packet into the corresponding first IP address (LOC1). The first IP address (LOC1) can be determined by the originating edge router according to ...
Embodiment 3
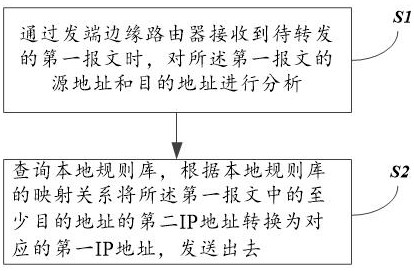
[0047] The first IP address of the sending terminal is consistent with the corresponding second IP address, and the first IP address of the receiving terminal is inconsistent with the second IP address. Such as Figure 5As shown, at this time, when the sending terminal sends the first packet, the source address of the first packet is the first IP address (LOC1), and the destination address is the second IP address (ID2). When the first packet arrives at the originating edge router, the originating edge router needs to convert the destination address in the forwarded first packet into the corresponding first IP address (LOC2), for example, check whether the local rule base has the corresponding first IP address The mapping relationship between (LOC2) and the second IP address (ID2). However, if the corresponding receiving terminal is in a new network, it is often impossible to find the matching record in the local rule base. At this time, it is necessary to query the correspon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com