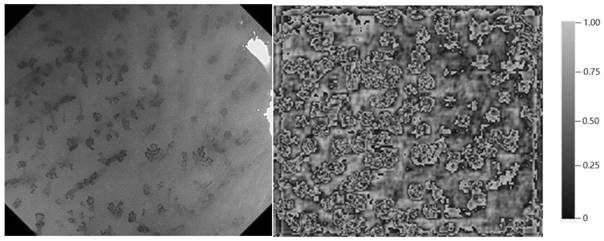
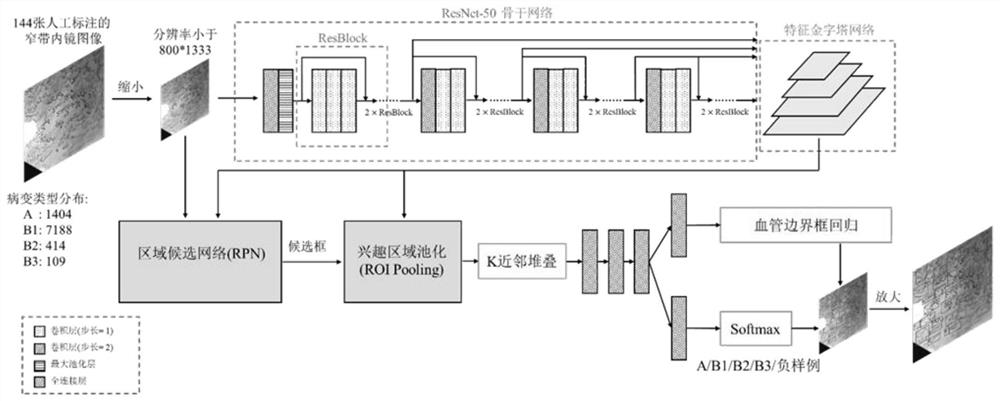
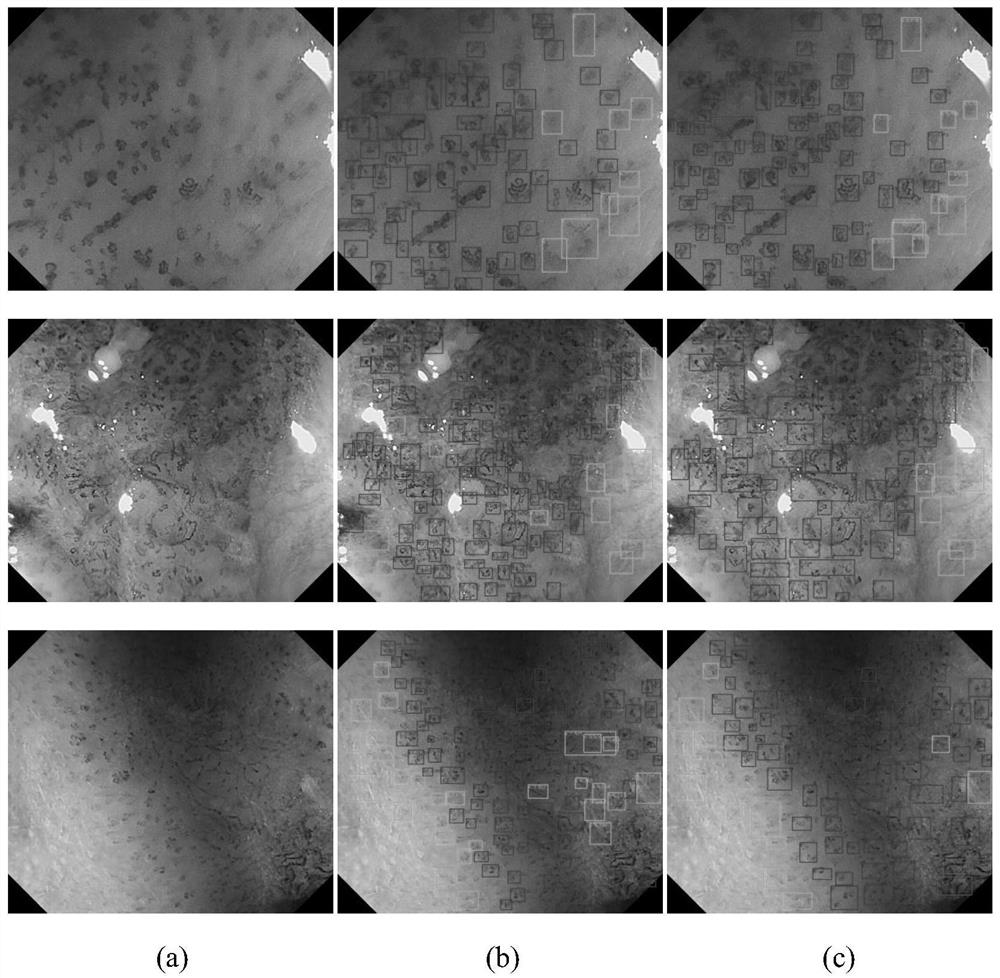
A deep detection network to quantify the vascular morphological distribution of esophageal mucosal IPCLs
An esophageal mucosa, depth detection technology, applied in the field of medical image processing, can solve the problems of lack of quantifiable concepts, medical decision errors, visual fatigue, etc., to improve the efficiency of diagnosis, improve efficiency and accuracy, and reduce the amount of calculation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] The embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the examples.
[0030] The present invention adopts figure 1 The network framework shown is trained using 144 narrow-band imaging endoscopic images that are collaboratively annotated by multiple experienced doctors, thereby obtaining a model that can automatically detect and diagnose esophageal squamous cell carcinoma foci from narrow-band imaging endoscopic images. The specific process is:
[0031] (1) Before training, the network parameters of the ResNet-50 model are randomly initialized, and the images in the training set are scaled so that the resolution does not exceed 800×1333, and the corresponding bounding box is also scaled at the same time. .
[0032] (2) During training, the image is first normalized according to mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406] and standard deviation=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225] to the three channels (R, G, B) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com