Compositions and methods relating to macrophages and/or monocytes with adhered particles
A macrophage and monocyte technology, which can be used in drug combinations, medical preparations with non-active ingredients, and medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc. It can solve problems such as failure and loss of macrophages.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0190] 1. An engineered cell composition comprising:
[0191] a. Monocytes or macrophages; and
[0192] b. A polymeric particle comprising an M1 polarizing cytokine polypeptide, wherein said particle is located on the cell surface of said monocyte or macrophage.
[0193] 2. The composition of paragraph 1, wherein the polymer particles are substantially disc-like in shape.
[0194] 3. The composition of paragraph 1, wherein the polymer particles are disc-like in shape.
[0195] 4. The composition of any of paragraphs 1-3, wherein the polymer particles have a size from about 3 μm x 150 nm to about 12 μm x 500 nm.
[0196] 5. The composition of any of paragraphs 1-4, wherein the polymer particles have a size of about 6 μm x 250 nm.
[0197] 6. The composition of any of paragraphs 1-5, wherein the polymer particles comprise:
[0198] a. A first region comprising one or more cell adhesion molecules (eg polyelectrolytes);
[0199] b. A second region comprising one or more struc...
Embodiment 1
[0396] Example 1: Cell backpack for adoptive macrophage therapy
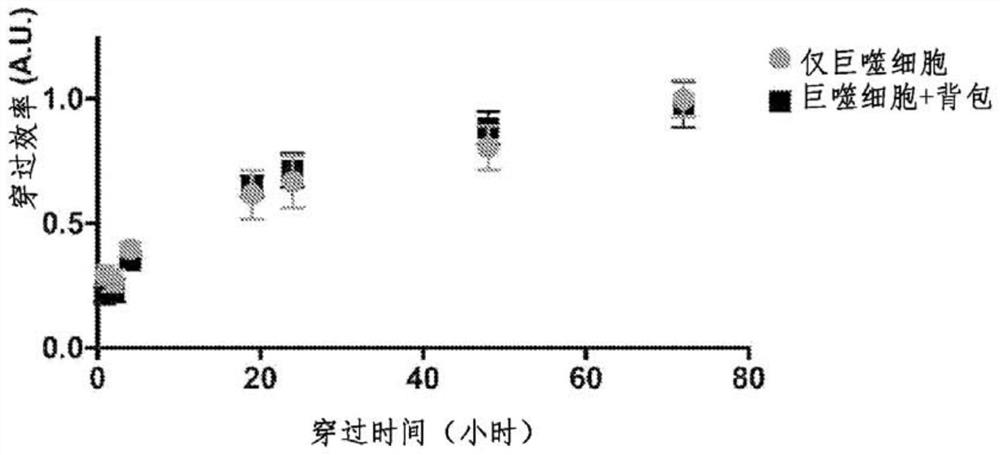
[0397] Adoptive T-cell therapy has shown great promise in the treatment of many cancers, however, its efficacy depends on the knowledge and presence of relevant tumor-specific antigens. On the other hand, adoptive macrophage therapy allows its use in a wider range of tumors due to its intrinsic immune properties that elicit antigen-independent anticancer responses. Previous attempts to translate macrophage-mediated adoptive immunotherapy to the clinic have failed because therapeutic macrophages lose their antitumor M1 phenotype once exposed to the tumor microenvironment. Described herein are methods and compositions that overcome this obstacle by attaching IFN-γ-loaded antiphagocytic backpacks to the surface of macrophages. Knapsack provides a pool of IFN-γ to prevent phenotypic shift of macrophages from an anti-tumor phenotype, thus preserving their therapeutic activity. This approach provides a practical cli...
Embodiment 2
[0419] Four objectives to demonstrate the therapeutic efficacy of this approach are described here: (i) IFN-γ can be loaded into a backpack and its activity and release profile studied. Optimal loading and release rates can be determined; (ii) the effect of backpacks on monocytes can be studied in vitro. Factors such as the ability of the knapsack to maintain M1 polarization in response to tumor cell conditioned media can be tested by examining gene expression with RT-PCR. The viability of monocytes can be confirmed. Infiltration of tumor spheroids by knapsack-loaded monocytes can also be tested; (iii) in vivo biodistribution of knapsacks can be determined. Monocytes can be modified ex vivo using backpacks and administered to mice. Tumor accumulation and off-target distribution of backpacks can be measured. The toxicity of the knapsack itself can be assessed; (iv) the therapeutic efficacy of the monocyte-knapsack can be tested in vivo using relevant tumor models for which m...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com