Macrocyclic tetrapyrrole compounds, compositions and methods for increasing abiotic stress resistance in plants
A tetrapyrrole compound, a technology for abiotic stress, applied in the directions of botanical equipment and methods, chemicals for biological control, preservation of plants, etc., capable of addressing impairment of plant health, quality and/or development, damage to crop yield and / or crop quality etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
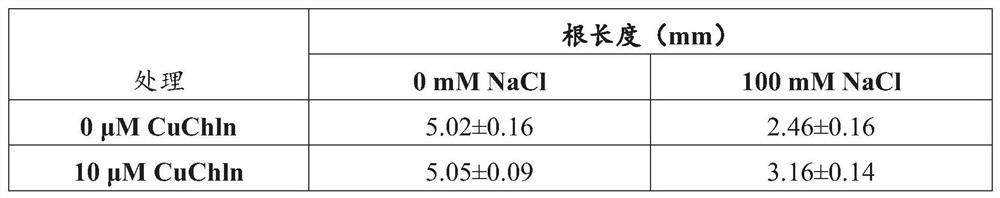
[0120] Example 1: Effects of treatments on primary root length of Arabidopsis seedlings under salt stress.
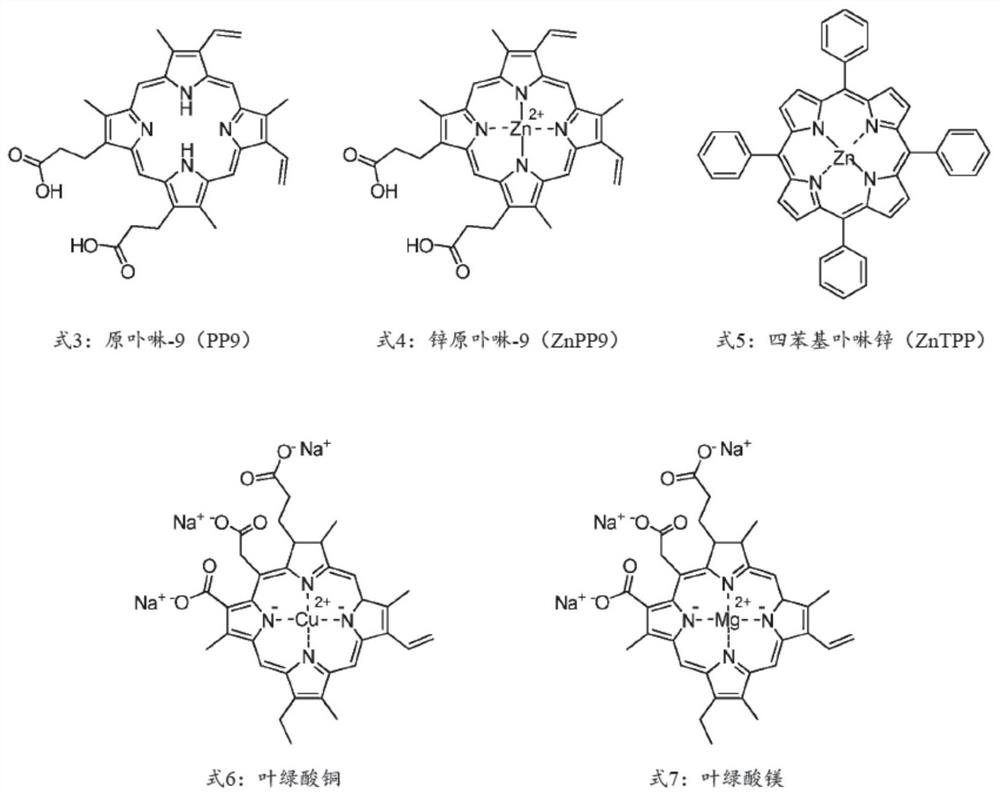
[0121] The experiments evaluated the effects of metallated chlorin compounds on salt-stress-treated seedlings by measuring the length of primary roots. Copper chlorophyllin (CuChln) was supplemented into media for germinating Arabidopsis thaliana seeds. The results showed that the plants were more salt-tolerant than untreated plants.
[0122] Arabidopsis seeds were surface sterilized by shaking in 50% bleach for 12 minutes and washed five times with sterile water. Seeds were inoculated on half-strength Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium containing 0.8% agar and 1% sucrose, buffered to pH 5.7 with KOH. For salt exposure, media was adjusted to contain 100 mM NaCl. For exposure to CuChln, CuChln was prepared as a 1 mM stock solution in water and added to the medium at a final concentration of 10 μM CuChln. Seeds were layered for 2 days at 4°C in the dark. Arabidopsis tha...
Embodiment 2
[0128] Example 2: Effect of treatments on plant senescence induced by salt stress.
[0129] In this example, the effects of metallated chlorin compounds and various additives on Arabidopsis senescence induced by salt stress were measured by a visual rating scale reflecting the symptoms of gradual leaf senescence. Specifically, this example shows that CuChln confers protection against senescence induced by salt stress. This example also shows that the addition of oils, particularly polyalphaolefins (PAOs), chelating agents, or combinations thereof further enhances protection.
[0130] After long-term exposure to salt stress, Na in shoots of seedlings + Accumulation of β leads to cytotoxic effects, whereby the most obvious symptom due to leaf senescence and death is yellowing followed by leaf drying. Leaf senescence can be assessed by visual scoring that reflects progressive leaf senescence symptoms.
[0131] Table 2A: Visual scores reflecting symptoms of progressive leaf sen...
Embodiment 3
[0139] Example 3: Effect of treatments on primary root length of white clover (Trifolium repens) seedlings under salt stress.
[0140] In this example, the effect of porphyrin compounds on the salt stress sensitivity of seedlings was evaluated. Specifically, the effects of protoporphyrin-IX (PP9), zinc protoporphyrin-IX (ZnPP9), and zinc tetraphenylporphyrin (ZnTPP)-treated white clover seedlings under salt stress conditions were evaluated.
[0141] White clover seeds were surface sterilized by shaking in 50% bleach for 12 min and washed five times with sterile water. Seeds in 10ml water at room temperature under LED light (PAR 24μmol m -2 / s -1 ) and a 16-hour:8-hour light:dark photoperiod for germination.
[0142] For salt exposure, the water was adjusted to contain 100 mM NaCl. Porphyrin compounds were prepared as 0.1% stock solutions in dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO). The porphyrin compound from the stock solution was added to a final concentration of 0.01% by volume for th...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap