Method for improving methane gas yield of anaerobic digestion of sludge and reducing ecological toxicity of heavy metals
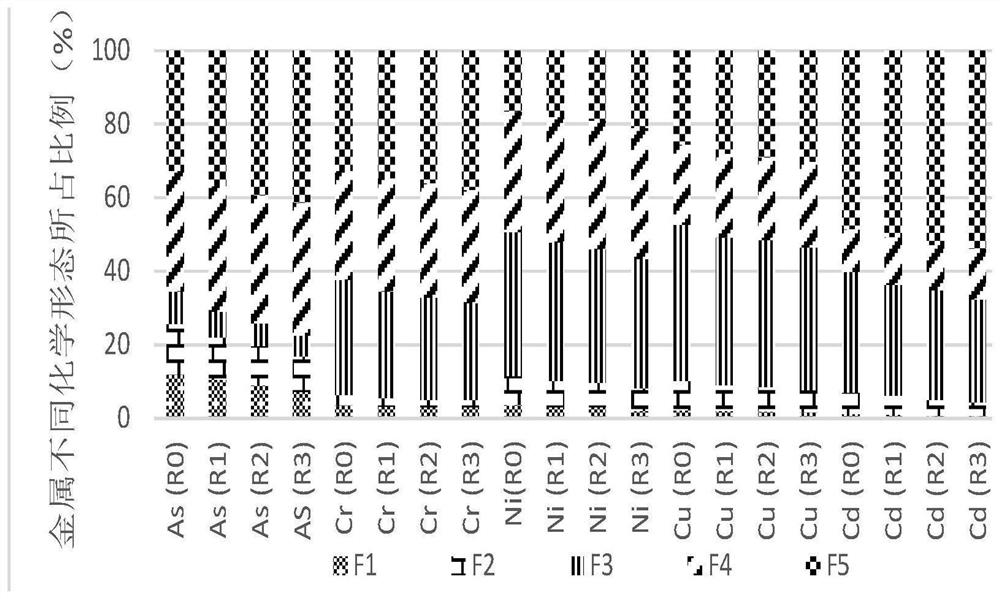
An anaerobic digestion and heavy metal technology, applied in sludge detoxification, chemical instruments and methods, sludge treatment, etc., can solve the problem of reducing the adsorption capacity of biochar to heavy metal ions, poor acid resistance of biochar, and poor adsorption capacity of heavy metals and other problems, so as to achieve the effects of not being prone to secondary pollution of the environment, increasing the specific surface area, and enhancing the adsorption and complexation ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
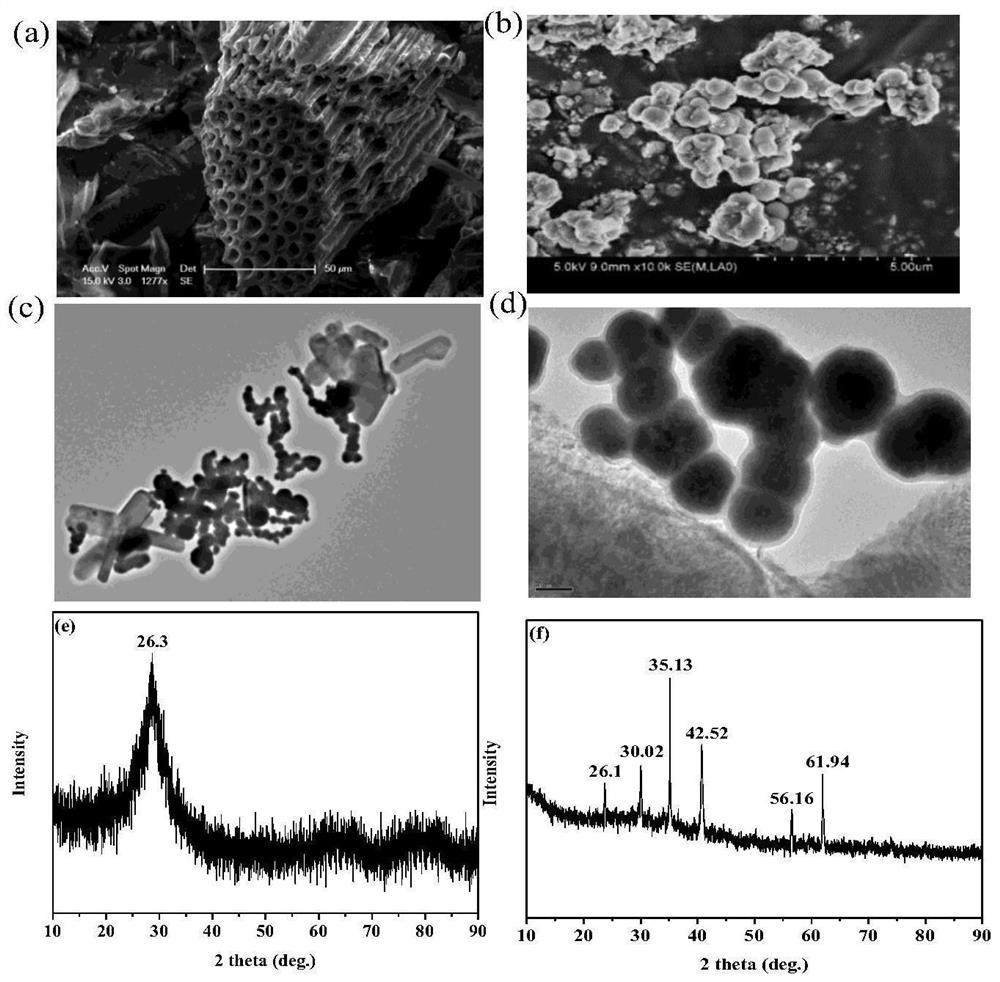
[0031] (1) Preparation of straw biochar BC:
[0032] Corn stalks (taken from a farmer’s market in Shanghai) were placed in a tube furnace. Under anaerobic conditions, the temperature of the tube furnace was raised to 600 °C at a rate of 18 K / min, and then kept at a constant temperature for 180 min. After natural cooling, it was ground and passed through 80 °C. mesh sieve to obtain straw biochar BC;
[0033] (2) Preparation of iron-manganese oxide nanoparticle-loaded biochar material FMBC:
[0034] Under stirring conditions, 5.56g FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O and 0.5g straw biochar BC were added to 70mL deionized water to obtain solution R1, and 1.053g KMnO 4 Add solution R2 to 60mL deionized water; add solution R2 dropwise to solution R1 under constant stirring, and then age at room temperature for 120min. During the reaction, add an appropriate amount of NaOH solution to keep the pH of the reaction system at 9.6. After the reaction is over, centrifuge, wash, and dry to obtain the iron-...
Embodiment 2
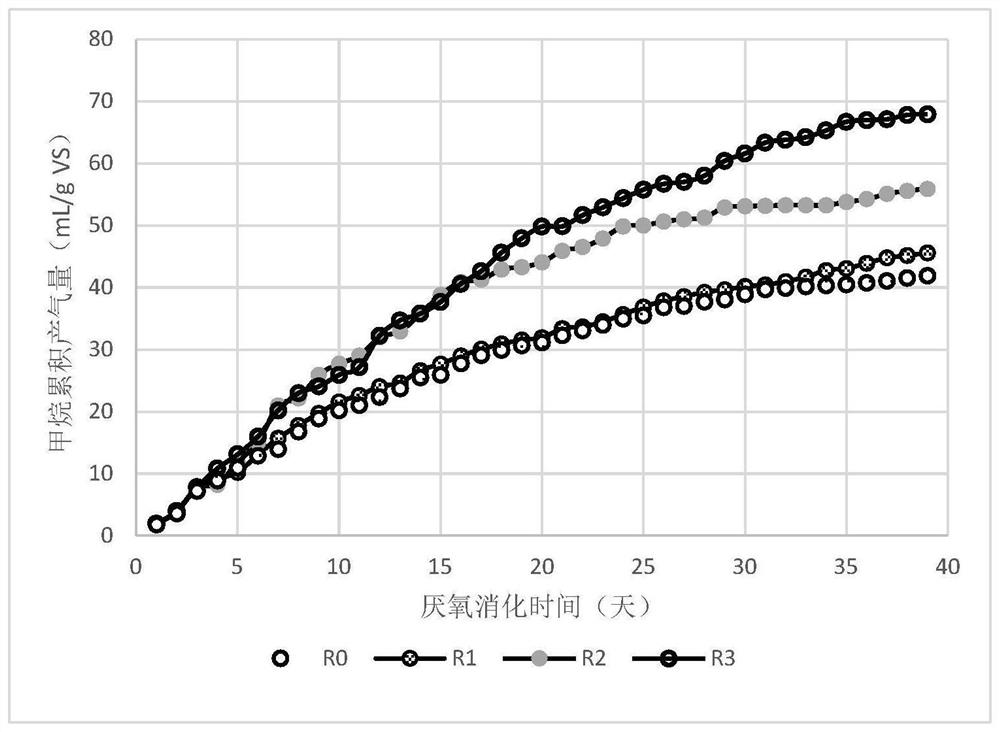
[0039] Using the same method as in Example 1, the only difference is that the dosage of FMBC added to the digestion unit in step (3) is 0.151g / g mixed sludge dry matter.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com