Intravascular stent applied to carotid artery
A vascular stent and carotid artery technology, applied in the field of carotid vascular stents, can solve the problem that the mesh area cannot cover the lesion to the greatest extent, and achieve the effect of preventing restenosis of blood vessels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Embodiment 1 A kind of vascular stent applied to carotid artery
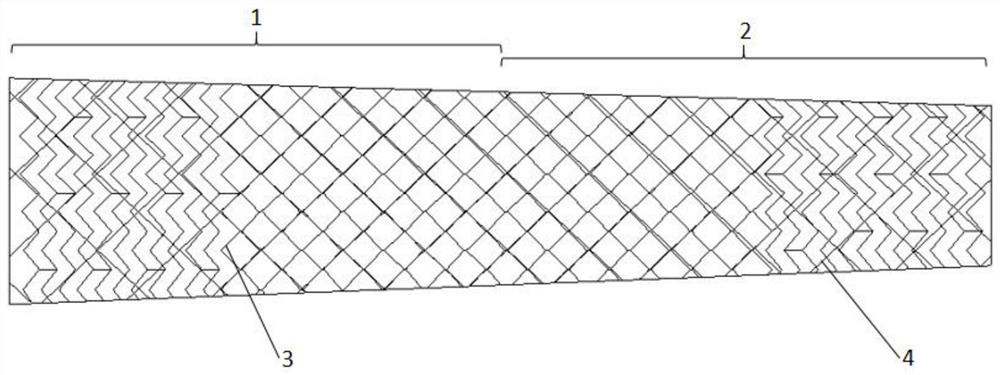
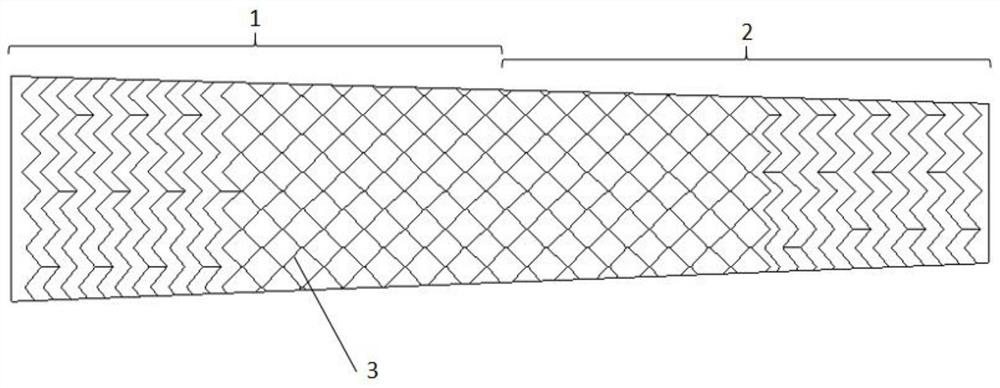
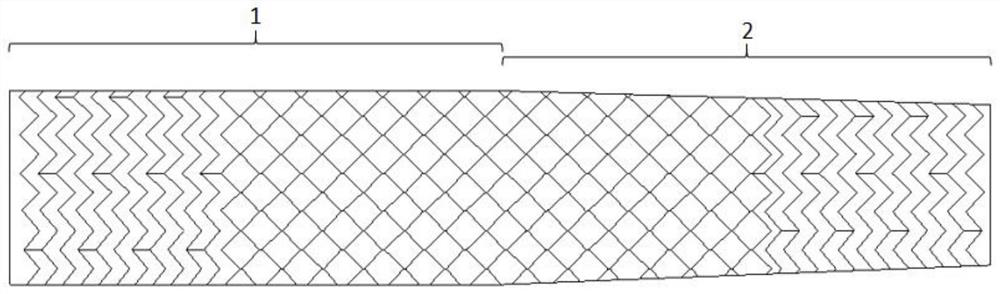
[0053] A vascular stent applied to the carotid artery, which includes a tubular stent body formed by docking a common carotid artery stent segment 1 and an internal carotid artery stent segment 2; it is characterized in that the internal carotid artery stent segment 2 is arranged to be connected to the carotid artery stent segment of a human body The first conical structure with an axial conical shape extending upwards in the shape of the internal artery, and the area of the upper cross-section of the first conical structure is smaller than the area of the lower cross-section of the first conical structure; the common carotid artery stent segment 1. It is set as a second tapered structure or a straight cylindrical structure extending upward in an axial tapered shape that matches the shape of the common carotid artery of the human body. The upper end of the second tapered structure is the same size as t...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Embodiment 2 A kind of vascular stent applied to carotid artery
[0070] A vascular stent applied to the carotid artery, which includes a tubular stent body formed by docking a common carotid artery stent segment 1 and an internal carotid artery stent segment 2; it is characterized in that the internal carotid artery stent segment 2 is arranged to be connected to the carotid artery stent segment of a human body The first conical structure with an axial conical shape extending upwards in the shape of the internal artery, and the area of the upper cross-section of the first conical structure is smaller than the area of the lower cross-section of the first conical structure; the common carotid artery stent segment 1. It is set as a second tapered structure or a straight cylindrical structure extending upward in an axial tapered shape that matches the shape of the common carotid artery of the human body. The upper end of the second tapered structure is the same size as t...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Embodiment 3 A kind of vascular stent applied to carotid artery
[0089] A vascular stent applied to the carotid artery, which includes a tubular stent body formed by docking a common carotid artery stent segment 1 and an internal carotid artery stent segment 2; it is characterized in that the internal carotid artery stent segment 2 is arranged to be connected to the carotid artery stent segment of a human body The first conical structure with an axial conical shape extending upwards in the shape of the internal artery, and the area of the upper cross-section of the first conical structure is smaller than the area of the lower cross-section of the first conical structure; the common carotid artery stent segment 1. It is set as a second tapered structure or a straight cylindrical structure extending upward in an axial tapered shape that matches the shape of the common carotid artery of the human body. The upper end of the second tapered structure is the same size as t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com