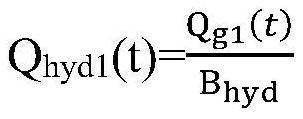A Calculation Method of Bottom-hole Sand Settling During Offshore Natural Gas Hydrate Drilling and Production
A calculation method and natural gas technology, which is applied in the direction of earthwork drilling, measurement, and fluid extraction, can solve the problems of jet drilling tools being stuck, stop production, and affect the effect of jet fragmentation, etc., to achieve easy operation, reliable principle, and avoid safety accidents Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Step 1, take a set of data as an example. Known volume coefficient B of natural gas hydrate decomposition hyd =164, the volume flow Q of the natural gas returned from the annular wellhead g1 (t) = 0.4445m 3 / s, the equivalent volume flow rate of natural gas Q g2 (t) = 0.323m 3 / s, the mud and sand flow rate Q returned from the annular wellhead sr (t) = 0.00705m 3 / s; Reservoir porosity Ф = 0.3, gas hydrate volume coefficient η = 0.8 in the pores;
[0034] Step 2, calculate the solid-state equivalent volume flow rate of the decomposed gas hydrate in the annular space:
[0035] Step 3, calculate the solid-state equivalent volume flow rate of gas hydrate returned from the annular wellhead:
[0036] Step 4, calculate the volume rate of solid-phase gas hydrate entering the wellbore annulus: Q hyd (t)=Q hyd1 (t)+Q hyd2 (t)=0.00467987804m 3 / s;
[0037] Step 5, calculate the volume rate of mud and sand entering the wellbore annulus:
[0038] Step 6, calcul...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Taking part of the working condition data as an example, the volume coefficient B of natural gas hydrate decomposition is known hyd =164. The porosity of the reservoir is Ф=0.3, and the volume coefficient of gas hydrate in the pores is η=0.8. Some working condition data are shown in Table 1.
[0042] Table 1 Partial working condition data and results
[0043] time / s Q g1 (t)m 3 / s
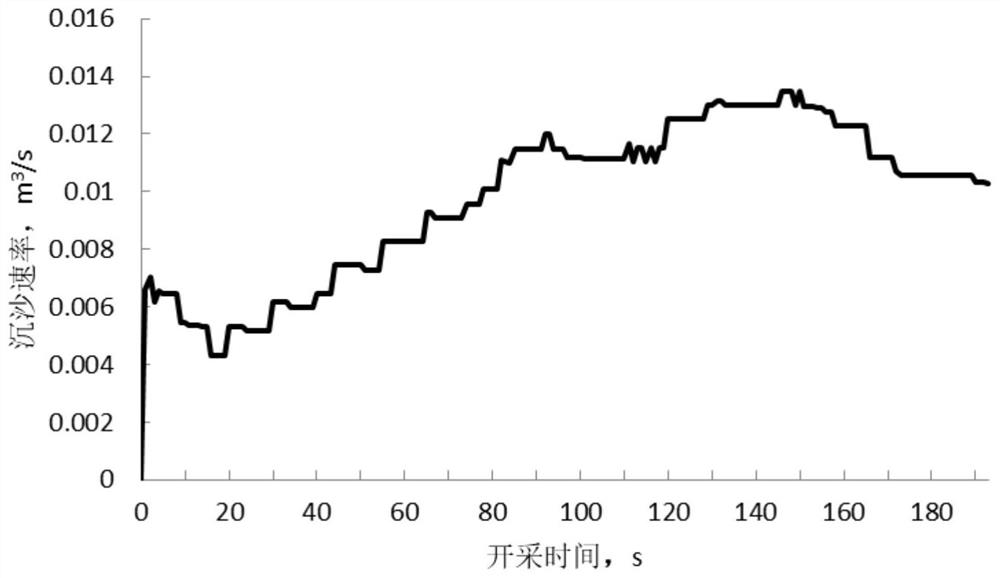
[0044] Apply the calculation method described in the present invention, obtain the relation of bottom-hole sedimentation rate and exploitation time such as figure 1 As shown, the relationship between the bottom hole sand volume and the production time is as follows: figure 2 As shown, the bottom hole sand volume increases with the increase of production time.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com