Interference mitigation and resource allocation method for underwater acoustic soft frequency reuse network
A technology of soft frequency multiplexing and resource allocation, which is applied in the field of interference mitigation and resource allocation of underwater acoustic soft frequency multiplexing networks, and can solve the problem of inaccurate long-delay feedback CSI
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0102] Table 1 Parameter settings
[0103]
[0104] According to the parameter given in above-mentioned table 1, verify the rationality of the embodiment of the present invention from 5 steps below:
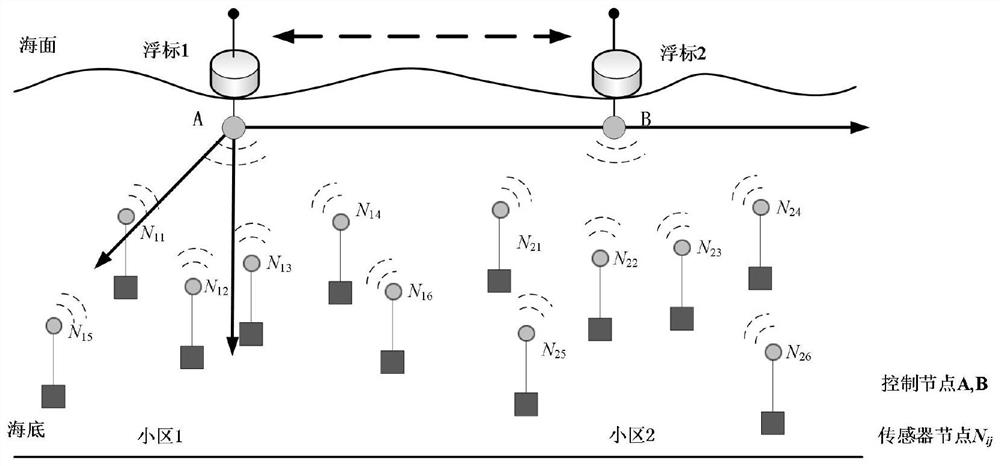
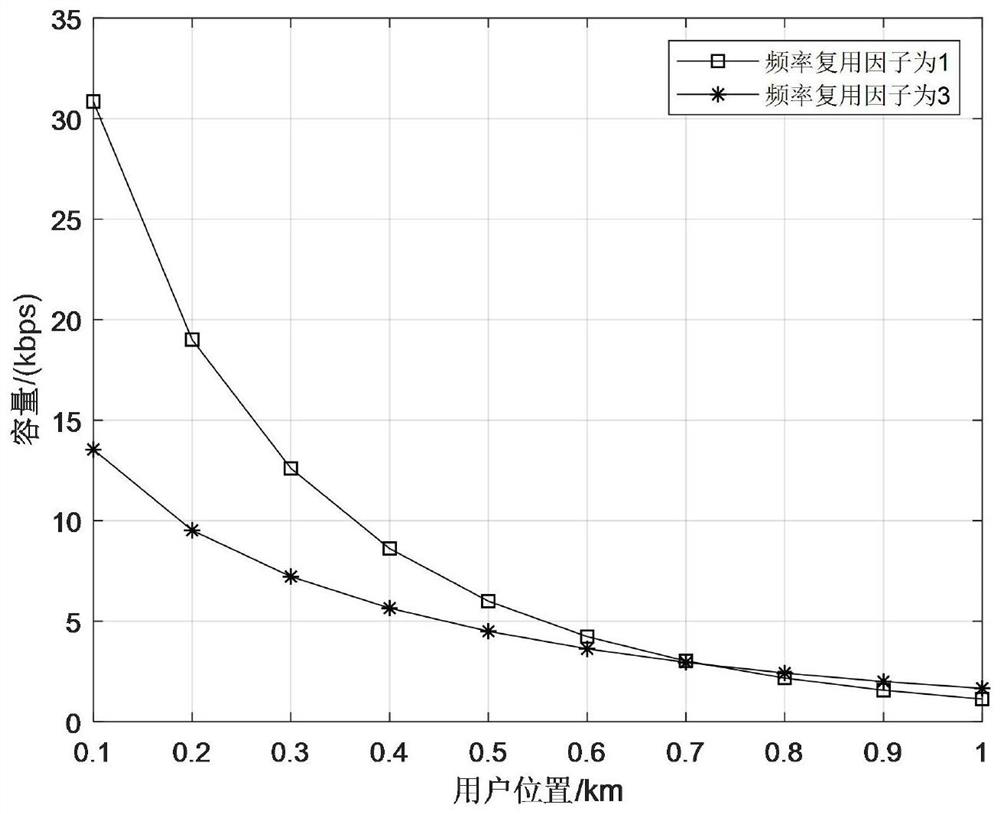
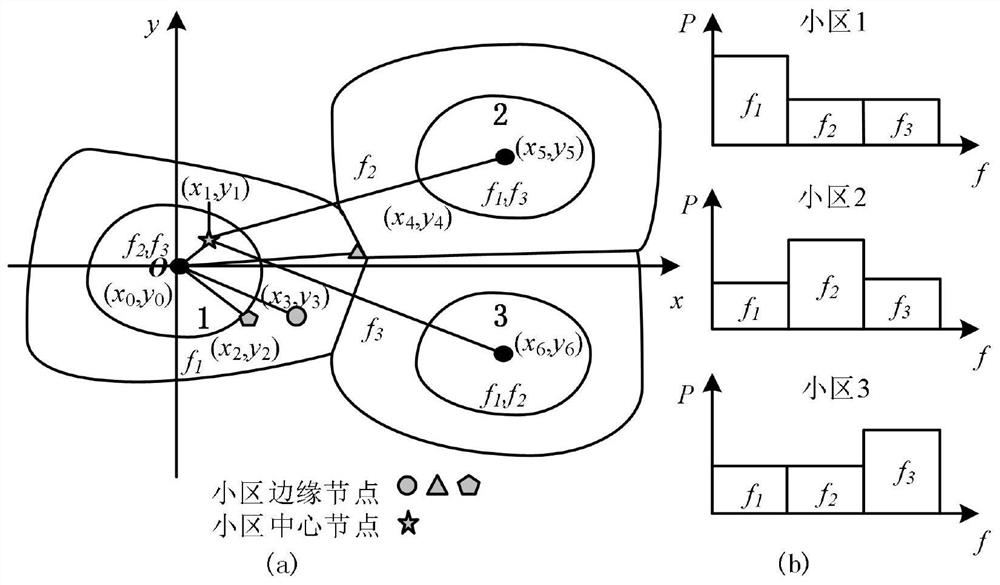
[0105] 1. In a cell containing a single control node and multiple data nodes, such as figure 2 The relationship between the geometric position of the cell data node and the system capacity is shown in the diagram, and the abscissa in the figure indicates the distance between the data node and the control node. Assuming that the cell radius is R, the position at 0.72 means that the distance between the data node and the control node is 0.72R. The simulation results show that the frequency reuse factor in the figure is 1 and 3, and the system capacity decreases as the distance between the data node and the control node increases. And it can be obtained that the reasonable division of the center and edge areas of the cell should take the radius ratio of 0.72 as the boundary po...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com