Method for regulating and controlling crystallization speed of crystal form II of isotactic polybutylene-1
A technology of isotactic polybutene and crystallization speed, which is applied in the field of macromolecule aggregate structure regulation, can solve the problems of harsh high pressure requirements, increased production costs, and inability to be applied, so as to speed up the crystallization speed, promote the production process, The effect of shortening the crystallization time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
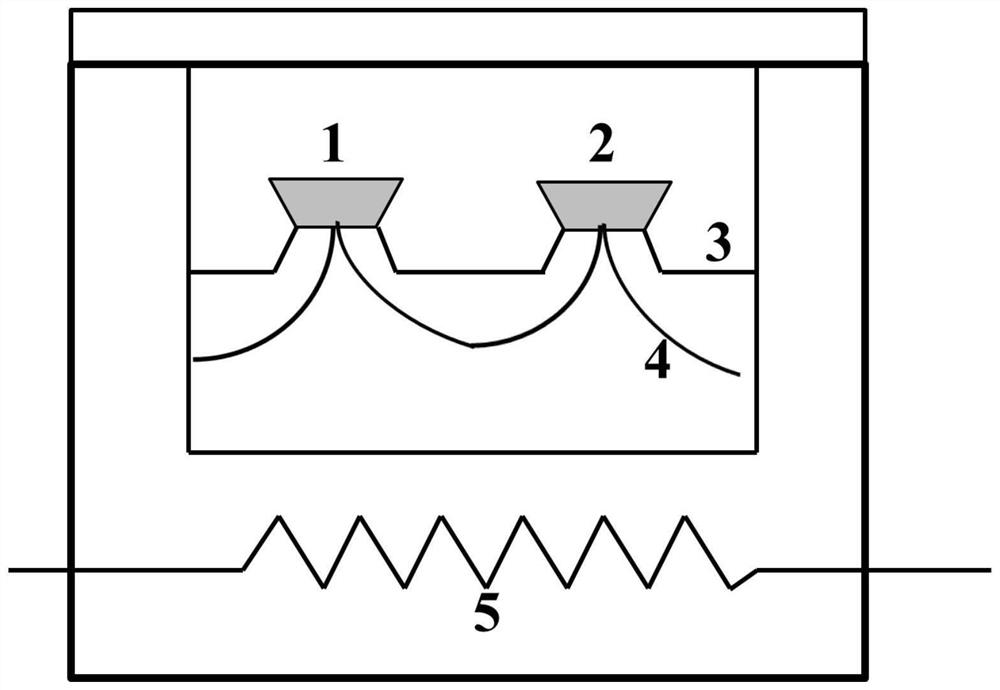
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] The blank melt of isotactic polybutene-1 prepared in this example is used as a comparison of the melt of isotactic polybutene-1 near melting point prepared in the present invention. The operation steps are as follows:
[0031] (1) Turn on the differential scanning calorimeter, pass in nitrogen gas (gas flow rate 50ml / min) for protection, and turn on the refrigeration program to reduce the temperature at the lower end of the furnace sensor to -80°C. After the temperature drops to the set temperature, the empty aluminum crucible without sample is used as a reference, and the sample crucible is placed on the reference end and the sample end of the furnace body of the differential scanning calorimeter respectively;
[0032] (2) Raise the temperature of the isotactic polybutene-1 crystal form I sample at 10°C / min to 150°C for 5min to eliminate thermal and mechanical history. At this time, the melt state is a blank melt without an ordered structure;
[0033] (3) Cooling at 1...
Embodiment 2
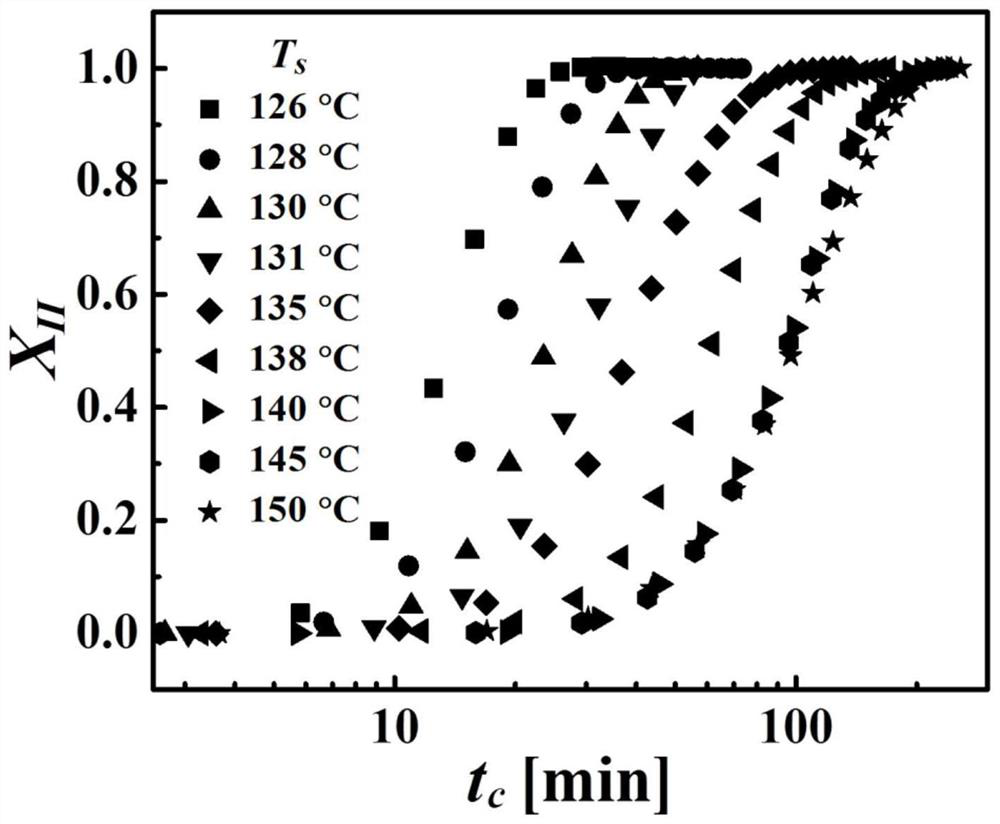
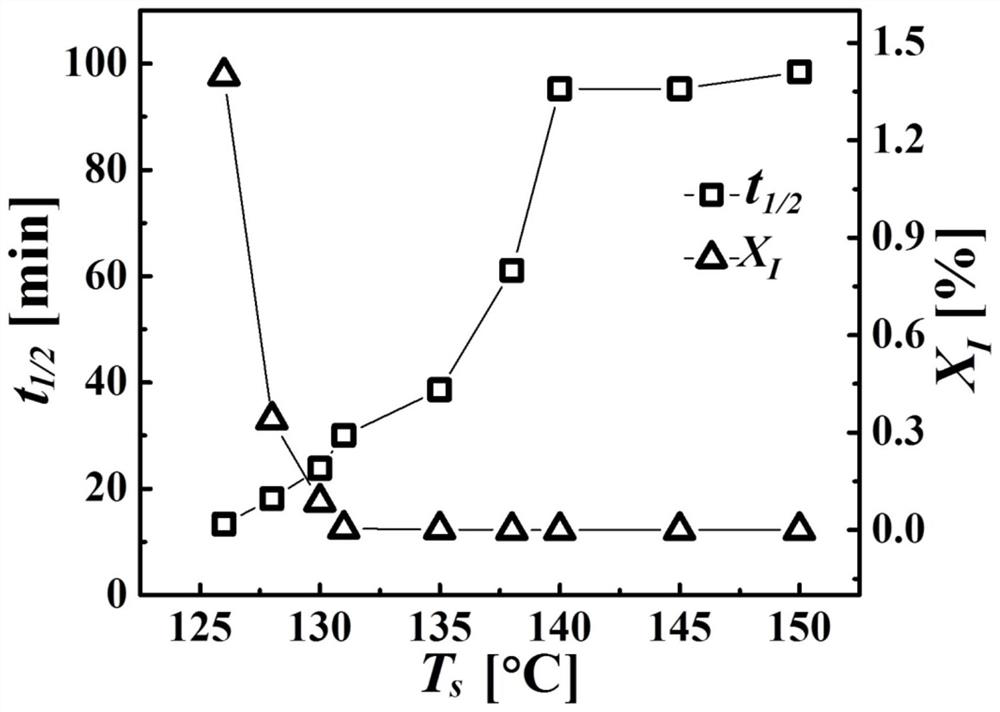
[0035] This example prepares an isotactic polybutene-1 melt containing crystal form I crystallites, and the content of crystal form I crystallites in the isotactic polybutene-1 melt is regulated by the melting temperature to achieve control of crystal form II crystallization purpose of speed. The operation steps are as follows:
[0036] (1) Turn on the differential scanning calorimeter, pass in nitrogen gas (gas flow rate 50ml / min) for protection, and turn on the refrigeration program to reduce the temperature at the lower end of the furnace sensor to -80°C. After the temperature drops to the set temperature, the empty aluminum crucible without sample is used as a reference, and the sample crucible is placed on the reference end and the sample end of the furnace body of the differential scanning calorimeter respectively;
[0037] (2) The isotactic polybutene-1 sample containing crystal form I was heated at 10°C / min to 126°C-140°C for 5 minutes to obtain isotactic polybutene-1...
Embodiment 3
[0042] In this example, an isotactic polybutene-1 melt containing crystal form I crystallites was prepared, and the content of crystal form I crystallites in the melt was regulated by the melting temperature to achieve the purpose of controlling the crystallization temperature of crystal form II. The operation steps are as follows:
[0043] (1) Turn on the differential scanning calorimeter, pass in nitrogen gas (gas flow rate 50ml / min) for protection, and turn on the refrigeration program to reduce the temperature at the lower end of the furnace sensor to -80°C. After the temperature drops to the set temperature, the empty aluminum crucible without sample is used as a reference, and the sample crucible is placed on the reference end and the sample end of the furnace body of the differential scanning calorimeter respectively;
[0044] (2) The isotactic polybutene-1 sample containing crystal form I was heated at 10°C / min to 126°C-140°C for 5 minutes to obtain isotactic polybuten...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com