T cell enriching method and application thereof to adoptive T cell therapy
A cell and enrichment technology, applied in the direction of cell culture active agents, receptors/cell surface antigens/cell surface determinants, animal cells, etc., can solve the problem of affecting cell activity, low T cell purity, and reduced T cell yield, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of increasing CAR expression rate, high T cell yield, and reducing operational risk
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
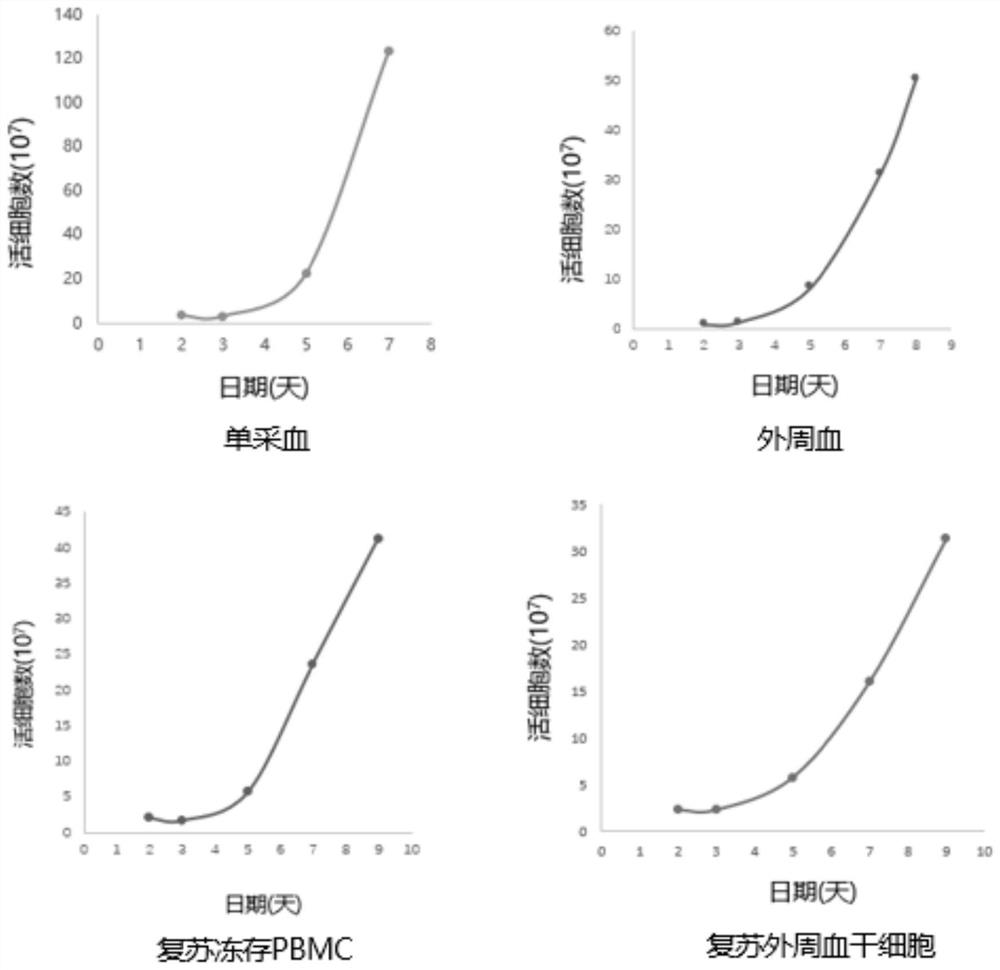
[0068] The isolation of the patient's autologous PBMCs of embodiment 1 different sources
[0069] The T cells used in the autologous CAR-T culture process are mainly derived from the patient itself, but in some cases, due to the patient's condition or the patient's own conditions, the content of T cells in PBMCs is low or the activity of T cells is insufficient, which increases the T cells in the process of CAR-T production. Difficulty in cell isolation and proliferation. For such patients, peripheral blood stem cells stored in a healthy state, PBMCs or highly active PBMCs stored in the early stage of patient onset can be used for CAR-T production, which can effectively avoid culture failure caused by low T cell activity.
[0070] Preparation of PBMCs from different sources
[0071] Scheme 1: PBMCs were obtained by separating autologous single blood using Ficoll separation fluid.
[0072] The experimental steps are as follows:
[0073] 1. The blood sample is diluted accordi...
Embodiment 2
[0092] Example 2 Obtaining the patient's own T cells
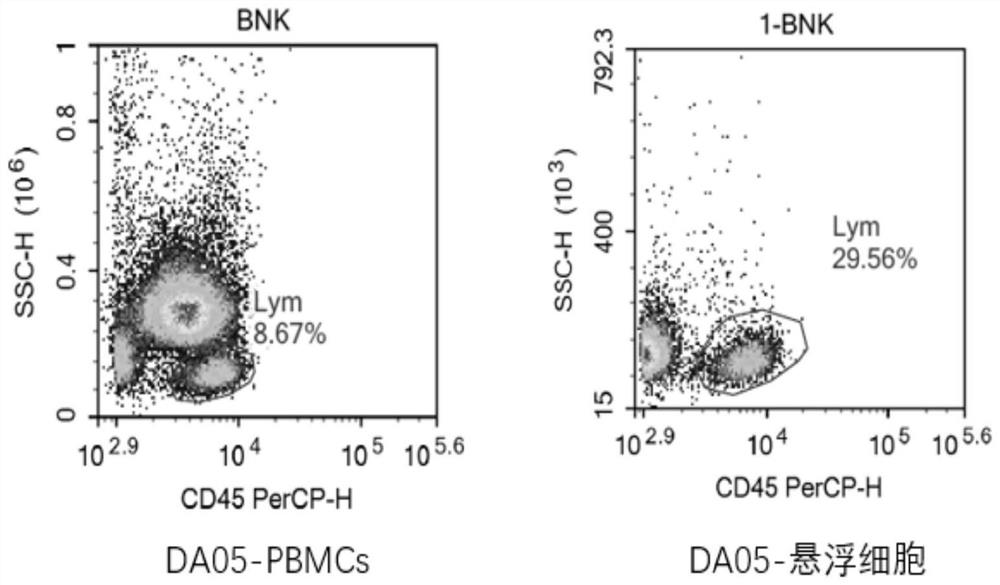
[0093] During the T cell sorting process, the isolated high-purity T cells can improve the activation efficiency of T cells, the proliferation multiple of T cells and the expression rate of CAR. However, in the process of CAR-T production, due to the patient's own reasons, PBMCs contain a large number of monocytes, which leads to a low content of T cells, and it is difficult to increase the isolation of high-purity T cells.
[0094] In this protocol, PBMCs are adhered to the wall, monocytes in PBMCs are removed, suspension cells are collected, and T cells are sorted by adding Dynabeads CD3 / CD28.
[0095] T cell isolation steps:
[0096] 1. Put the isolated PBMCs in 30mL / bottle (total 1×10 8 cells) into T175 culture flasks, placed in a carbon dioxide incubator (37°C, 5% CO 2 )nourish.
[0097] Take it out after 2.2 hours, absorb the suspended cells, and centrifuge (400g / 6min / liter 8 to 8).
[0098] 3. After resuspensio...
Embodiment 3
[0108] Virus infection steps:
[0109] 1. Collect T cells after 24-48 hours of activation, according to 1.5×10 6 cells / mL spread to the culture flask.
[0110] 2. Calculate the amount of virus needed according to the multiplicity of infection (MOI).
[0111] 3. Aspirate the required volume of virus, add it to the cell suspension, mix gently, and place in a carbon dioxide incubator (37°C, 5% CO 2 )nourish.
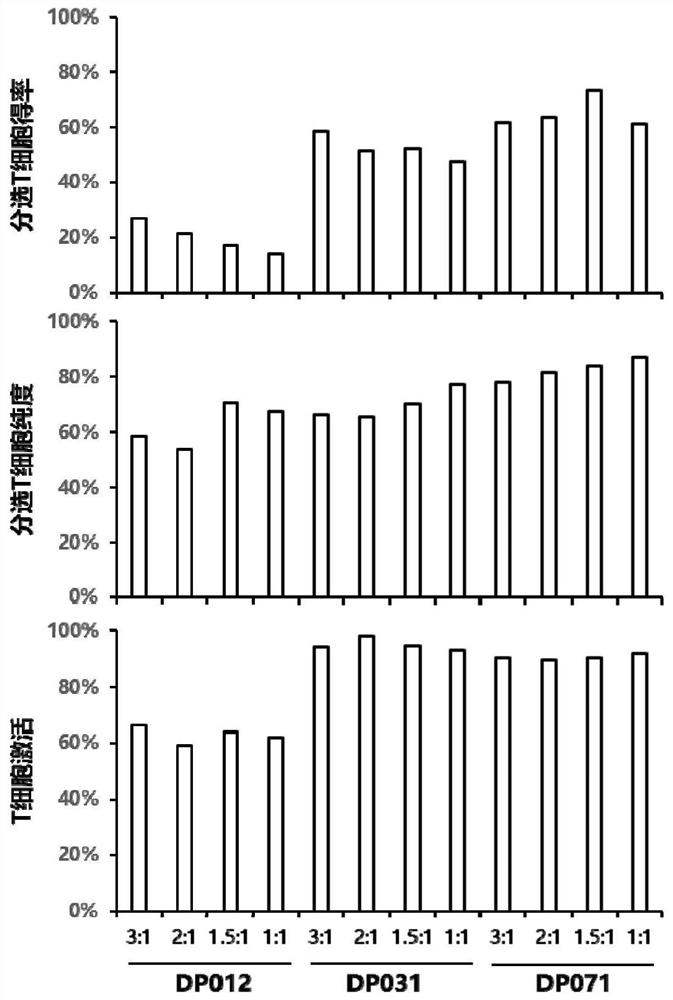
[0112] In this scheme, the inventors found that the use of viral infection cofactors had no significant effect on the expression rate of CAR (Table 2 and Figure 4 ). Therefore the present invention does not add viral infection cofactors.
[0113] Different infection times had a significant effect on the CAR expression rate (Table 3), among which 48 hours after activation was better than 24 hours after virus infection. To meet the needs of clinical production, virus infection was carried out 24 to 48 hours after T activation.
[0114] From the influence of the number ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com