Method for extracting elastin peptide from bovine cartilage
A technology of elastin peptide and cartilage, which is applied in the preparation method of peptide, chemical instruments and methods, animal/human protein, etc., which can solve the problems of unfavorable food absorption and large molecular weight of protein peptide
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
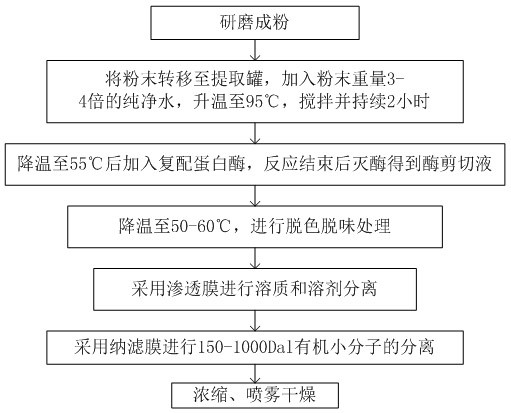
[0024] Such as figure 1 Shown a kind of method extracting elastin peptide from bovine cartilage, comprises the following steps:
[0025] A, the bovine cartilage is ground into powder;
[0026] B. Transfer the powder to the extraction tank, add pure water 3-4 times the weight of the powder, raise the temperature to 95°C, stir and continue for 2 hours;
[0027] C. Lower the temperature to 50°C-55°C, adjust to the optimal reaction conditions of the enzyme, add the compound protease, and inactivate the enzyme after the reaction to obtain the enzyme cutting solution; specifically, the method of inactivating the enzyme can be carried out by heating. The added amount of the compound protease is 0.2% by weight of bovine cartilage powder, so as to ensure the saturation of the compound protease, and the compound protease will not be excessively wasted.
[0028] D. Cool down to 50-60°C, and carry out decolorization and deodorization treatment; this step preferably uses a plate-and-fram...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Based on the principles of the above embodiments, this embodiment discloses a specific embodiment, specifically:
[0034] Pre-treatment: Wash the bovine cartilage, refine it and pulverize it.
[0035] Add 1kg bovine cartilage powder and 4kg hot water in the extraction tank, keep the water temperature at 95°C, and extract for 2 hours.
[0036] Lower the temperature to 55°C, add 0.2% bovine cartilage powder compound protease, and control the water temperature at 50°C-55°C for enzymatic hydrolysis. After the enzymatic hydrolysis, the temperature was raised to 95°C and kept for 30 minutes.
[0037] Cool down to 50-60°C for deodorization and decolorization treatment; pre-coat the plate and frame filter with diatomaceous earth, add 30g of activated carbon and mix and stir for 0.5h, then pressurize and pass through the plate and frame filter until the filtrate is yellow, clear and transparent liquid .
[0038] Composite tubular membrane and other permeable membranes are use...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com