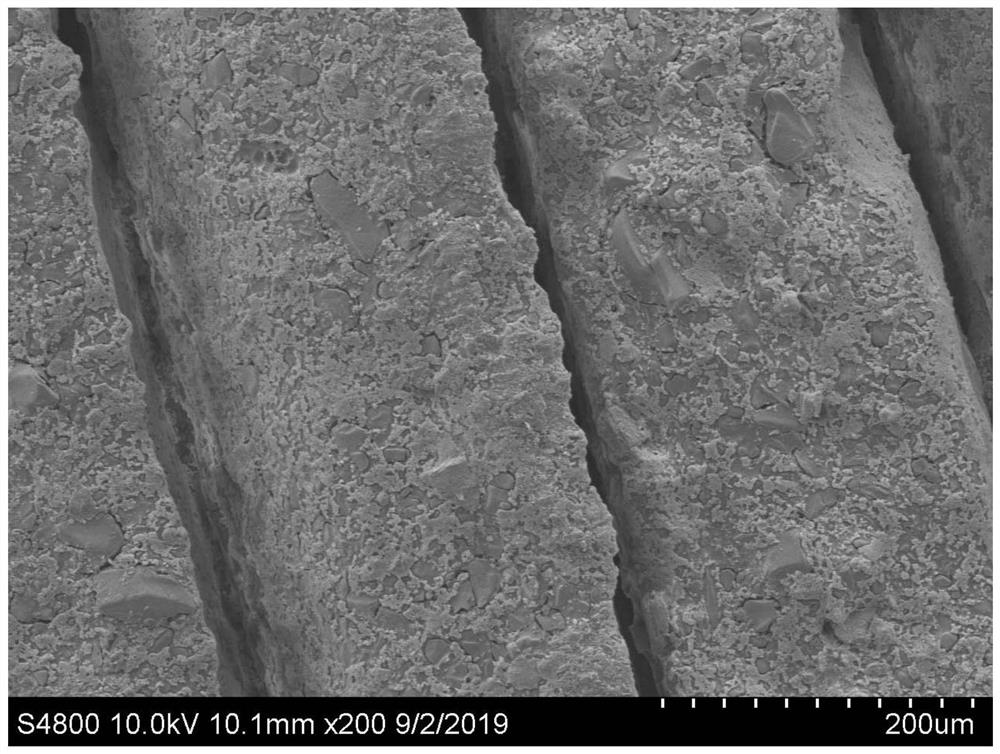
Preparation process of ceramic sheet
A ceramic thin plate and preparation technology, which is applied in the field of building decoration materials, can solve the problems of poor market competitiveness, high raw material costs, and high equipment investment, and achieve the effects of improving yield and consistency, process control, and less equipment investment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] The present embodiment adopts following raw material and process to make ceramic sheet:
[0036] (1) Take each component with the following weight and set aside:
[0037] Clay particles 1000g; Surfactant and binder (one material with two functions): 88% hydrolyzed PVA, 200g; Water: 1500g; Plasticizer: propylene glycol, 300g; Additive: n-butanol, 100g.
[0038] (2) Prepare a mixture containing clay particles, surfactants, binders, additives and water, and form a layer of the mixture prepared in step S1 on the substrate by casting method; then, dry the mixture at 30°C to remove The water in the water forms a film layer;
[0039] (3) Peel off the film layer from the substrate, and according to the thickness requirements of the final product, laminate the film to form a layered structure, and hot press it at 10MPa to form a blank; finally, heat treat the blank at 1280°C for 2 hours to make it Sintered to make a thin ceramic plate for performance testing.
Embodiment 2
[0041] The present embodiment adopts following raw material and process to make ceramic sheet:
[0042] (1) Take each component with the following weight and set aside:
[0043] Clay particles 1000g; Surfactant and binder (one material with two functions): 88% hydrolyzed PVA, 500g; Water: 3000g; Plasticizer: propylene glycol, 300g; Additive: n-butanol, 100g.
[0044] (2) Prepare a mixture comprising clay particles, surfactants, binders, additives and water, and use a coating method to form a layer of the mixture prepared in step S1 on the substrate; then, dry and remove the mixture at 30°C The water in the water forms a film layer;
[0045] (3) Peel off the film layer from the substrate, and according to the thickness requirements of the final product, laminate the film to form a layered structure, and hot press it at 20MPa to form a blank; finally, heat treat the blank at 1280°C for 2 hours to make it Sintered to make a thin ceramic plate for performance testing.
Embodiment 3
[0047] The present embodiment adopts following raw material and process to make ceramic sheet:
[0048] (1) Take each component with the following weight and set aside:
[0049]Clay particles 1000g; surfactant: polysorbate 80, 310g; binder: polyacrylic acid, 300g; water: 1500g; plasticizer: propylene glycol, 300g; additives: n-butanol 100g + zirconium dioxide whiskers 10g.
[0050] (2) Prepare a mixture containing clay particles, surfactants, binders, additives and water, and form a layer of the mixture prepared in step S1 on the substrate by tape casting; then, dry naturally to remove the water, forming a film;
[0051] (3) Peel off the film layer from the substrate, and according to the thickness requirements of the final product, laminate the film to form a layered structure, and hot press it at 10MPa to form a blank; finally, heat treat the blank at 1280°C for 2 hours to make it Sintered to make a thin ceramic plate for performance testing.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| water absorption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com