Stress safety judgment method for layered pouring concrete first-layer beam
A concrete beam, layered pouring technology, applied in bridges, buildings, bridge construction, etc., can solve problems affecting the safety and durability of concrete, reduce the corrosion resistance of structures, reduce the strength and stability of concrete beams, and save later Operation and maintenance funds, significant economic and social benefits, and the effect of simple and easy procedures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
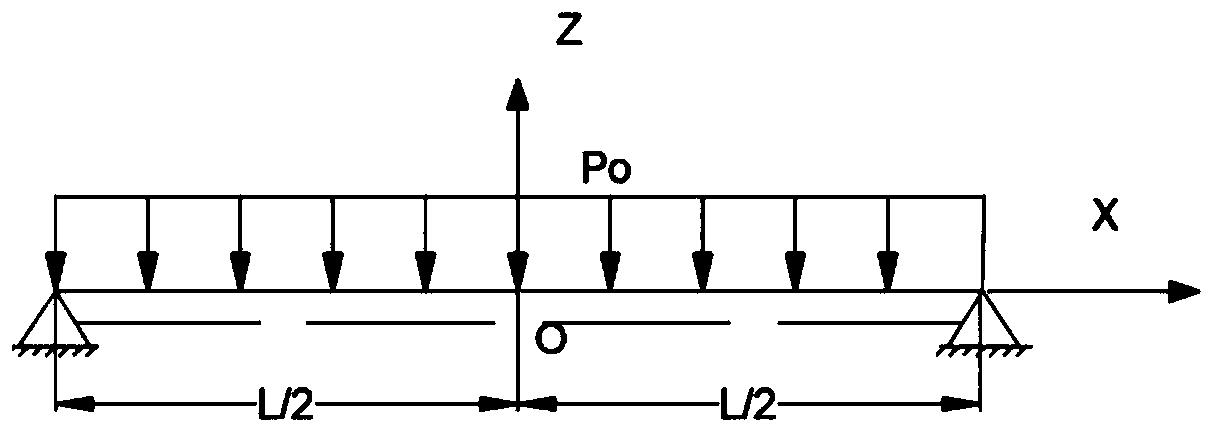
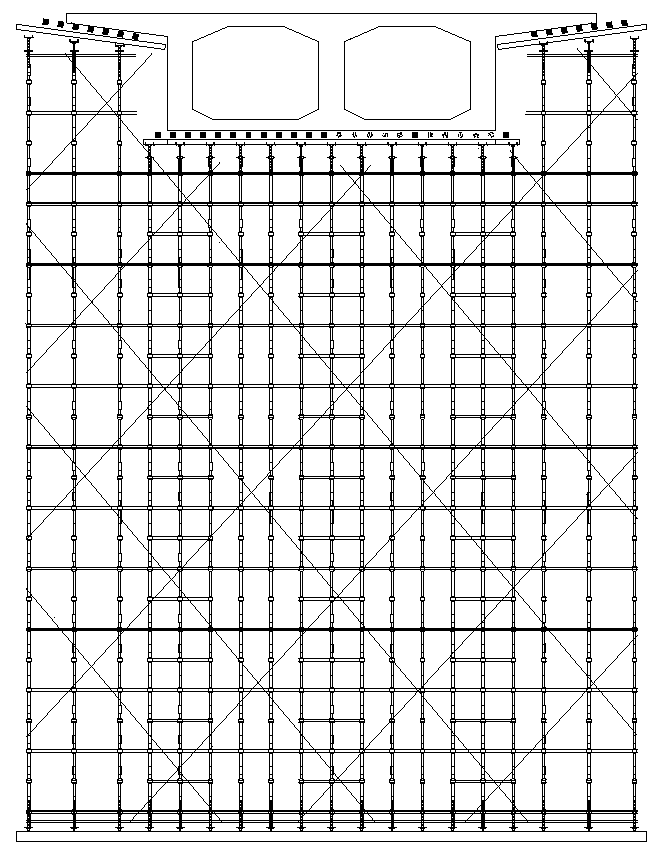
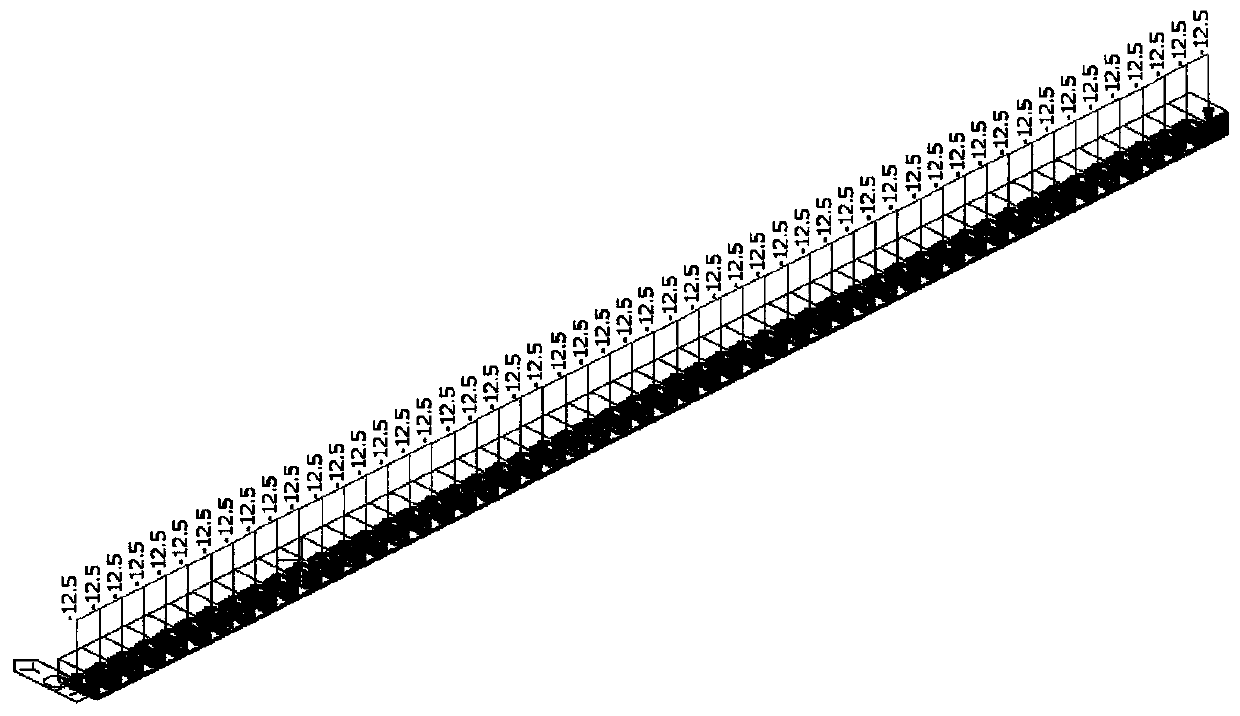
[0081] Take a simply supported girder bridge as an example, the minimum height of the clearance under the bridge is 6.0 meters, the vehicle load level is road-level I, the maximum height of the support is 6.8m, and the maximum height of the support is 16m. Vertical pole cross-bridge spacing × vertical pole vertical bridge spacing x cross-bar step distance is 60cm × 60cm × 120cm, and the bracket is set on the strip foundation Spiral steel pipe, as follows Figure 4 shown. The pouring height of the first stage is 500mm, and when the first floor beam is a simply supported beam, the pouring height of the first floor should account for 0.3-0.7 of the total height, and the pouring height of the second stage is 500mm, and the priority is given to setting the construction joints near the neutral axis, and dividing the construction joints Finally, the second-floor pouring layer is equivalent to a support system that transmits uniformly distributed loads to the first floor.
[0082] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com