Self-adaptive identification method for particles in asphalt mixture CT image
A technology of asphalt mixture and CT images, which is applied in the field of adaptive recognition of particles in asphalt mixture CT images, can solve the problem of low extraction accuracy and achieve the effect of improving the accuracy of mesostructure extraction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0049] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the specific process of an adaptive recognition method for particles in an asphalt mixture CT image in this embodiment is:
[0050] Step 1. Determine the radius and center position of the specimen in the asphalt mixture CT image;
[0051] Step 2, performing void grayscale zeroing processing on the CT image of the determined specimen radius and circle center, to obtain a CT image after void grayscale zeroing processing;
[0052] Step 3, performing statistical gray distribution along the radial direction on the CT image processed by zeroing the gray scale of the gap;
[0053] Step 4, performing uniform processing on the brightness of the image after the step 3 statistically distributes the gray scale along the radial direction;
[0054] Step 5, performing filtering and noise reduction on the image after the homogenization processing in step 4;
[0055] Step 6, performing global threshold segm...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0057] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: in the step one, determine the specimen radius and the center of circle position in the asphalt mixture CT image; the specific process is:
[0058] Because in the actual CT scanning process, the specimen is not always in the center position, which leads to the difference in the center position of the specimen in the image, and determining the center and radius of the specimen is of great significance for subsequent image processing operations, so It is necessary to identify the center and radius of the specimen in the image.
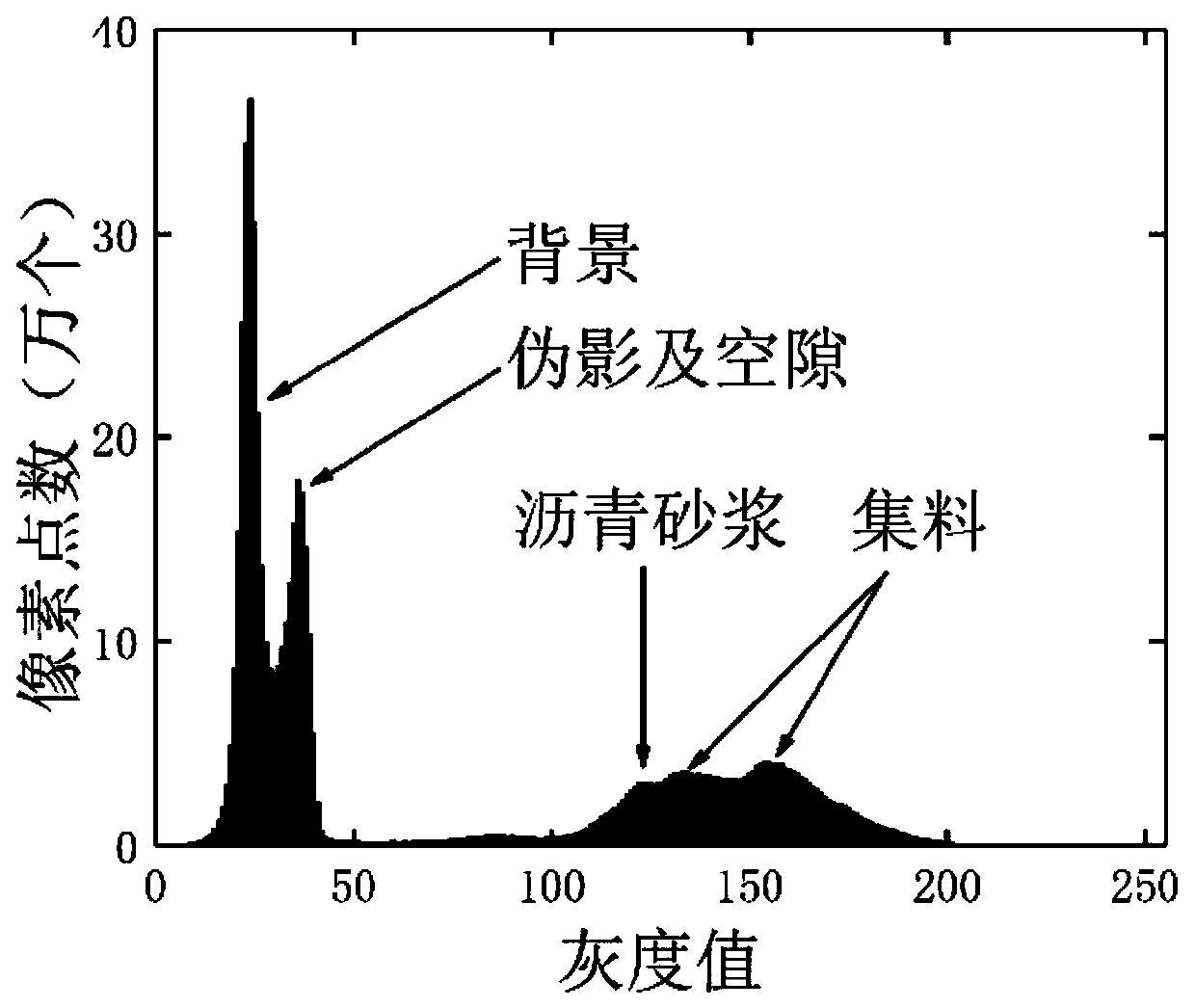
[0059]In the CT image of asphalt mixture: the gray value of voids < the gray value of asphalt mortar < the gray value of aggregate particles;
[0060] Step 11. Abstract the matrix of the entire asphalt mixture CT image into a Cartesian coordinate system. The row number and column number of the pixel points are the y coordinates and x coordinates of the ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0066] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: in the step two, the CT image of the determined specimen radius and the center of the circle is processed to zero the gray scale of the gap; the specific process is:
[0067] Since the extraction target of the present invention is aggregate, both the mortar and the void need to be removed as the background, and the mortar cannot be removed due to the existence of the black core and the overlap of the gray value of the aggregate, so first use multi-threshold segmentation and image subtraction Eliminate the gaps in the CT image specimen whose radius and center of the circle have been determined (the gap is found by threshold segmentation, because the gray value of the gap is relatively small, you can use the multi-threshold segmentation method to calculate multiple thresholds, representing The gray value of the gap is between a certain two thresholds, and the gap will b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com