Wound adhesion hydrogel material as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology for hydrogels and wounds, applied in applications, surgical adhesives, surgery, etc., can solve the problems of easy inhibition, reduction of inhibition effect, and restrictions, and achieve emergency response, ultra-high adhesion efficiency, and ultra-high adhesion The effect of indirect efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0050] The embodiment of the present invention also provides a preparation method of the above-mentioned wound adhesive hydrogel material, which adopts a one-pot polymerization method, and specifically includes:
[0051] Using the electrostatic interaction between polyacrylic acid and chitosan to form an interpenetrating network;
[0052] Cross-linking tannic acid with polyacrylic acid and chitosan in an interpenetrating network using aluminum ions as chelating agents; and
[0053] Adding methylene acrylamide BIS and bathing in water at 60-80° C. for 30-60 minutes obtains a wound-adhesive hydrogel material capable of repeated biological soft tissue-specific bonding.
[0054] In the preparation method of the above-mentioned wound adhesive hydrogel material, the hardness of the wound adhesive hydrogel material is regulated by changing the content of the aluminum ion chelating agent; and / or the adhesive is synthesized by changing the content of tannic acid Wound-adhesive hydroge...
Embodiment 1
[0057] Preparation method of wound adhesive hydrogel material and performance test of prepared wound adhesive hydrogel material
[0058] The preparation method of the wound adhesive hydrogel material: add 3g of acrylic acid and 0.2-0.3g of chitosan into 10-13g (77%) of distilled water and stir fully, then add 0.06-0.08g of nonahydrate aluminum nitrate, add 0.2-0.3 g tannic acid, add 10mg nitrogen nitrogen methylenebisacrylamide, and finally add 0.08g ammonium persulfate, stir well and put in a water bath at 60-80°C for 30-60 minutes to obtain a re-adhesive adhesive with super high adhesion efficiency. The attached wound adhesive hydrogel material.
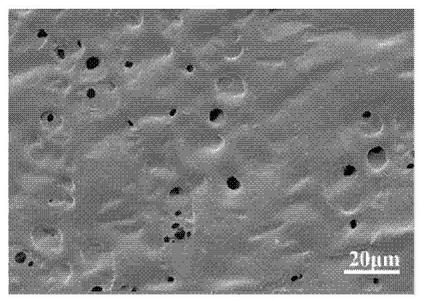
[0059] The interaction of the components of the above wound-adhesive hydrogel materials was analyzed using infrared spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy: infrared is figure 2 , comparing the infrared spectra of different substances, it shows that P-0.08Al-0.3C-0.3T (that is, the present invention, P represents polyacryli...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Example 2: Potential of the described wound-adhesive hydrogel materials as wearable device substrates.
[0066] Cut a spline with a length of 30mm, a width of 10mm, and a thickness of 2mm, and place it at the finger joint. Connect an external electrochemical workstation, bend your fingers 45° and 90°, and observe the changes in electrical signals, such as Figure 11 As shown, weak current stimulation can promote wound healing, indicating that the wound-adhesive hydrogel material has the potential as a substrate for wearable devices.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com