Fluorescent quantitative PCR method for detecting infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus of mandarin fish and corresponding kit
A spleen and kidney necrosis virus, fluorescence quantitative technology, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming, complicated operation, and inability to meet fast, simple and sensitive detection, etc., and achieve high sensitivity High performance, wide application range and stable detection results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
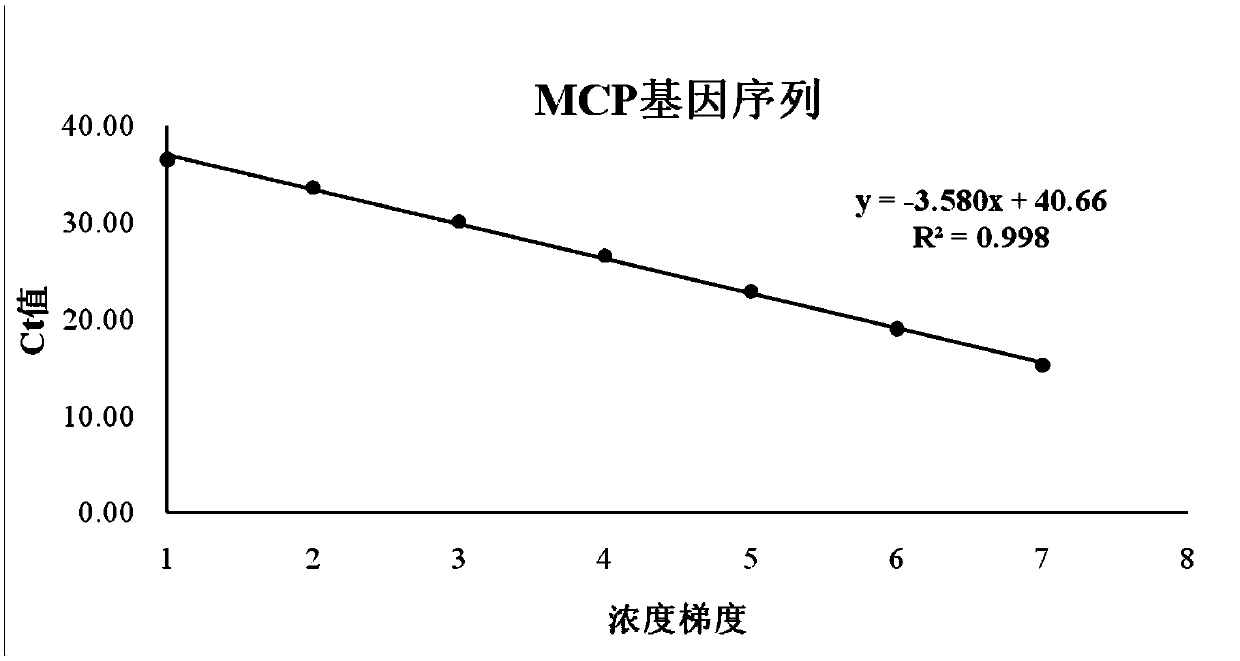
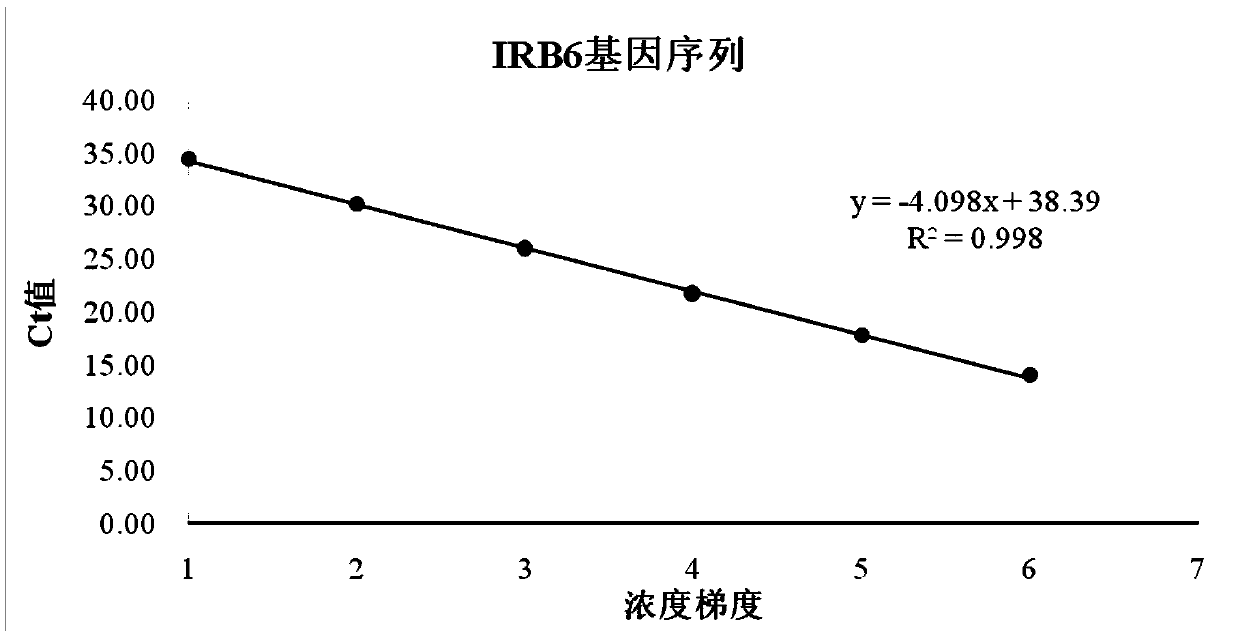
[0060] Embodiment 1 detection primer amplification standard curve and plasmid sensitivity experiment
[0061] 1. Microbial culture
[0062] The LB medium is used as the medium of the mandarin fish infectious spleen-kidney necrosis virus plasmid, and it grows well in the plate with pH 7.0~7.4. The diameter of the colony on the plate is 2mm, round, smooth and transparent. The vigorously growing microbial samples were selected for subsequent experiments.
[0063] 2. Genomic DNA Extraction
[0064] Genomic DNA was extracted according to the instructions of Qiagen's QIAamp DNA Mini Kit.
[0065] 3. Production of standard plasmids for amplified products
[0066] DNA extracted from mandarin fish infectious spleen-kidney necrosis virus was used to amplify with primers of ATPase, MCP and IRB6 genes respectively. After induction of competent cells, the plasmids were amplified on a large scale. The primer sequences and TaqMan probe sequences of the three genes are shown in SEQ ID N...
Embodiment 2
[0084] Example 2 Plasmid Repeatability Experiment
[0085] 1. Microbial culture
[0086] With embodiment 1.
[0087] 2. Genomic DNA Extraction
[0088] With embodiment 1.
[0089] 3. qPCR detection of 3 target genes
[0090] Carry out qPCR amplification of the sample according to the instructions of TaKaRa Taq PCR Mix, and obtain the Ct value reading corresponding to each pair of primers. The qPCR reaction in this experiment was set at two concentrations of 1×10 6 fg / μL and 1×10 5 fg / μL, 4 biological replicates and 5 technical replicates were set up for each concentration, and the qPCR reaction system and amplification reaction conditions are shown in Table 7.
[0091] Table 7
[0092]
[0093] 4. Result analysis
[0094] In this example, the correlation coefficient and reliability of the amplification curves of the three genes were analyzed, as well as the amplification efficiencies at two concentrations. The measured CT values were all less than 35 cycles, and a...
Embodiment 3
[0102] Embodiment 3 Positive and negative sample detection situation
[0103] 1. Microbial culture
[0104] With embodiment 1.
[0105] 2. Genomic DNA Extraction
[0106] With embodiment 1.
[0107] 3. qPCR detection of 3 target genes
[0108]Carry out qPCR amplification of the sample according to the instructions of TaKaRa Taq PCR Mix, and obtain the Ct value reading corresponding to each pair of primers. Each qPCR reaction was set up with 3 biological repetitions and 3 technical repetitions, and the qPCR reaction system and amplification reaction conditions were the same as in Example 2.
[0109] 4. Result analysis
[0110] as shown in Table 11 and Figure 10 As shown, the qPCR amplification results of three pairs of primers showed that the mandarin fish infectious spleen-kidney necrosis virus showed all positive results of ATPase, MCP and IRB6 genes, while other viruses or bacterial genera showed negative results. Therefore, the detection of ATPase, MCP and IRB6 gene...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com