Novel microorganism having minimal genome and method of producing the same
一种微生物、基因组的技术,应用在基于微生物的方法、生物化学设备和方法、微生物等方向,能够解决难以构建最小基因组等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0047] For the purposes of the present disclosure, it is required that the preparation method comprises the step of continuously culturing the microorganism in a medium containing LB broth of decreasing concentration.
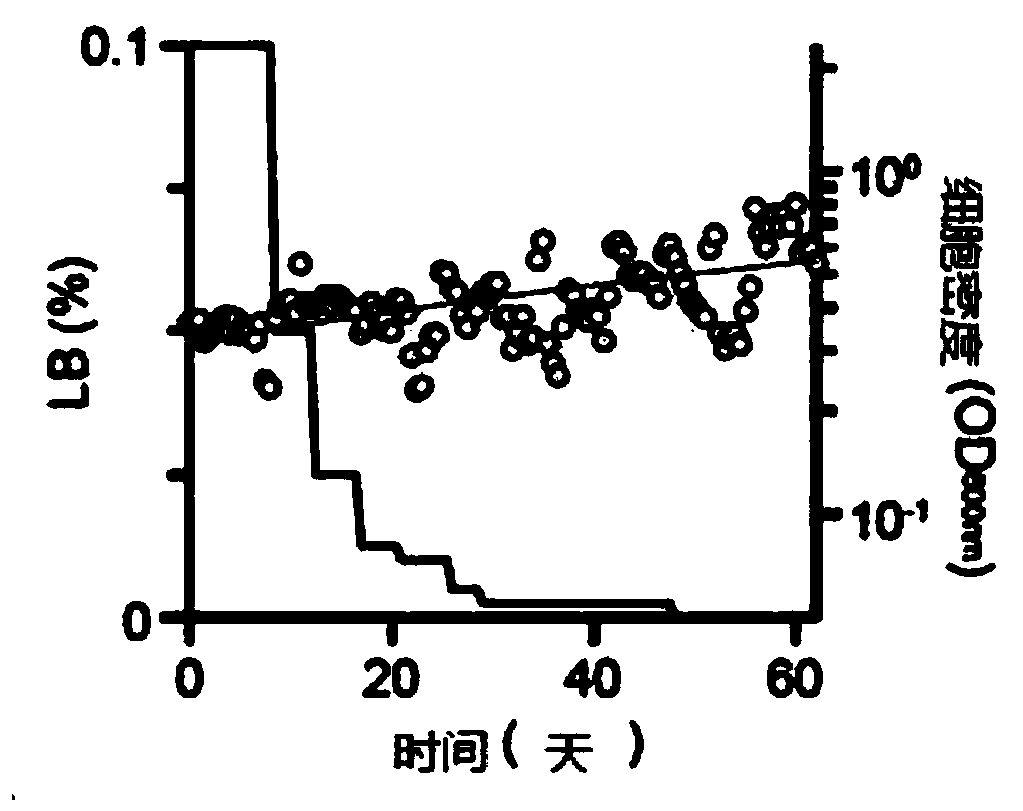
[0048] Specifically, this step may be the process of Adaptive Laboratory Evolution (ALE). ALE is a method for obtaining mutants of microorganisms in which appropriate stresses are applied during the growth of the microorganisms to cause genotypic and phenotypic changes. The purpose of the present disclosure is to produce microorganisms with a minimal genome while having increased viability, thereby producing microorganisms capable of efficiently surviving even with less nutrients by gradually depleting LB broth of nutrients contained in the medium.
[0049] Specifically, by gradually reducing the concentration to 0.12% (v / v) to 0.08% (v / v), 0.07% (v / v) to 0.03% (v / v), 0.015% (v / v) to 0.005% (v / v), 0.003% (v / v) to 0.001% (v / v) and 0%; and more specifically 0.1%...
Embodiment 1
[0056] Example 1. Generation of eMS57 strain with minimal genome and excellent growth rate
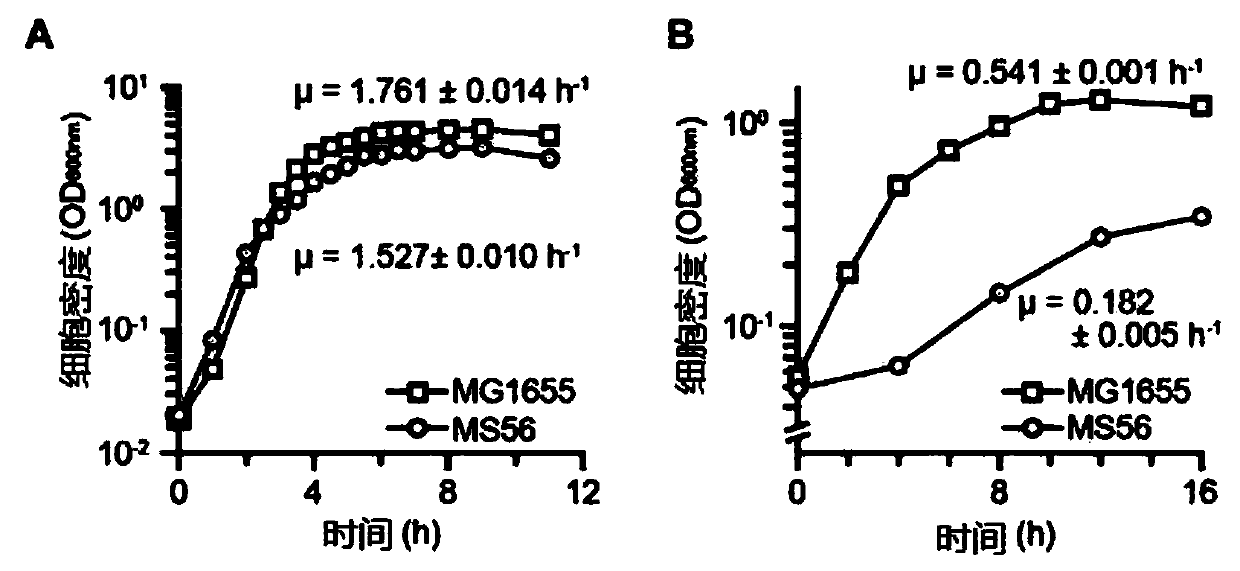
[0057] To generate strains showing high growth rates with minimal genomes, ALE was used. Specifically, the "MS56" strain with the smallest genome size (approximately 3.6 Mbp), which was generated by the systematic deletion of 55 genomic regions of the wild-type E. coli "MG1655" strain, was used as the starting strain for ALE .
[0058] Meanwhile, Escherichia coli MS56 was grown in M9 glucose medium at 37°C under agitation. Transfer cultures to fresh medium every 12 hours, initial OD 600nm About 0.005. The growth rates of MS56 and MG1655 were checked, and as a result, MS56 showed a comparable growth rate to MG1655 in the rich medium, but showed a severe decrease in growth in the minimal medium ( figure 1 ).
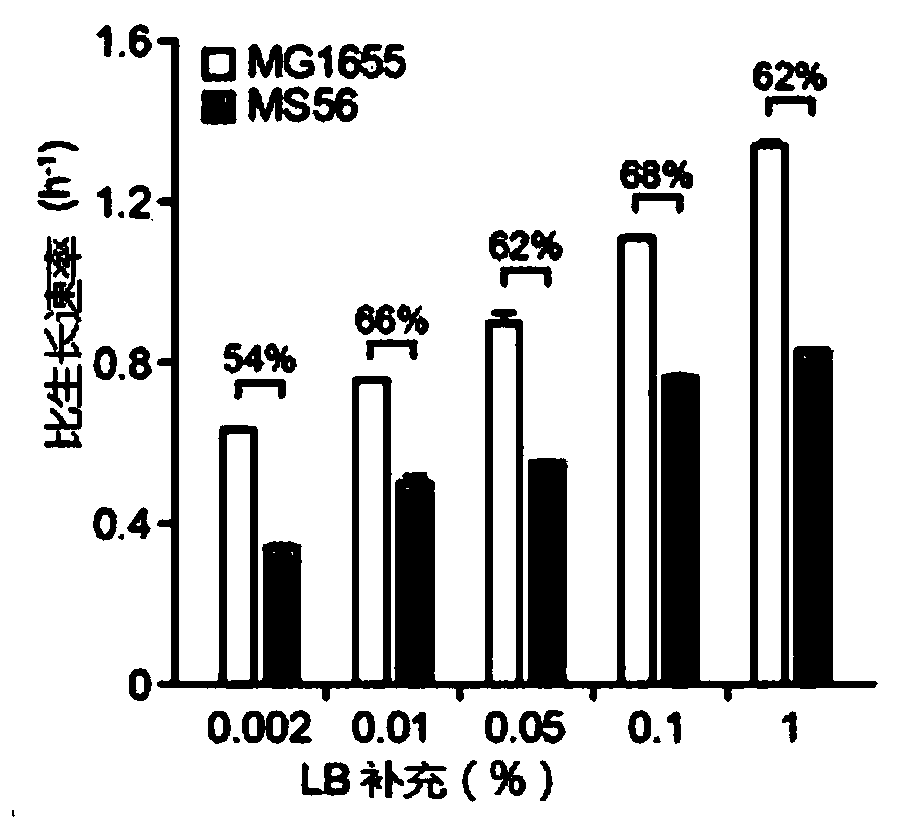
[0059] As described, since MS56 showed low growth rate in M9 minimal medium, it was aimed to generate a strain that showed high growth rate in minimal medium and had a minim...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Phenotype inspection of embodiment 2.eMS57
[0064] For phenotypic examination of eMS57, the morphology of eMS57, MS56 and MG1655 was compared using electron microscopy.
[0065] 1 mL of the exponential phase culture was added to a 2.5% paraformaldehyde-glutaraldehyde mixture buffered with 0.1% phosphate buffer (pH 7.2) for 2 hours at a temperature of 4°C. The premixed samples were treated with 1% osmium tetroxide solution buffered with 0.1M phosphate buffer (pH 7.2) for 1 hour at room temperature (25°C). The fixed samples were dehydrated in ethanol, replaced with isoamyl acetate, and incubated in liquid CO 2 critical point drying. Finally, the samples were finally sputter-plated with gold to a thickness of 20 nm in a Sputter Coater SC502 (Polaron, Quorum Technologies, East Sussex, UK), and were sputtered using SEM images were obtained with a FEI Quanta250FEG scanning electron microscope (FEI, Hillsboro, OR, USA). For transmission electron microscopy, samples fixe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com