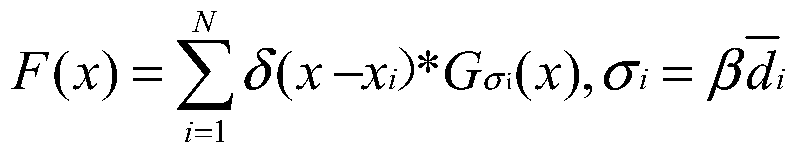Crowd counting method and system based on feature pyramid, medium and electronic equipment
A feature pyramid and crowd counting technology, applied in the field of computer vision, can solve the problems of missing more detailed information, difficulty in dealing with scale changes, and poor counting ability of small targets
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
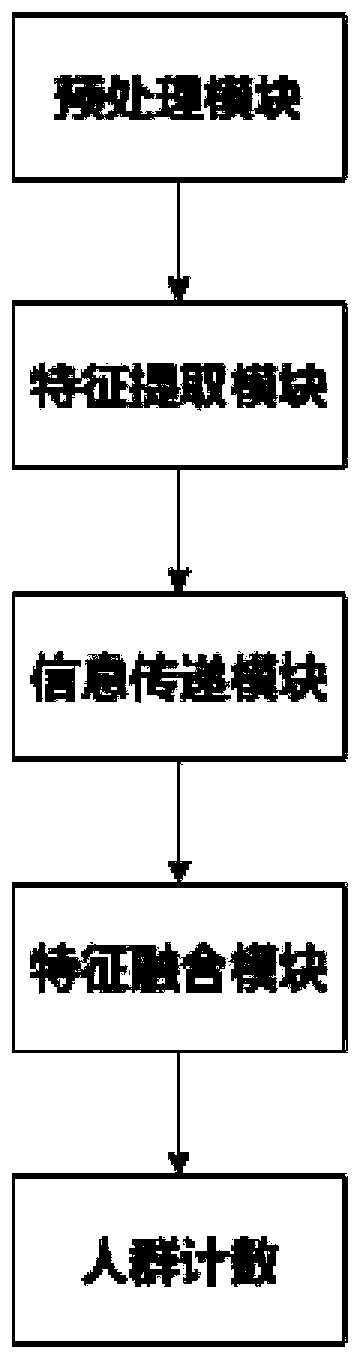
[0036] Such as figure 1 As shown, Embodiment 1 of the present disclosure provides a crowd counting method based on a feature pyramid, including the following steps:
[0037] Preprocessing the acquired image to obtain the initial crowd density map corresponding to the image;
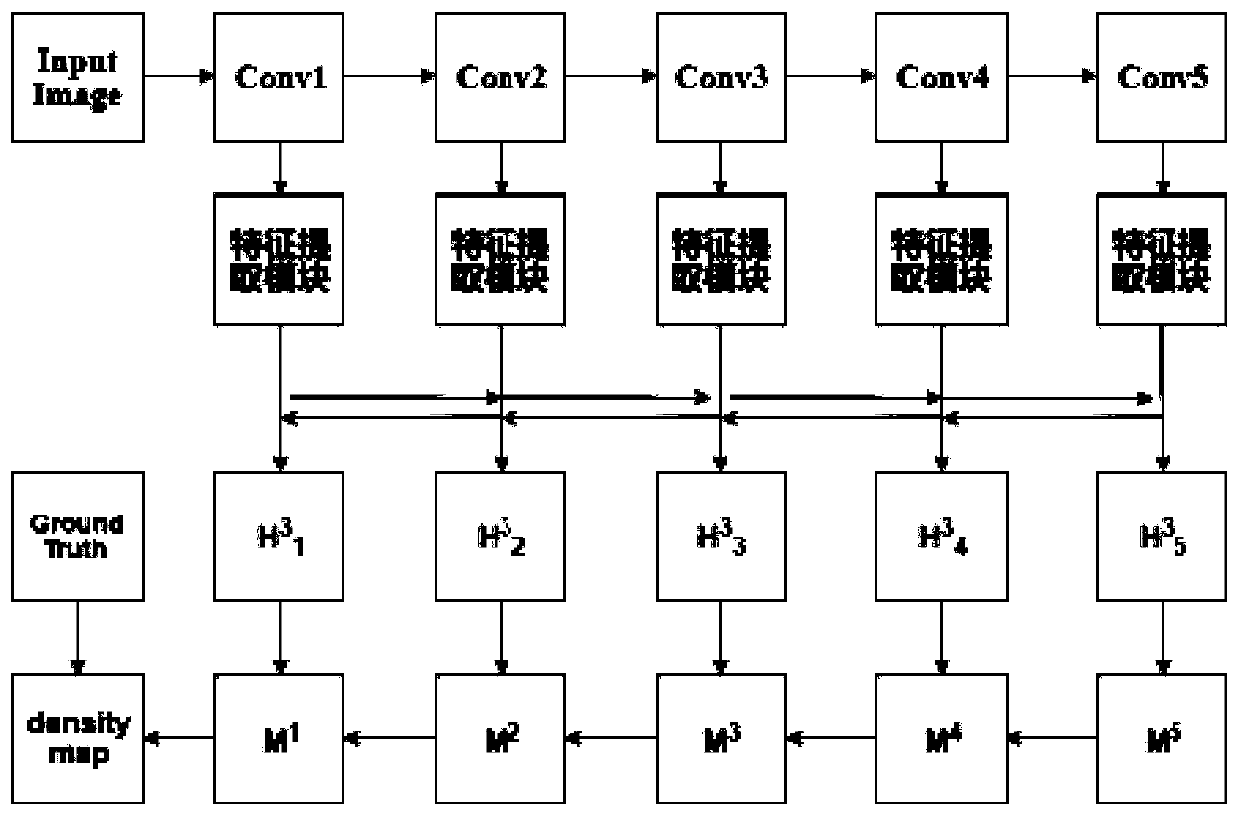
[0038] Input the obtained initial crowd density map into the preset feature pyramid network model, extract feature maps at multiple levels, and obtain feature maps that integrate multi-scale context information at each level;
[0039] From the bottom layer to the top layer, the information transmission is updated layer by layer, and then the reverse information transmission is carried out to the bottom layer, and the feature maps of each layer obtained by the two-way information transmission are fused to obtain the final feature map of each layer;
[0040] The obtained final feature maps of each layer are reversely connected layer by layer to obtain the final crowd density map, and then the final crowd c...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Embodiment 2 of the present disclosure provides a feature pyramid-based crowd counting system, including:
[0076] The data preprocessing module is configured to: preprocess the acquired image to obtain an initial crowd density map corresponding to the image;
[0077] The feature extraction module is configured to: input the obtained initial crowd density map into the preset feature pyramid network model, extract feature maps at multiple levels, and obtain a feature map incorporating multi-scale context information at each level ;
[0078] The feature processing module is configured to: perform information transfer and update layer by layer from the bottom layer to the top layer, and then perform reverse information transfer to the bottom layer, and fuse the feature maps of each layer obtained by bidirectional information transfer to obtain the final feature map of each layer;
[0079] The crowd counting module is configured to: reversely connect the obtained final fea...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Embodiment 3 of the present disclosure provides a medium on which a program is stored. When the program is executed by a processor, the steps in the feature pyramid-based crowd counting method described in Embodiment 1 of the present disclosure are implemented, specifically:
[0083] Preprocessing the acquired image to obtain the initial crowd density map corresponding to the image;
[0084] Input the obtained initial crowd density map into the preset feature pyramid network model, extract feature maps at multiple levels, and obtain feature maps that incorporate multi-scale context information at each level;
[0085] From the bottom layer to the top layer, the information transmission is updated layer by layer, and then the reverse information transmission is carried out to the bottom layer, and the feature maps of each layer obtained by the two-way information transmission are fused to obtain the final feature map of each layer;
[0086] The obtained final feature maps...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com