Deep-sea organism transfer case
A transfer box, deep-sea technology, applied in fish farming, fishing, applications, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, high cost, and low utilization rate of pressure-holding trapping containers in deep-sea biological traps, so as to reduce costs and increase the frequency of use. , to avoid uncomfortable effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
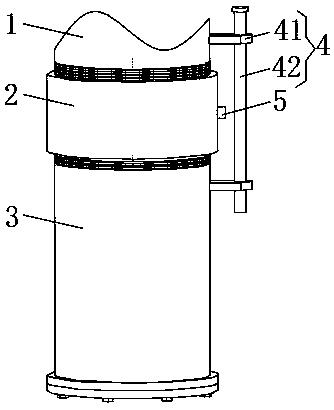
[0037] Example 1: Please refer to Figure 1-4 , this embodiment discloses a deep-sea biological transfer box, which includes a casing 2 and an inner hollow shell 3, the outer side of the casing 3 is extended with a first connecting circular pipe, the outer side of the first connecting circular pipe is provided with an external thread, and the sleeve Both sides of the inner wall of the pipe 2 are provided with internal threads, and the directions of the two internal threads in the casing 2 are opposite, and the outer side of the first connecting circular pipe is fitted with one side of the inner wall of the casing 2 .
[0038] An installation hole connecting the inside and outside of the sleeve 2 is opened in the middle in the longitudinal direction of the outer side of the sleeve 2 , and a gas nozzle 5 is installed on the outside of the installation hole.
[0039] The outer side of the casing 3 is provided with an opening that communicates with the inside and the outside, the ...
Embodiment 2
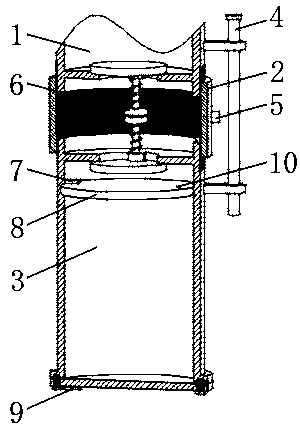
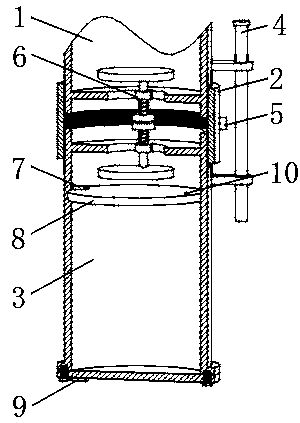
[0047] And in the prior art, when the deep-sea organisms in the pressure-holding trapping container are transferred on the research vessel, it is difficult to realize the pressure-holding transfer due to the space and cost constraints of the research vessel. Forcible transfer will cause interference to the research of deep-sea organisms. In the prior art, the pressure-maintaining trapping container is once trapped and brought back; the deep-sea biological transfer box utilizes a simple structure to realize the low-cost pressure-maintaining transfer of deep-sea organisms in the pressure-maintaining trapping container. Embodiment 2: as figure 2 and image 3 As shown, this embodiment discloses a deep-sea biological transfer box, the structure of which is roughly the same as that of the first embodiment, the difference is that this embodiment also includes a sliding plate 8, the outer peripheral side of the sliding plate 8 and the inner wall of the shell 3 For sliding connection...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example three: as figure 2 and image 3 As shown, this embodiment discloses a deep-sea biological transfer box, the structure of which is roughly the same as that of the second embodiment, the difference is that in this embodiment, a first electromagnet is fixed on the inner wall of the housing 3 close to the sealing member 6 7, the sliding plate 8 is a magnetic plate; initially the sliding plate 8 is close to the first electromagnet 7, the first electromagnet 7 is energized, and the first electromagnet 7 and the sliding plate 8 are magnetically adsorbed to fix the position of the magnetic plate; the first electromagnet 7 Power off and stop working, the magnetic attraction between the first electromagnet 7 and the sliding plate 8 disappears, and the sliding plate 8 can slide along the inner wall of the housing 3, thereby ensuring the slow descending effect of the sliding plate 8 on the seawater.
[0053] Preferably, a hall sensor 9 is fixed on the bottom side of the h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com