Multi-satellite distributed cooperative rescheduling method for emergency tasks
A re-scheduling and distributed technology, applied in data processing applications, instruments, resources, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to increase revenue, prone to conflicts and repeated observations, and loss of large observation opportunities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
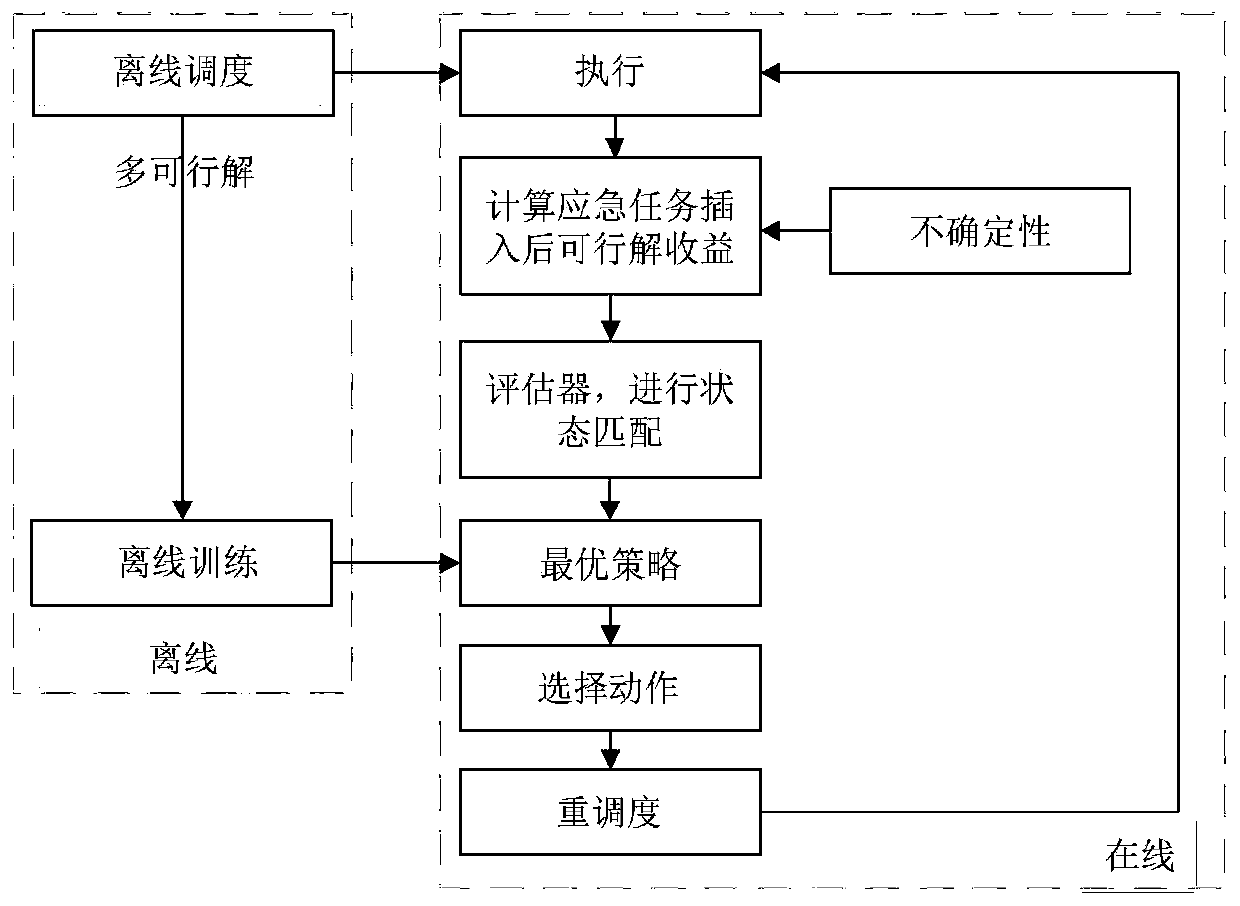
[0081] A multi-satellite distributed cooperative rescheduling method for emergency tasks, such as figure 2 shown, including the following steps:
[0082] Step 1: Generate multiple offline feasible solutions on the ground;
[0083] The way to generate multiple offline feasible solutions is:
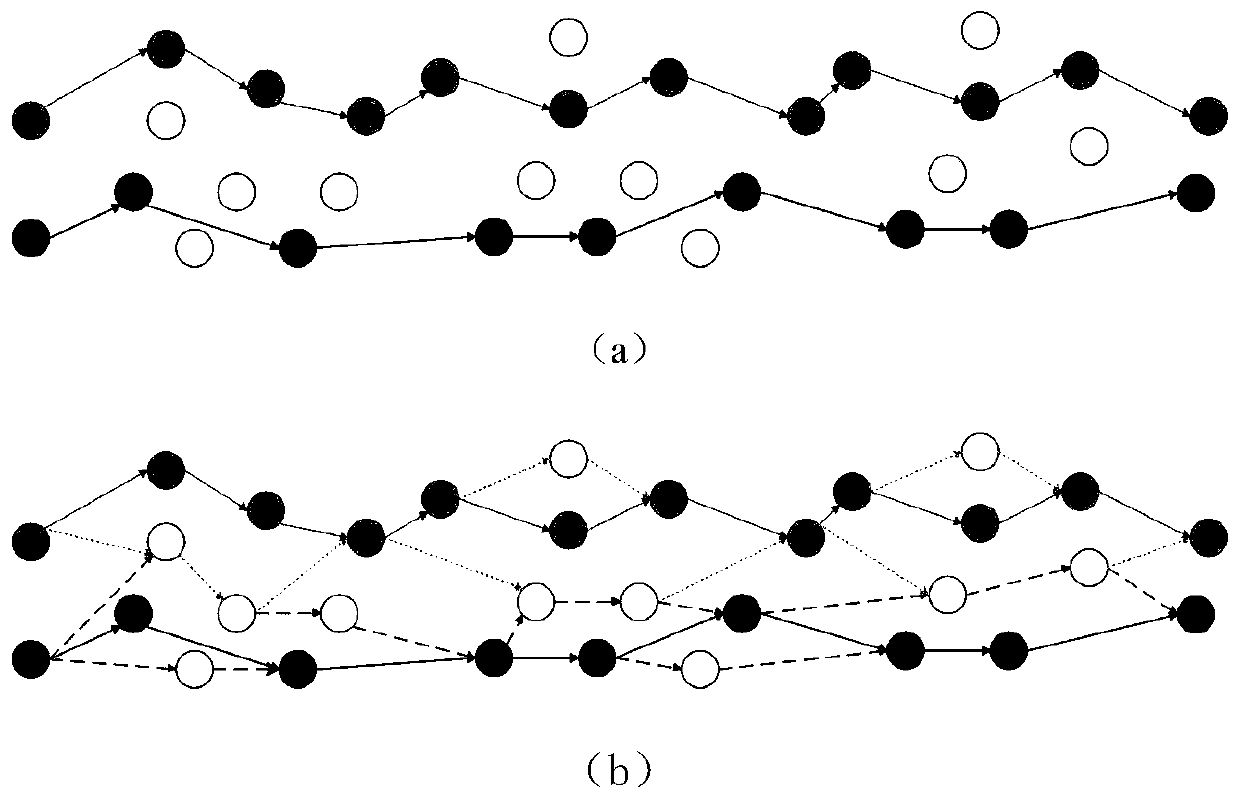
[0084] Step 1.1: Assign the task set to different satellites according to the large neighborhood search algorithm A-ALNS (Adaptivetask assignment based adaptive large neighborhood search) of adaptive task assignment to obtain an initial solution; figure 1 as shown in (a);
[0085] Step 1.2: Assign the successfully scheduled tasks to corresponding satellites according to the initial solution;
[0086] Step 1.3: Assign the unsuccessfully scheduled tasks to all satellites to form a new task set for each satellite;
[0087] Step 1.4: For the new task set on each satellite, use the hybrid adaptive large neighborhood search algorithm ALNS / TPF (Adaptive large neighborhood search with tabu se...
Embodiment 2
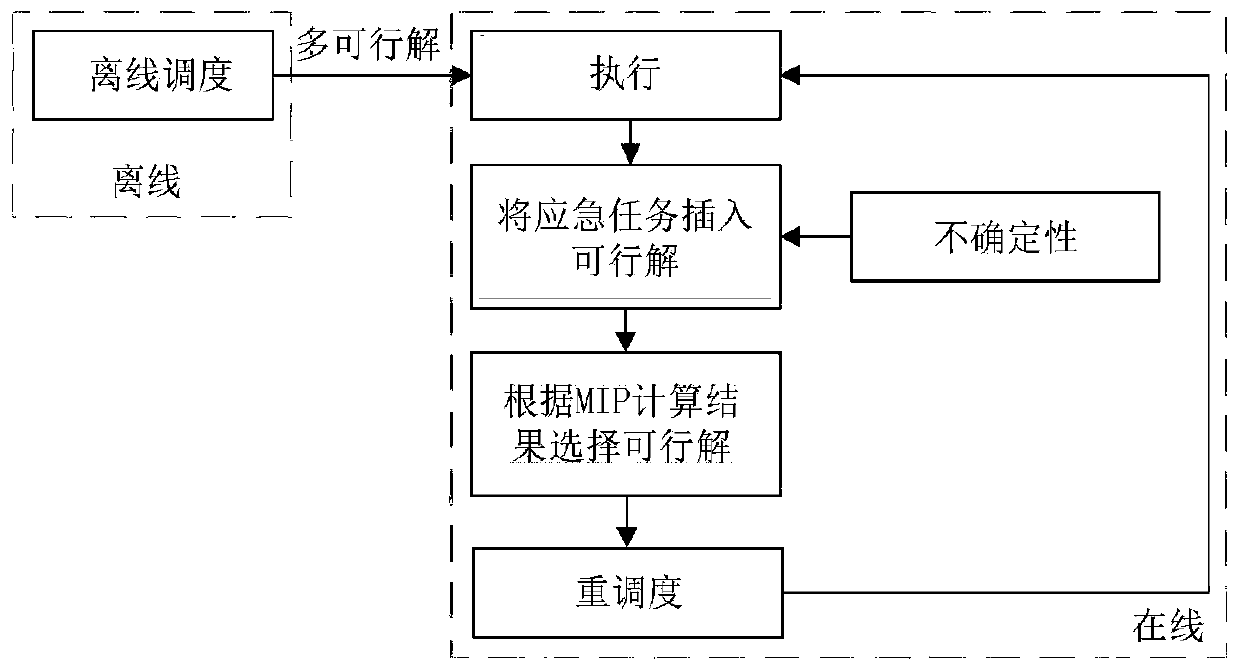
[0132] A multi-satellite distributed cooperative rescheduling method for emergency tasks, such as image 3 shown, including the following steps:
[0133] Step 100: Generate multiple offline feasible solutions on the ground and send them to the satellite;
[0134] The method for generating multiple offline feasible solutions on the ground is the same as that in Embodiment 1.
[0135] Step 200: When the satellite receives the emergency task, judge whether the emergency task can be inserted into multiple offline feasible solutions, and use the solution set after the emergency task is inserted into the offline feasible solution as the feasible solution set;
[0136] In this embodiment, the method for judging whether the emergency task can be inserted into the offline feasible solution is to use the fast insertion method introduced in Document 2 to quickly judge whether each task can be inserted.
[0137] Step 300: Select an optimal feasible solution from the set of feasible solu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com