Three-generation sequencing data overlapping detection method and system
A technology for overlapping detection and sequencing data, which is applied in electrical digital data processing, sequence analysis, multi-programming devices, etc. The effect of improving parallel computing speed and thread scalability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
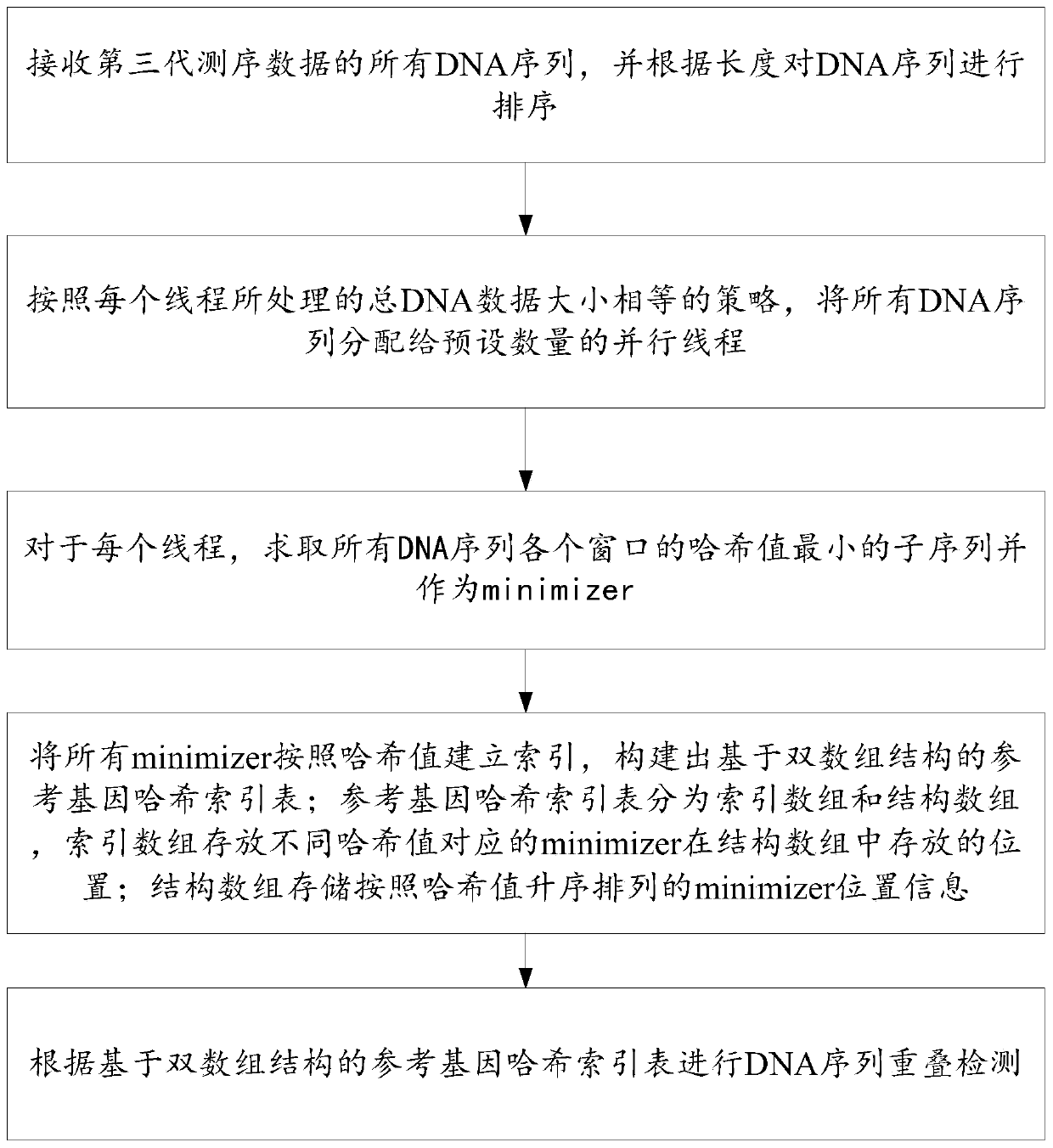
[0036] figure 1 A flow chart of a method for detecting overlapping of third-generation sequencing data in this embodiment is given.
[0037] Combine below figure 1 The specific implementation process of the third-generation sequencing data overlap detection method in this embodiment is given.
[0038] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a three-generation sequencing data overlap detection method, including:
[0039] Step S101: receiving all DNA sequences of the third generation sequencing data, and sorting the DNA sequences according to length.
[0040] The benefit of sorting can reduce the difference in computing tasks corresponding to two adjacent sequences. Since parallel optimization includes vectorized optimization, if the lengths of adjacent sequences are too different, most of the calculation channels in the vector register will be idle. So ordering is critical to keep the parallel implementation load balanced.
[0041]Step S102: According to the p...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Figure 5 A schematic structural diagram of a three-generation sequencing data overlap detection system in this embodiment is given.
[0066] Combine below Figure 5 The structural principle of the third-generation sequencing data overlap detection system in this embodiment is given:
[0067] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the three-generation sequencing data overlap detection system of this embodiment includes:
[0068] (1) a sequencing data preprocessing module, which is used to receive all the DNA sequences of the third generation sequencing data, and sort the DNA sequences according to the length;
[0069] The benefit of sorting can reduce the difference in computing tasks corresponding to two adjacent sequences. Since parallel optimization includes vectorized optimization, if the lengths of adjacent sequences differ too much, most of the calculation channels in the vector register will be idle. So ordering is critical to keep the parallel implementation load bala...
Embodiment 3
[0091] This embodiment is a computer-readable storage medium, on which a computer program is stored, and when the program is executed by a processor, the following figure 1 Steps in the overlap detection method for three-generation sequencing data are shown.
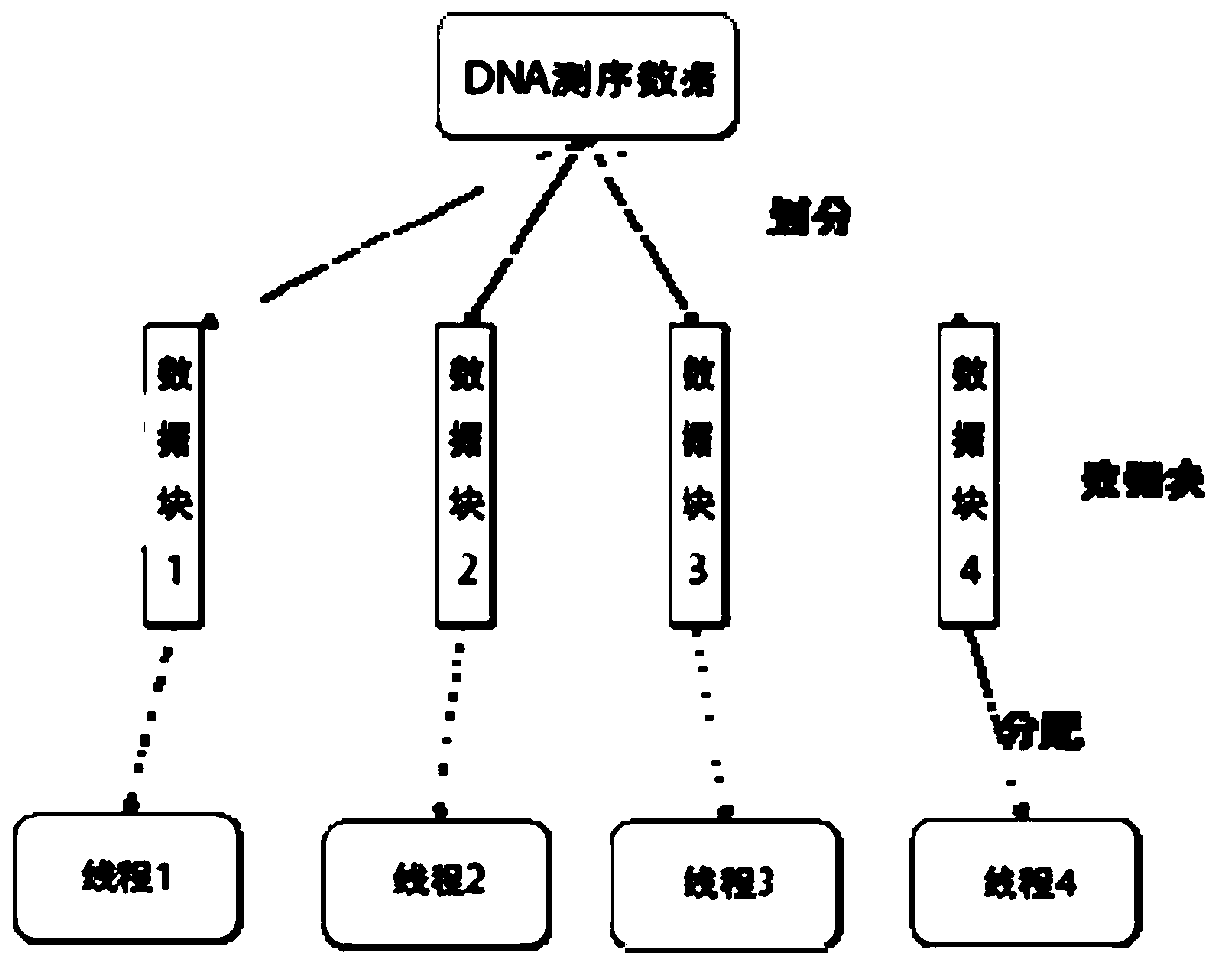
[0092] In this embodiment, according to the strategy that the size of the total DNA data processed by each thread is equal, all DNA sequences are allocated to a preset number of parallel threads, so that the load of the multithreading is balanced, and the acceleration ratio of the multithread parallel implementation is guaranteed at the same time;
[0093] This embodiment constructs a reference gene hash index table based on a double-array structure; wherein, the reference gene hash index table is divided into two arrays, and the index array stores the positions where the minimizers corresponding to different hash values are stored in the structure array, and the structure The position information of the minimizer is s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com