A Supermode Optical Fiber for Transmission of Orbital Angular Momentum
A technology for transmitting orbit and angular momentum, which is applied in the field of optical fiber communication, can solve the problems of reducing the mode area, small difference in refractive index between the ring core and the outer cladding, and easy deformation, so as to achieve high mode coupling intensity, enhanced light energy leakage, and limited The effect of low loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] In order to more clearly illustrate the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention or the prior art, the following will briefly introduce the drawings that need to be used in the description of the embodiments or the prior art. Obviously, the accompanying drawings in the following description These are some embodiments of the present invention. Those skilled in the art can also obtain other drawings based on these drawings without creative work.
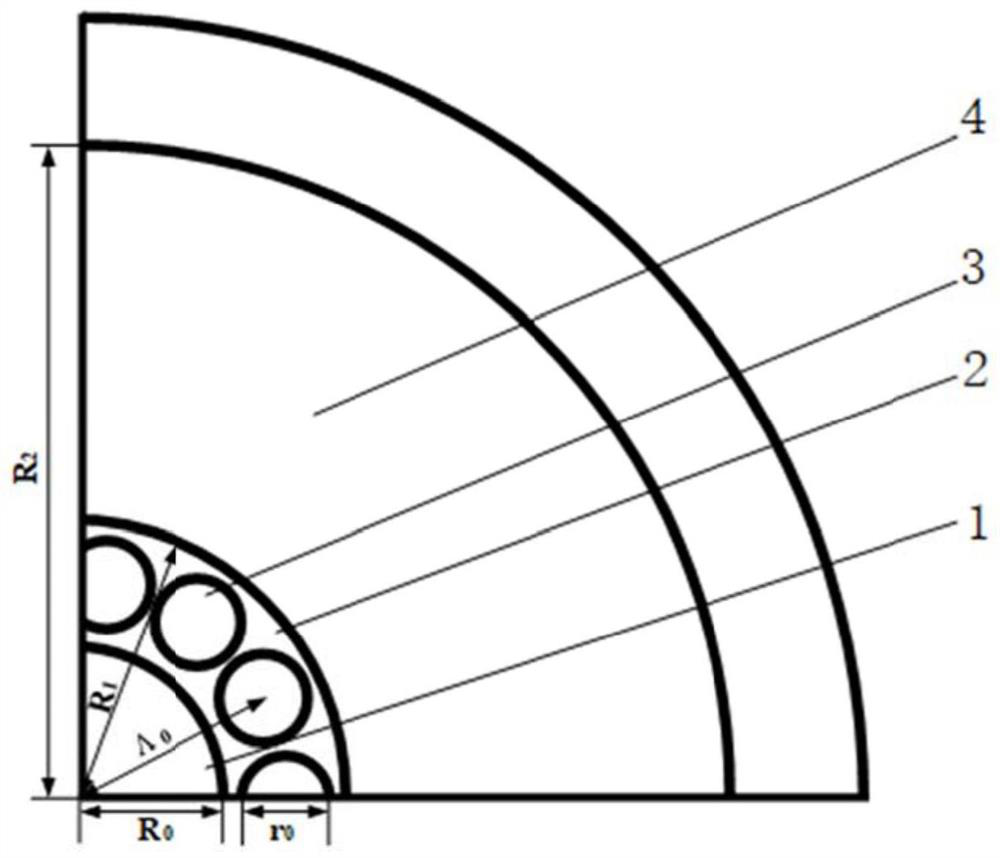
[0033] see figure 1 with figure 2 , a supermode optical fiber for transmitting orbital angular momentum proposed by the present invention, including a central solid cylinder 1 and an inner solid ring 2 arranged in sequence from the center to the outside, and the axial equiangular distribution on the inner solid ring 2 The high refractive index column 3 and the outer solid ring 4, the central solid cylinder 1 constitutes the inner cladding area of the optical fiber, the inner solid ring 2 and the high r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com