Preparation method and applications of fiber-phase red phosphorus nanoparticles
A nanoparticle and fiber phase technology, applied in nanotechnology, nanotechnology, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of low antibiotic efficiency, damage to healthy tissues, etc. repeatable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
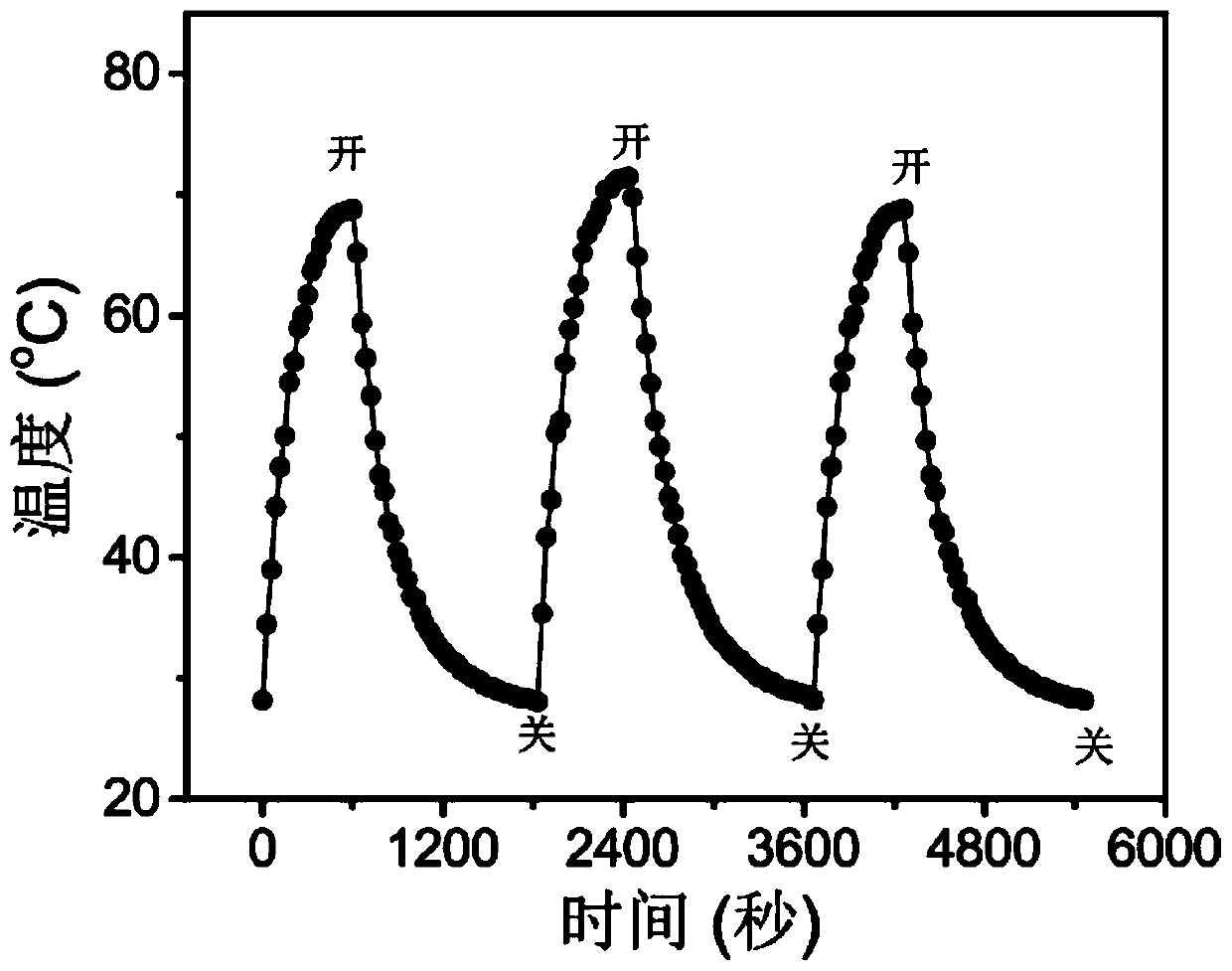
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] A fiber-phase red phosphorus nanoparticle, specifically prepared through the following steps:
[0035] (1) Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles: 1.885 g of zinc nitrate hexahydrate, 2.185 g of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate and 6 g of sodium hydroxide were weighed and dissolved in 60 mL of ethanol with a balance. The solution is sonicated until the solute is uniformly dispersed in the solution. Put the sonicated solution into a 100mL reactor, put the reactor in a muffle furnace at 100°C, and react at high temperature for 9h. The reacted solution was centrifuged (9000r / min, 10min) to collect zinc oxide nanoparticles. Then centrifuged 3 times with absolute ethanol, and then centrifuged 3 times with deionized water. The precipitate after centrifugation was vacuum-dried in a vacuum oven at 60°C.
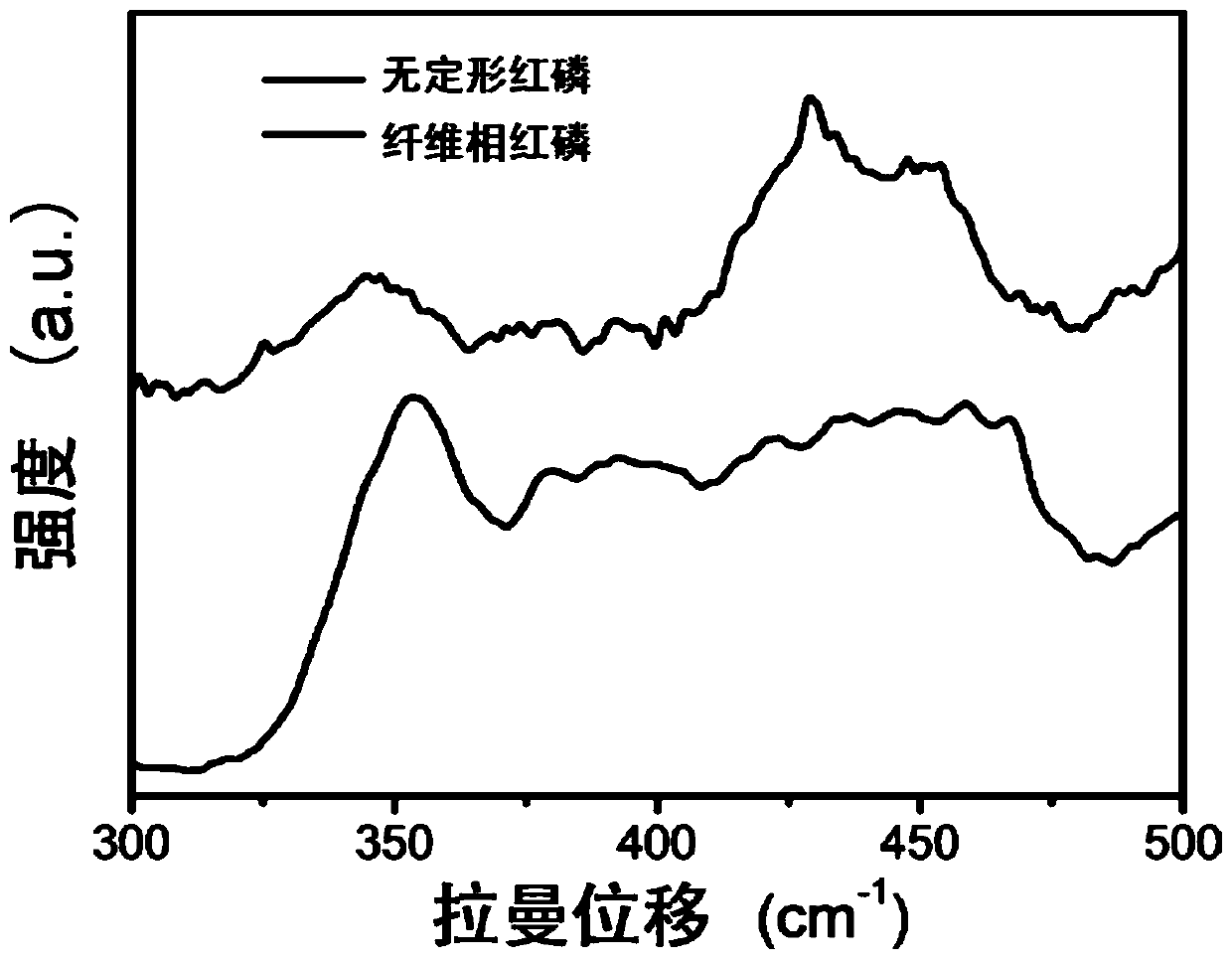
[0036] (2) Preparation of amorphous pure red phosphorus: Weigh 5.9 g of commercial amorphous red phosphorus and add it to 60 mL of deionized water, transfer the solution to a ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] A fiber-phase red phosphorus nanoparticle, specifically prepared through the following steps:
[0051] (1) Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles: 1.885 g of zinc nitrate hexahydrate, 2.185 g of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate and 4.8 g of sodium hydroxide were weighed and dissolved in 60 mL of ethanol with a balance. The solution is sonicated until the solute is uniformly dispersed in the solution. Put the sonicated solution into a 100 mL reaction kettle, put the reaction kettle in a muffle furnace at 90°C, and react at high temperature for 11 hours. The reacted solution was centrifuged (9000r / min, 10 min) to collect zinc oxide nanoparticles. Then centrifuged 3 times with absolute ethanol, and then centrifuged 3 times with deionized water. The precipitate after centrifugation was vacuum-dried in a vacuum oven at 50°C.
[0052] Steps (2) (3) (4) are consistent with embodiment 1.
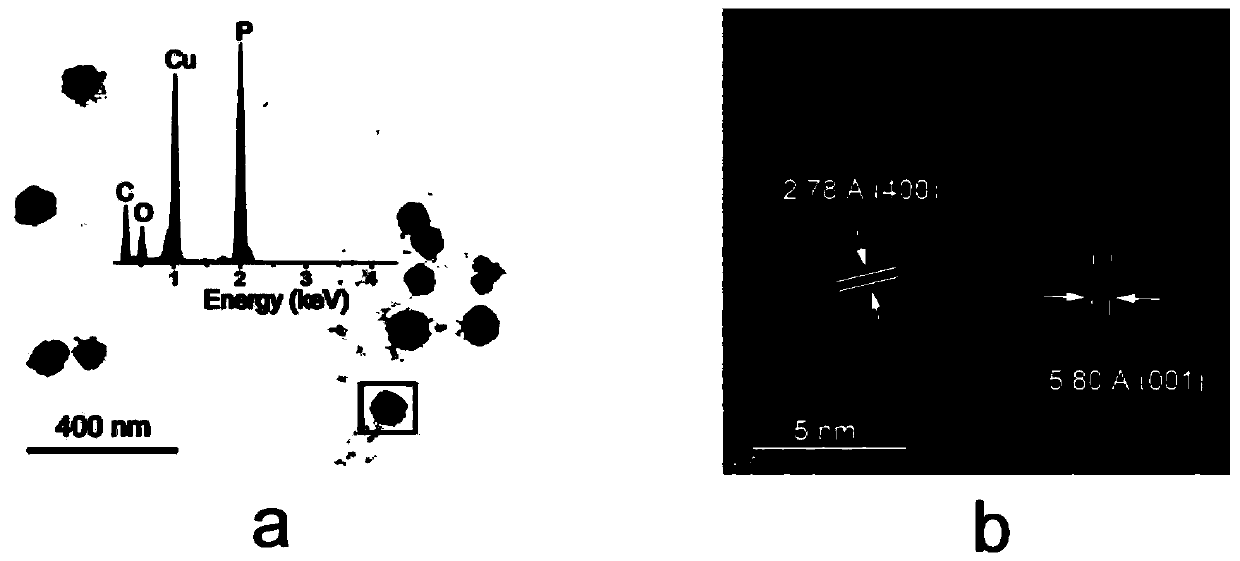
[0053] Scanning electron microscopy was carried out to the fiber-phase red phosphorus na...
Embodiment 3
[0055] A fiber-phase red phosphorus nanoparticle, specifically prepared through the following steps:
[0056] (1) Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles: 1.885 g of zinc nitrate hexahydrate, 2.185 g of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate and 6 g of sodium hydroxide were weighed and dissolved in 60 mL of ethanol with a balance. The solution is sonicated until the solute is uniformly dispersed in the solution. Put the sonicated solution into a 100mL reaction kettle, put the reaction kettle in a muffle furnace at 105°C, and react at high temperature for 10h. The reacted solution was centrifuged (9000r / min, 10min) to collect zinc oxide nanoparticles. Then centrifuged three times with absolute ethanol, and then centrifuged three times with deionized water, and the precipitate after centrifugation was vacuum-dried at 65°C.
[0057] Step (2) (3) (4) is the same as embodiment 1;
[0058] The compound of zinc oxide nanoparticles and red phosphorus prepared above was detected by scanning e...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com