Method and system for analyzing biological sequence with known sequence
A biological sequence and sequence technology, applied in the field of bioinformatics, can solve problems such as increased computational complexity, inability to predict target sequences, and low recognition sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0107] The inventor selected four plants as test objects, and predicted their periodic repeat sequences respectively. In order to compare the performance of the present invention, the inventor compares it with TRF software, and the results are shown in Table 1.
[0108] Table 1: Comparison of TRF and SearchPRE prediction results for repetitive sequences
[0109]
[0110] Note: For the above two software, only one CPU is used, and the default parameters are used for others.
[0111] Through testing, it can be seen that the present invention predicts more periodic repeat sequences, including number and length, for the four plants, and the results include most of the TRF prediction results, indicating a higher accuracy, while other parts mainly This is because the present invention allows differences in the repeating units and special cases of other sequences between adjacent repeating units. And the present invention is all lower than conventional method aspect running time...
Embodiment 2
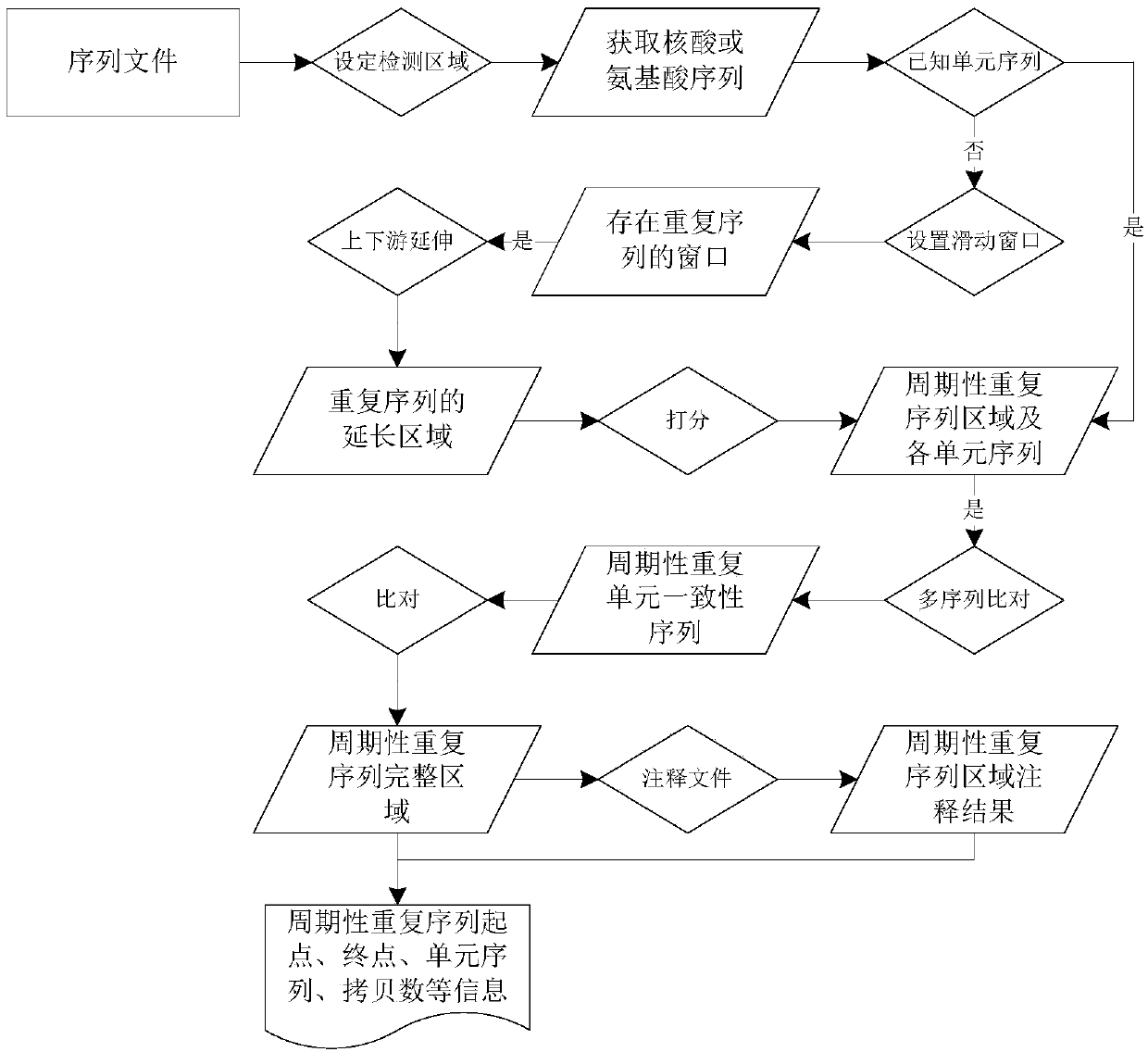
[0113] In this example, the X species region Chr1:500000-600000 is taken as the research object to explore whether there is a periodic repeat sequence in this region, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0114] 1) Since the analyzed area is local, it can be realized by setting the parameter -Region: -Region Chr1, 500000, 600000;
[0115] 2) For the nucleic acid sequence corresponding to the region, use the present invention to predict, run commands and parameters, as follows:
[0116] SearchPRE-InFile Ref.fasta-Region Chr1,500000,600000-Window 1000–K10–Hkmer 0.3–HkR 20–HkRGap 200-HkRExt 1000-PRElen 0.8-1.2–PREgap 3-PRscore0.5-PRCratio 0.8-Outdir All
[0117] From the results, if Figure 6 and Table 2, only 1 periodic repeat sequence region was detected in this region, located in the coding region. In order to verify the authenticity of the periodic repeat sequence in the coding region, the protein sequences of all genes in this region were predicted.
[0118] 3) Accordi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com