Production process of biodegradable electrostatic flocked paper product
A biodegradation and production process technology, applied in the direction of paper/cardboard layered products, layered products, paper, etc., can solve the problems of difficult degradation of polyurethane, environmental pollution, and difficult flow of adhesives, so as to improve environmental performance and reduce production. Cost, the effect of easily attaching electric charges
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
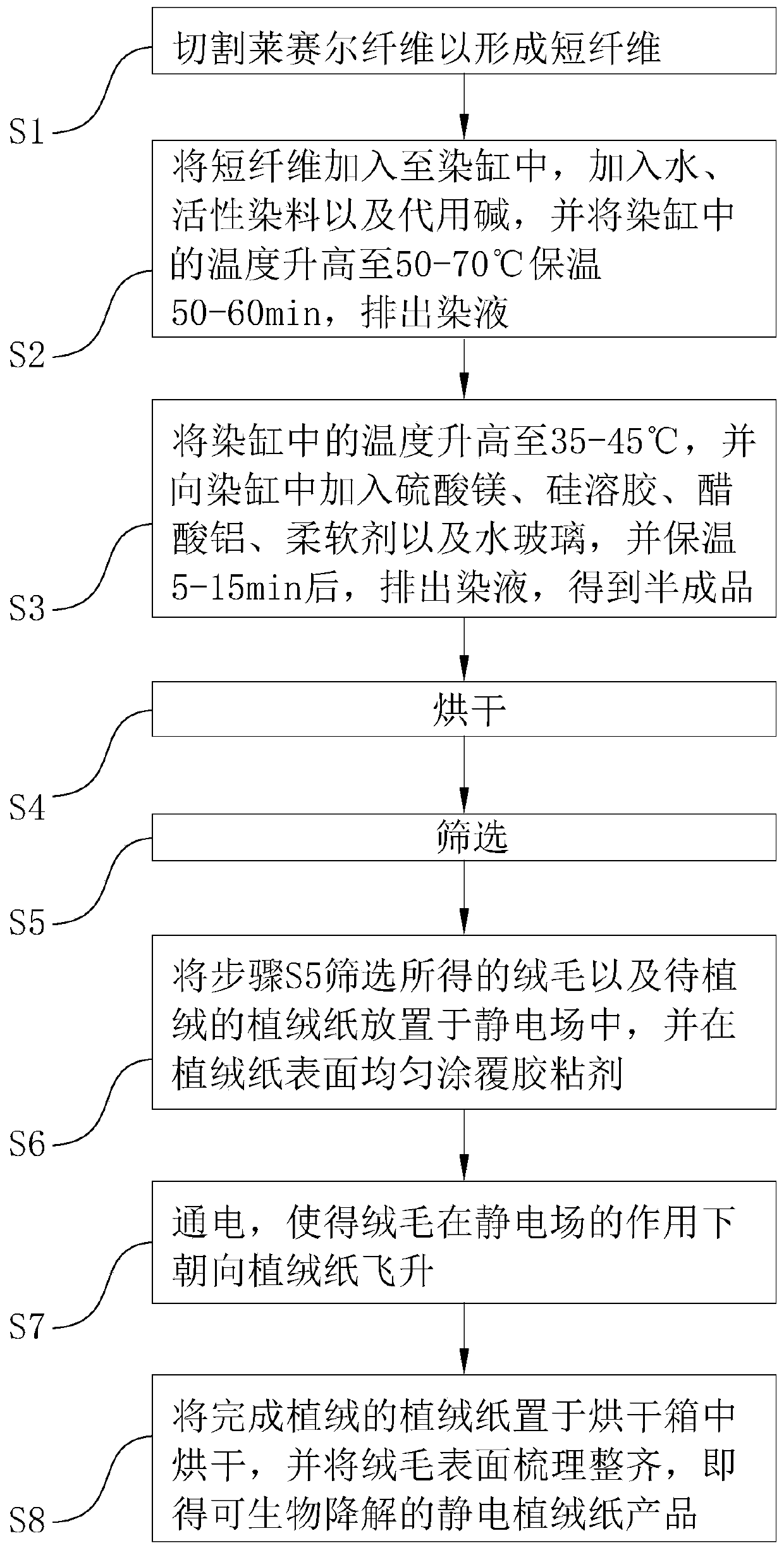
[0082] A production process of a biodegradable electrostatic flocking paper product, comprising the following steps:
[0083] S1, cutting, as follows:
[0084] The lyocell fibers are cut into short fibers with a length of 0.4-0.5 mm using a cutting machine.
[0085] S2, dyeing, specifically as follows:
[0086] Add 50kg of short fibers into the dyeing vat, and add 180kg of water into the dyeing vat, and stir and mix evenly at a speed of 200r / min. After adding water for 5 minutes, add 5 kg of substitute alkali while stirring, and add it after adding substitute alkali for 5 minutes. Stir again Add 12.5 kg of reactive dyes, and then feed steam into the dyeing vat while keeping stirring, so that the temperature of the mixture in the dyeing vat increases at a rate of 0.5°C / min. When the temperature in the dyeing vat rises to 50°C, keep The temperature in the dye vat is 50°C, keep warm for 60 minutes, and then discharge the dye solution in the dye vat.
[0087] Then add 100kg of ...
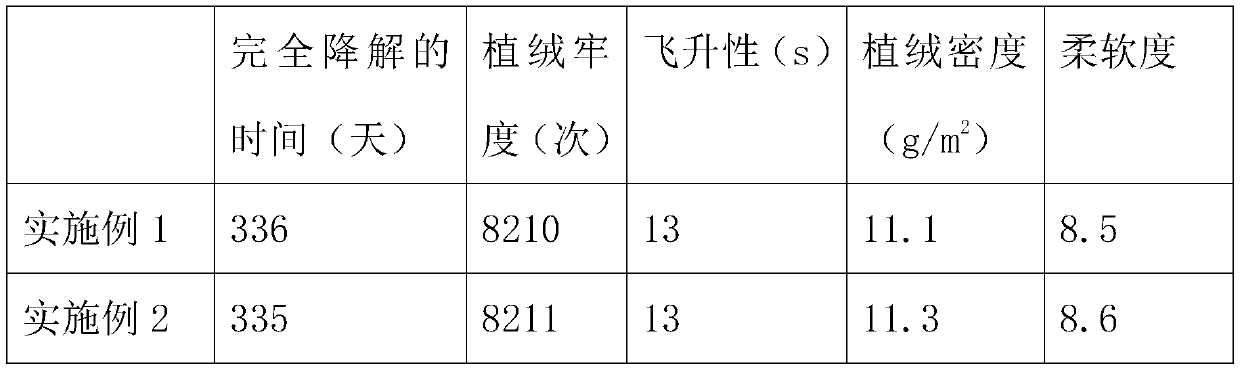
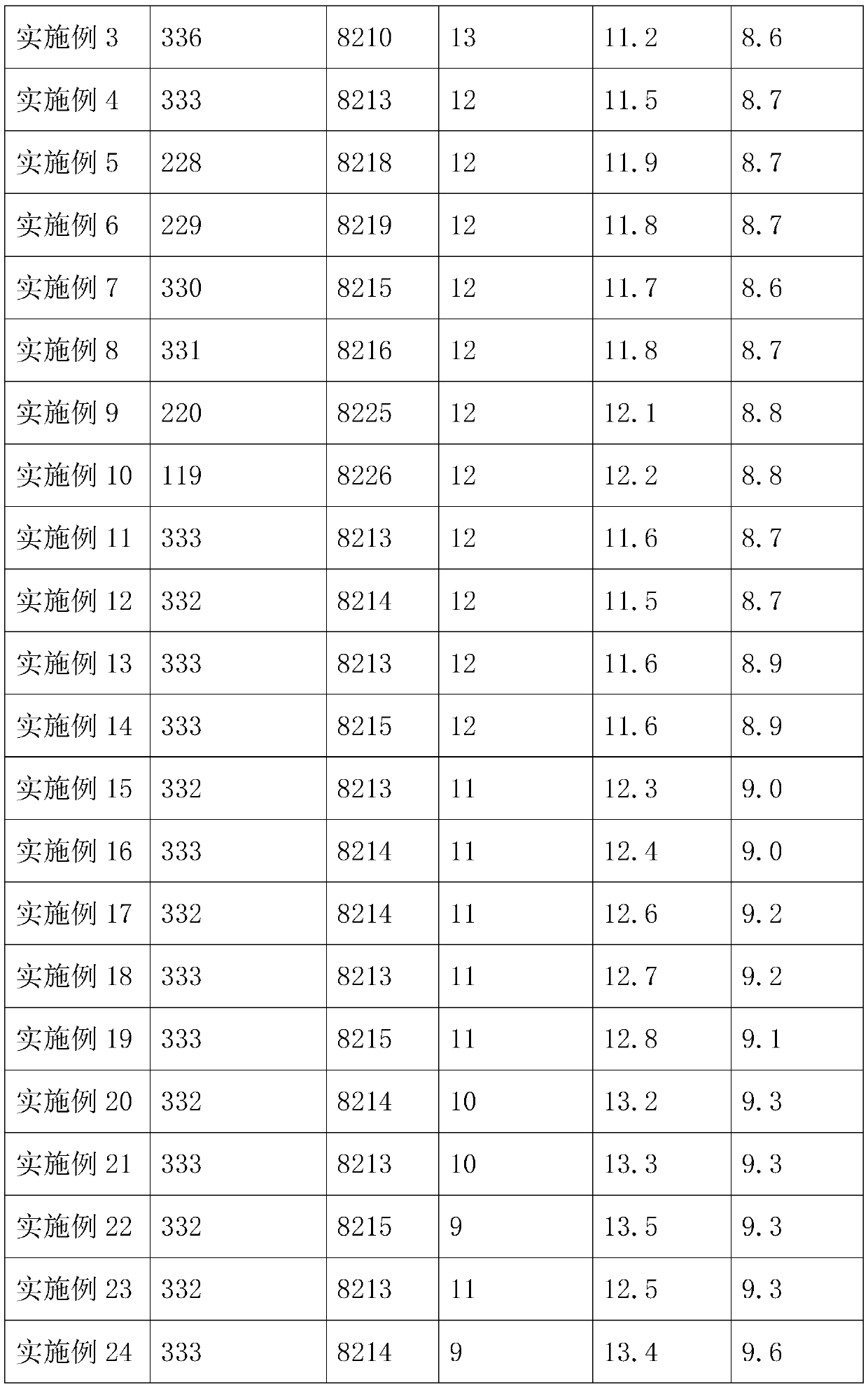
Embodiment 2
[0103] The difference with embodiment 1 is:
[0104] The consumption of each component in the step S2 is as follows: short fiber 50kg; water 190kg; substitute alkali 4kg; reactive dye 15kg. And the temperature in step S2 is raised to 60° C., and the dye solution is discharged after being kept warm for 55 minutes.
[0105] The dosage of each component in step S3 is as follows: water glass 0.4kg; softener 1.5kg; aluminum acetate 0.8kg; silica sol 1kg; magnesium sulfate 1.5kg. And the temperature in step S3 is increased to 40° C., and finally kept for 10 minutes.
[0106] The dosage of each component of the adhesive in step S6 is as follows: polylactic acid 82.5kg; sodium hydroxymethylcellulose 2kg; chitosan 0.75kg.
Embodiment 3
[0108] The difference with embodiment 1 is:
[0109] The consumption of each component in step S2 is as follows: short fiber 50kg; water 200kg; substitute alkali 3kg; reactive dye 10kg. And the temperature in step S2 is raised to 70° C., and the dye solution is discharged after being kept warm for 50 minutes.
[0110] The dosage of each component in step S3 is as follows: water glass 0.3kg; softener 1kg; aluminum acetate 0.4kg; silica sol 0.5kg; magnesium sulfate 1kg. And the temperature in step S3 is raised to 45° C., and finally kept warm for 5 minutes.
[0111] The amount of each component of the adhesive in step S6 is as follows: 85 kg of polylactic acid; 1 kg of sodium hydroxymethyl cellulose; 0.5 kg of chitosan.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com