High-voltage power supply circuit
A high-voltage power supply and circuit technology, applied in the direction of high-efficiency power electronic conversion, electrical components, adjusting electrical variables, etc., can solve the problem of dissipating large power consumption, and achieve the effect of improving efficiency, reducing loss, and improving EMI performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
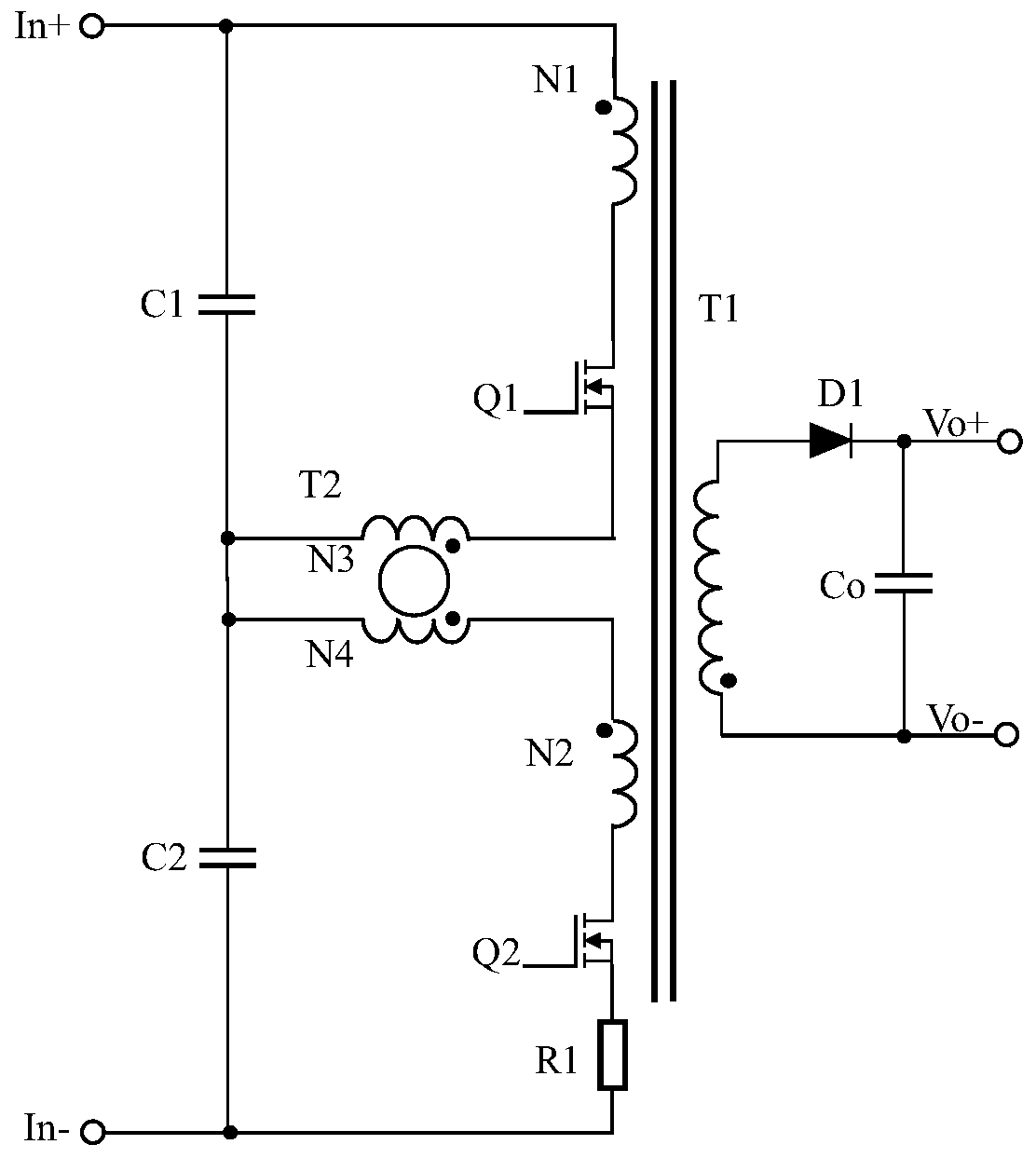
[0022] image 3 Shows the circuit diagram of the first embodiment, including the primary side composed of input voltage in+, input voltage in-, voltage equalizing transformer T2, first capacitor C1, second capacitor C2, first switching tube Q1, and second switching tube Q2 circuit, transformer T1, resistor R1, diode D1, and output capacitor Co to form the secondary side circuit. In the primary side circuit, the input voltage in+ is connected to one end of the capacitor C1, and the other end of the capacitor C1 is connected to one end of the capacitor C2, and at the same time connected to the opposite end of the third winding N3 and the opposite end of the fourth winding N4 in the equalizing transformer T2, The other end of the capacitor C2 is connected to the input voltage in-; the same-named end of the first winding N1 in the transformer T1 is connected to the input voltage in+, and the opposite-named end of the first winding N1 is connected to the drain of the switching tran...
no. 2 example
[0029] Figure 4 The circuit diagram of the second embodiment is shown, and the difference from the first embodiment is that this embodiment also includes a capacitor C3 and a capacitor C4, one end of the capacitor C3 is connected to the positive input terminal in+, and the other end of the capacitor C3 is connected to a voltage equalizing transformer The same-named end of the third winding N3 of T2, one end of the capacitor C4 is connected to the same-named end of the fourth winding N4 of the voltage equalizing transformer T2, and the other end of the capacitor C4 is connected to the negative input terminal in-.
[0030] This embodiment is a simple modification of the first embodiment, and its working principle is the same as that of the first embodiment, so details are not repeated here.
no. 3 example
[0032] Figure 5 The circuit diagram of the third embodiment is shown. The difference from the first embodiment is that the secondary side circuit includes a diode D1, a diode D2, an inductor L1 and a capacitor Co, and the connection relationship is as follows: the output winding of the transformer T1 is connected to The anode of the diode D1, the cathode of the diode D1 is connected to one end of the inductor L1, and its connection point is connected to the cathode of the diode D2, and the other end of the inductor L1 is connected to the positive pole of the output capacitor Co as the positive output terminal Vo+, the negative pole of the output capacitor Co and the diode D2 The anode is connected to the opposite end of the output winding of the transformer T1 as the negative output terminal Vo-.
[0033] The working principle of this embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment, and will not be repeated here.
[0034] The transformer T1 works in a forward mode in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com