Unsupervised domain adaptive fault diagnosis method
A fault diagnosis and unsupervised technology, applied in the field of fault diagnosis, can solve the problem of fault diagnosis performance degradation, achieve good intra-class compactness and inter-class separability, and improve performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
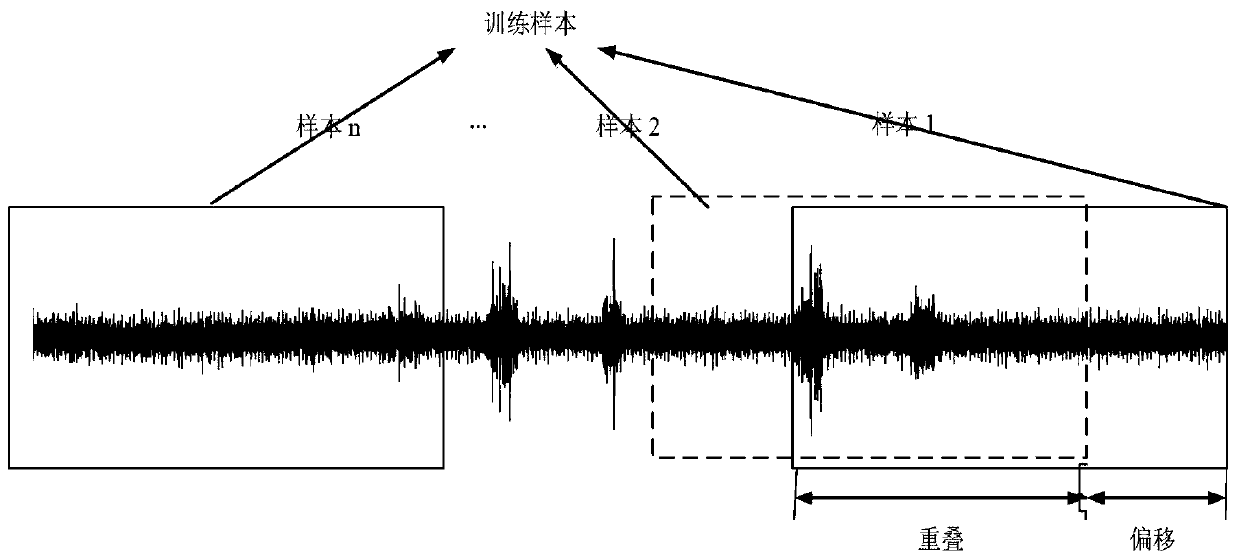
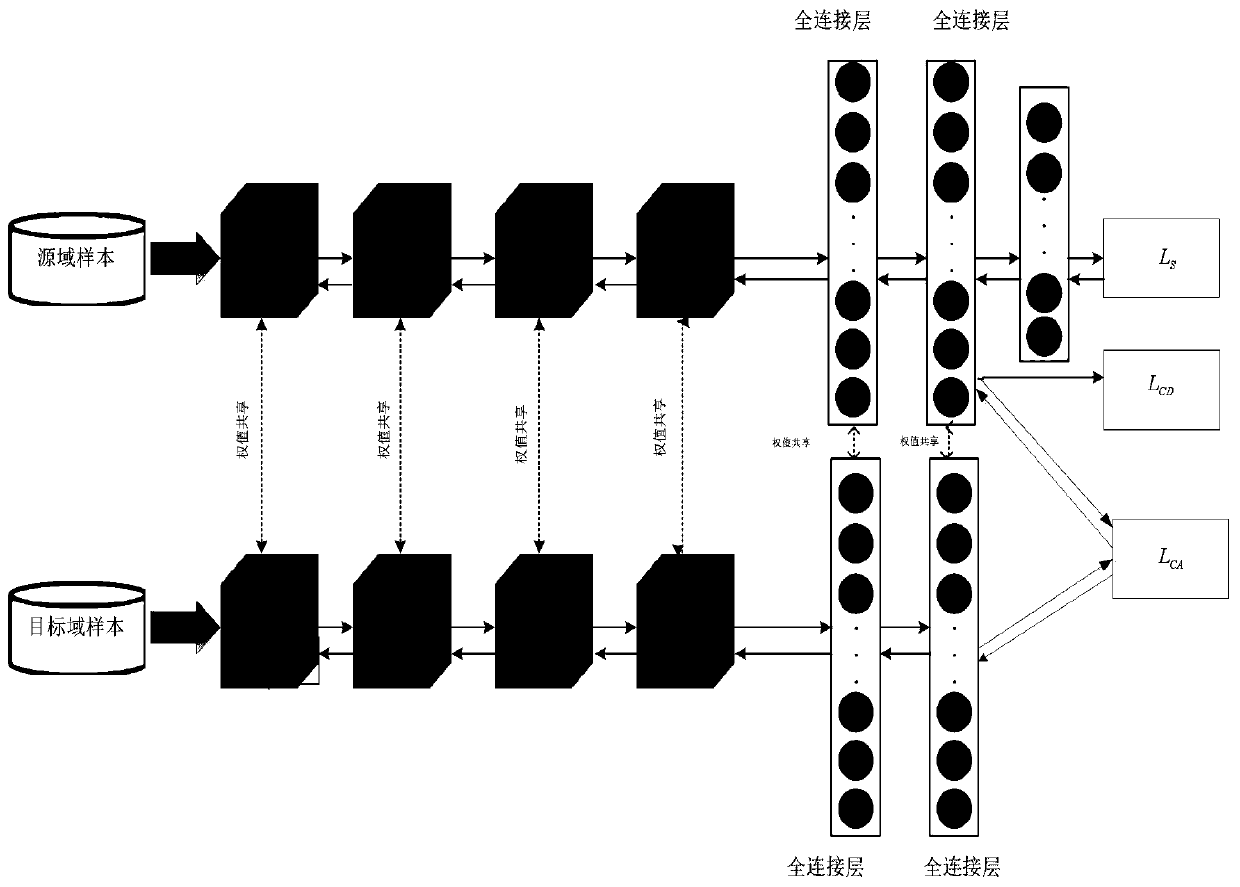
[0060] refer to figure 1 , which provides a schematic diagram of the overall structure of an unsupervised domain adaptive fault diagnosis method, as shown in Figure 4. An unsupervised domain adaptive fault diagnosis method includes,
[0061] The objective function of the model proposed by the present invention includes the cross-entropy classification loss of the source domain, the discriminative loss based on the center and the relative alignment loss based on the features of the source domain and the target domain. The latter two losses are performed in the last fully connected layer. After model training, not only The representation learned in the source domain can be applied to the target domain, and the extracted domain-invariant features can be guaranteed to have better intra-class compactness and inter-class separability, and the extracted features can effectively improve the performance of cross-domain testing. performance.
[0062] Specifically, the main structure of...
Embodiment 2
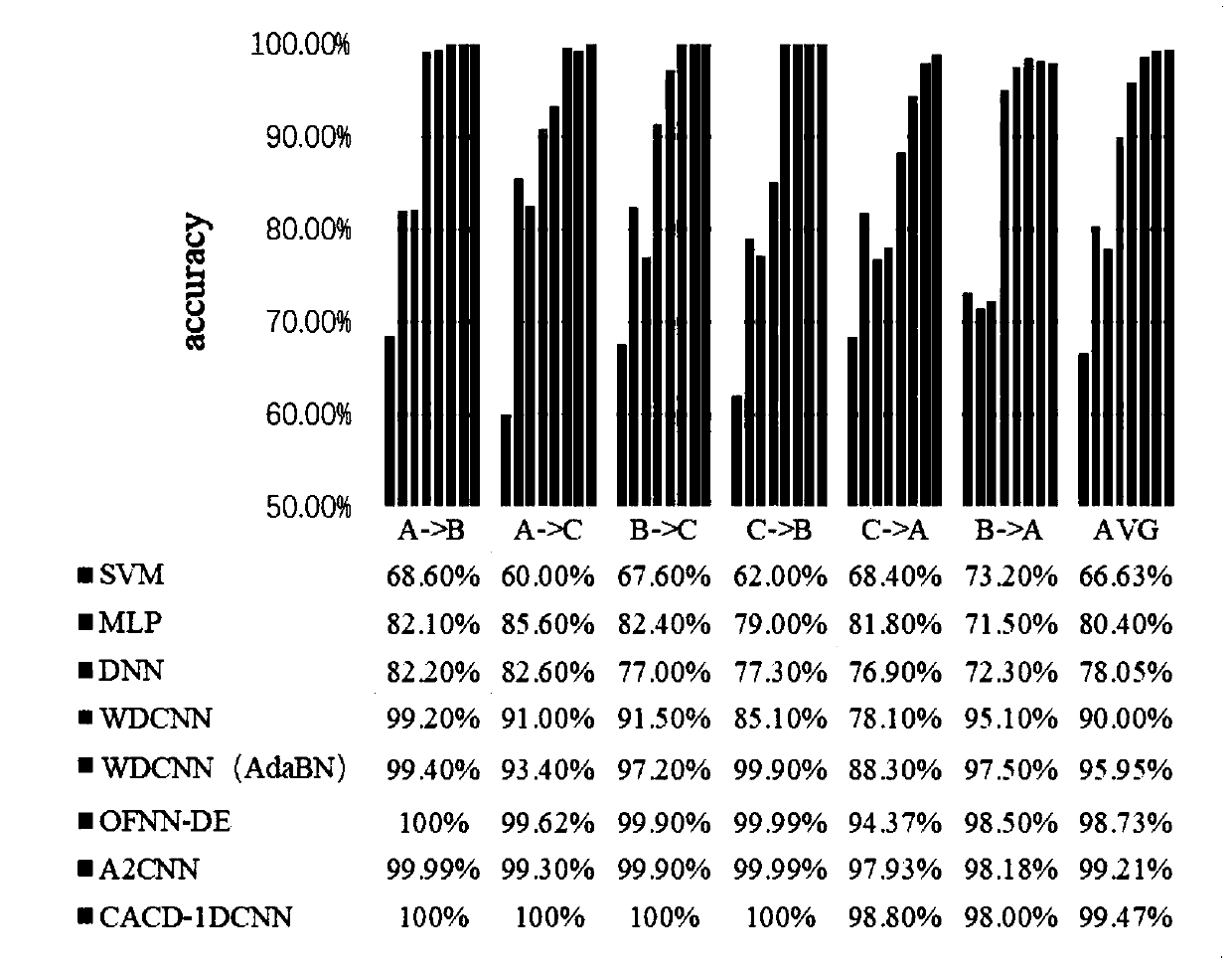
[0109] In order to verify the effectiveness and feasibility of the proposed method, the bearing test device includes a motor, a torque sensor, a power tester and an electronic controller. An acceleration sensor is placed on the bearing seat of the motor drive end and the fan end. The data is collected by the acceleration sensor placed above the bearing seat of the motor drive end. The sampling frequency includes 12KHz and 48KHz, which are collected under 4 different loads (0-3HP) respectively; this bearing test system simulates the bearing There are 4 types of normal state (N), outer ring fault (OF), inner ring fault (IF) and rolling element fault (RF), and each type of fault has 3 fault degrees, including damage diameter of 0.007inch, 0.014 inch, 0.021inch, you can get 10 kinds of health status.
[0110] In this example, the sampling frequency of the driving end of the rolling bearing is 12kHz for different fault locations and vibration signals of different health states for ...
Embodiment 3
[0118] For each fault detection type, in order to further analyze the sensitivity of the proposed CACD-1DCNN model, this method introduces three new evaluation indicators, namely Precision (precision), Recall (recall rate) and F value. Called precision, recall is also called recall.
[0119] In the fault diagnosis multi-classification problem, the definitions for each fault category c are:
[0120] Accuracy (c)=TP / TP+FP
[0121] Recall (c)=TP / TP+FN
[0122] Among them, true positives (TP) represent the number of faults that are correctly identified as fault category c, false positives (FP) represent the number of faults that are incorrectly identified as fault category c, and false negatives (FN) represent the number of faults that are incorrectly identified as not belonging to c, i.e. no The number of faults that were correctly labeled.
[0123] The failure category c has an accuracy of 1, which means that when each sample is marked as belonging to a certain failure class ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com